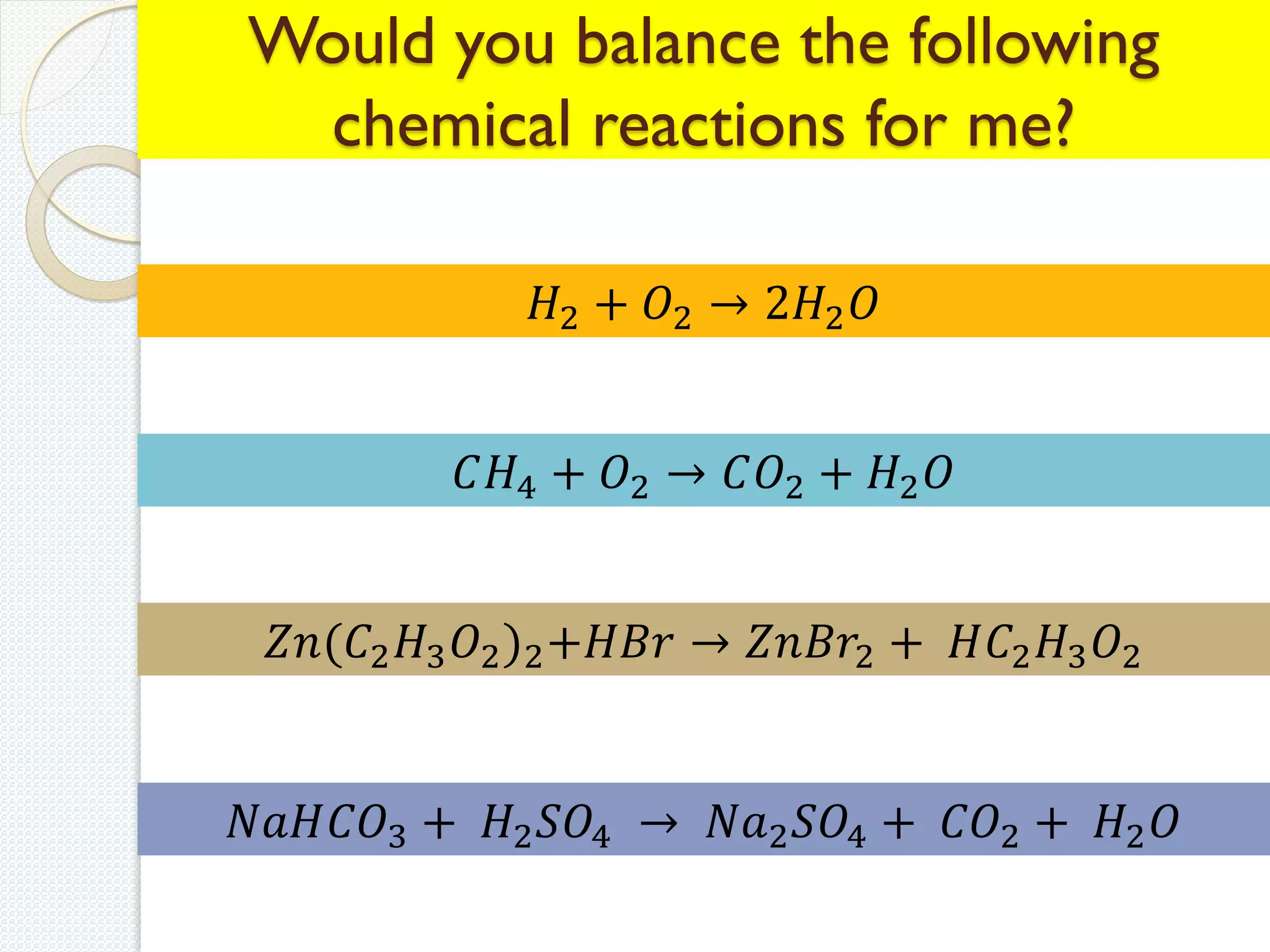
