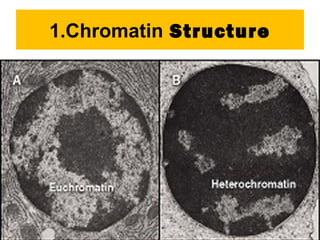
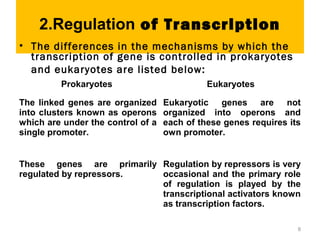
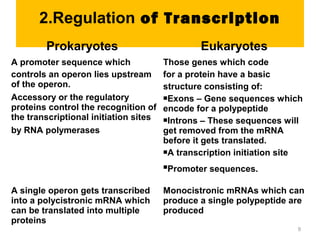
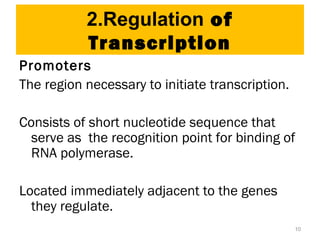
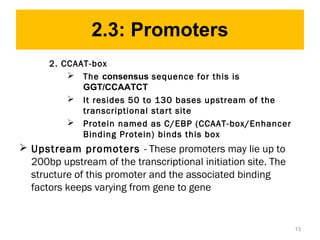
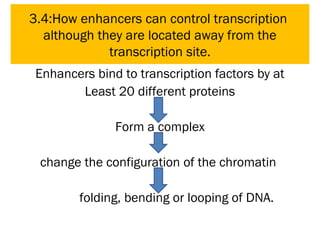
Gene expression in eukaryotes is controlled at multiple levels, including chromatin structure, transcription, RNA processing, and translation. Chromatin structure determines if genes are transcriptionally active or inactive. Transcription is regulated by the interaction of promoters, transcription factors, and enhancers. RNA processing controls splicing and transport of mRNA. Finally, translation and post-translational modifications further regulate gene expression. Overall, eukaryotic gene expression is tightly controlled through complex mechanisms at the chromatin, transcription, RNA, translation, and protein levels.