AP Biology Ch. 14 part 2 Translation
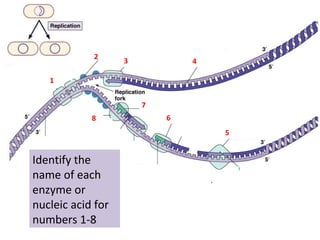
- 1. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Identify the name of each enzyme or nucleic acid for numbers 1-8
- 2. All late work due by Monday Feb 1st
- 3. From Genes to Proteins - Translation Ch. 14
- 4. AP Biology Plans for the week of January 25th through January 29th , 2016 • Monday 1-25-16: Ch. 14 part 1 notes • Tuesday 1-26-16: Ch. 14 part 2 notes • Wednesday 1-27-16: big group diagram of transcription and translation • Thursday & Friday 1-28 & 1-29: Review and practice questions for Ch. 13 and 14 Homework: Study Fig 14.24 on page 287 for a diagram quiz on MONDAY 2-1-16
- 5. To assist you in your note taking… Key vocabulary terms are in green, bold, underlined font
- 6. Overview of Concepts 1. The genetic code is a triplet code 2. Translation is directed by RNA molecules 3. RNA plays many different roles in protein synthesis 4. Point mutations may affect protein formation
- 7. Objective Describe the process of translations Identify the role each type of RNA plays in the process
- 8. The triplet code There are 20 amino acids (the monomers of proteins) but only 4 nucleotides (the monomers of nucleic acids) How can just 4 bases code for 20 different amino acids?
- 9. The triplet code The genetic code is based on triplets of bases: a series of non- overlapping, three nucleotide “words” We call these base triplets in the mRNA codons How did scientists figure out it was 3 bases for each codon?
- 10. The triplet code 4 nucleotides (A,C,T,G) x 1 in a sequence = 4 different combinations 4 nucleotides x 2 in a sequence = 16 different combinations 4 different nucleotides x 3 in a sequence = 64 different combinations (for 20 AA’s)
- 11. The triplet code The code is redundant but unambiguous Each codon codes for only 1 amino acid - unambiguous Some amino acids are coded for by more than one codon - redundant Only UGG codes for tryptophan AGU, AGC, UCA, UCC, UCG, UCU all code for serine
- 12. How did scientists figure out what amino acid each codon codes for? 1960s - Nierenberg & Mathaei Used artificial RNA triplets in tubes with the components for building proteins Made chains of uracil first - UUUUUUUUU Got all phenylalanines in a chain, so UUU must code for phenylalanine. Within a few years, they had decoded all 64 codons
- 13. What is translation? Translation is the process by which a cell interprets the codons along an mRNA molecule and builds a polypeptide
- 14. Who translates the code? Transfer RNA (tRNA) is the interpreter of the genetic code tRNA is the molecule responsible for converting the genetic code of nucleotides toto the protein code of amino acids
- 15. How does tRNA work? The cell already has all 20 amino acids in its cytoplasm (either makes them itself or they are taken in through the organism’s diet) Each tRNA is a strand about 80 bases long Some bases are complementary to each other so it can hydrogen bond to itself Takes on a clover-leaf shape
- 16. tRNA On one end of the tRNA is an amino acid On the other end is an anticodon The anticodon is complementary to the codon in the mRNA
- 17. So codon by codon, the tRNAs deposit amino acids in the prescribed order, and the ribosome joins them into a polypeptide chain
- 18. Some practice DNA template strand: ACCGGTCAGTAC 1. Make the mRNA from this template 2. What will be the tRNA anticodons?
- 19. Which of the following is NOT true of a codon? A. It consists of three nucleotides. B. It is the basic unit of the genetic code. C. It never codes for more than one amino acid. D. It may code for the same amino acid as another codon. E. It extends from one end of a tRNA molecule.
- 20. The anticodon of a particular tRNA molecule is __________. A. complementary to the corresponding triplet in rRNA B. complementary to the corresponding mRNA codon C. catalytic, making the tRNA a ribozyme D. changeable, depending on the amino acid that attaches to the tRNA E. the part of tRNA that bonds to a specific amino acid
- 21. Which of the following is NOT true of RNA processing? A. RNA splicing can be catalyzed by spliceosomes. B. A primary transcript is often much longer than the final RNA molecule that leaves the nucleus. C. Nucleotides may be added at both ends of the RNA. D. Ribozymes may function in RNA splicing. E. Exons are cut out before mRNA leaves the nucleus
- 22. Ribosomes Ribosomes are the sites of protein synthesis They are made up of ribosomal RNA (rRNA) & protein Composed of 2 subunits: large & small Subunits are made in the nucleolus They join together at the mRNA to make a functional ribosome
- 23. Quick Think What are the 3 types of RNA and what do they do?
- 24. Ribosomes Ribosomes bring together the mRNA and the tRNAs bearing the correct amino acids and bond those amino acids in the correct order There are 3 sites on the ribosome that function in this capacity: the E site, the P site, and the A site
- 25. A site - holds the tRNA with the next amino acid to be added to the chain P site - holds the tRNA carrying the growing polypeptide chain E site - releases tRNAs from the ribosome here P A
- 26. Let’s practice • mRNA reads: AUGCCCGACUACGGACGACGGUUUACGUGGGGCCUC • What amino acids do we need?
