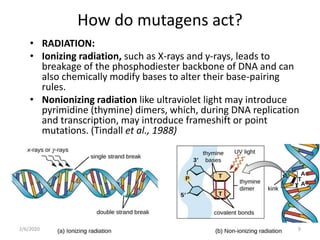
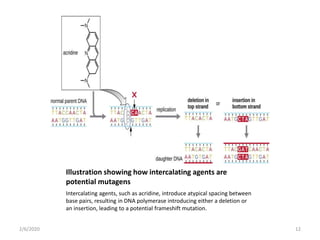
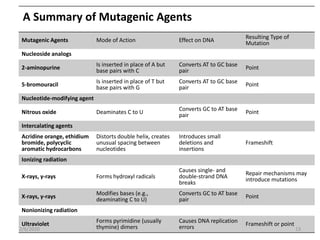
Mutations are changes in genetic material that can occur spontaneously or due to mutagens. There are different types of mutations such as point mutations, frameshift mutations, and missense mutations. Mutagens are physical or chemical agents that cause mutations by damaging DNA. Common mutagens include radiation, chemicals, and viruses. Cells have DNA repair mechanisms but some mutations still occur and can have various clinical implications such as cancer, genetic disorders, antibiotic resistance, and in some cases provide benefits like resistance to malaria and HIV.