- 29. AUGCCCGACUACGGACGACGGUUUACGUGGGGCCUCUAG AUG = methionine CCC = proline GAC = aspartic acid UAC = tyrosine GGA = glycine CGA = arginine CGG = argnine UUU = phenylalanine ACG = threonine UGG = tryptophan GGC = glycine CUC = leucine UAG = stop
- 30. Come forward • Would the tRNA with methionine please come up and bring the amino acid for this protein? – What is the anticodon? •UAC AUGCCCGACUACGGACGACGGUUUACGUGGGGCCUC AUG = methionine CCC = proline GAC = aspartic acid UAC = tyrosine GGA = glycine CGA = arginine CGG = argnine UUU = phenylalanine ACG = threonine UGG = tryptophan GGC = glycine CUC = leucine UAG = stop – release factor
- 31. Translation has 3 stages Initiation Elongation Termination
- 32. Initiation mRNA, the first tRNA with the first amino acid, and the large & small subunits of the ribosome come together The first amino acid is methionine (codon AUG, the start codon) This establishes the reading frame The whole thing is called a “translation initiation complex” and GTP energy is required to build it
- 33. Elongation More amino acids are added to the growing chain There are 3 steps catalyzed by protein elongation factors
- 34. STEP 1 - Codon Recognition the anticodon on the tRNA H-bonds with the codon in the A site 1. 2 GTPs for energy are used up here 2. An elongation factor protein catalyzes this step
- 35. STEP 2 - Peptide Bond Formation The large subunit catalyzes the formation of a peptide bond between the amino acid in the A site and the amino acid in the P site
- 36. STEP 3 - Translocation The ribosome moves the tRNA in the A site to the P site The empty tRNA in the P site is moved to the E site and released GTP energy is required here
- 38. Termination Happens when one of the 3 stop codons reaches the A site on the ribosome A release factor protein binds to the stop codon & hydrolysis occurs to free the polypeptide chain
- 39. Which component is NOT directly involved in translation? A. mRNA B. DNA C. ribosomes D. tRNA E. GTP
- 40. Which of the following mutations would be most likely to have a harmful effect on an organism? A. a single nucleotide deletion near the end of the coding sequence B. a deletion of three nucleotides near the middle of a gene C. a single nucleotide deletion in the middle of an intron D. a nucleotide-pair substitution E. a single nucleotide insertion downstream of, and close to, the start of the coding sequence
- 41. Polyribosomes Several ribosomes can be working at the same mRNA strand at the same time Strings of these ribosomes are called polyribosomes This helps the cell make more proteins more quickly
- 42. Proteins As the polypeptide chain is being formed, it will begin to coil & fold in to its 3-D shape The gene determines the order of the amino acids - the primary structure The primary structure determines the secondary and tertiary structure
- 43. Proteins Proteins may be further modified by the addition of sugars, lipids, or phosphate groups Enzymes may cleave the polypeptide chain into smaller chains 2 or more polypeptide chains may join to make the quaternary structure of a functional protein
- 44. Proteins All translation begins in the cytosol on free ribosomes If the protein is destined to become part of an organelle or is to be shipped outside the cell, the ribosome will move to the ER and become an attached ribosome
- 45. Proteins signal recognition particle (SRP) brings the ribosome to the ER and translation continues there
- 46. Types of RNA mRNA - messenger RNA (the code) tRNA - transfer RNA (brings amino acids) rRNA - ribosomal RNA (the ribosome) Pre-mRNA - the primary transcript before editing snRNA - part of sliceosomes SRP RNA - part of the signal recognition particle & others
- 48. What makes RNA so versatile? 1. It can H-bond to itself & to other nucleic acids 2. It has functional groups that allow it to act as an enzyme
- 49. Point Mutations A point mutation is a change in a single base pair in a gene They can have catastrophic consequence, or none at all There are 3 main types: Substitution Insertion Deletion
- 50. Substitution mutations A base pair is replaced with a different base pair Because there is redundancy in the genetic code, this may cause no problem at all It could also lead to a malformed protein and be the difference between life and death
- 51. Substitution Think of it like a sentence: Normal sentence would read THE DOG BIT THE CAT A point mutation might make the sentence read: THE DOG BIT THE CAR This changes the meaning of the sentence, but not dramatically.
- 52. Changing a single base can cause a dramatic change: The base change codes for a different amino acid, making a different protein Example: sickle cell anemia
- 53. Changing a single base may not cause any change at all: The changed base may still code for the same amino acid Proline is coded for by CCC, CCA, CCG, and CCU, So a change in the last base won’t make any difference to the amino acid that is added to the protein chain.
- 54. Insertions & Deletions •These mutations add an extra letter or two or delete letters •These mutations disrupt the reading frame and are usually more severe •Because of this they are called frameshift mutations
- 55. Frameshift Mutations Think of it as a sentence again: THE DOG BIT THE CAT Adding an extra letter makes it: THH EDO GBI TTH ECA T It changes the entire sentence to nonsense. This kind of mutation has a more dramatic effect on the DNA sequence and is usually lethal
Editor's Notes
- 1. Helicase 2. ss binding proteins 3. DNA pol III 4. leading strand 5. ligase 6. DNA pol I 7. primer 8. primase
- e
- b
- e
- b
- e