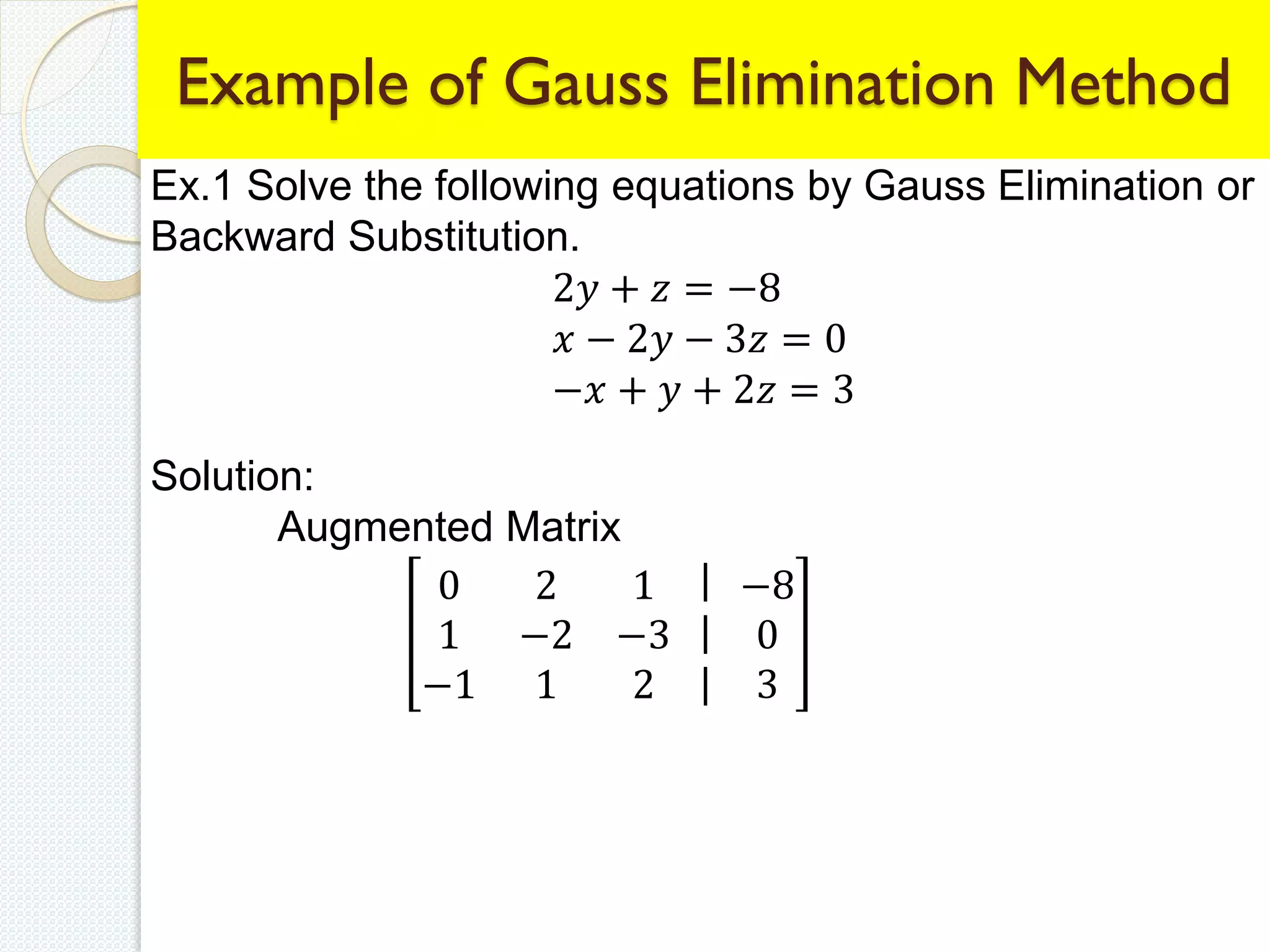
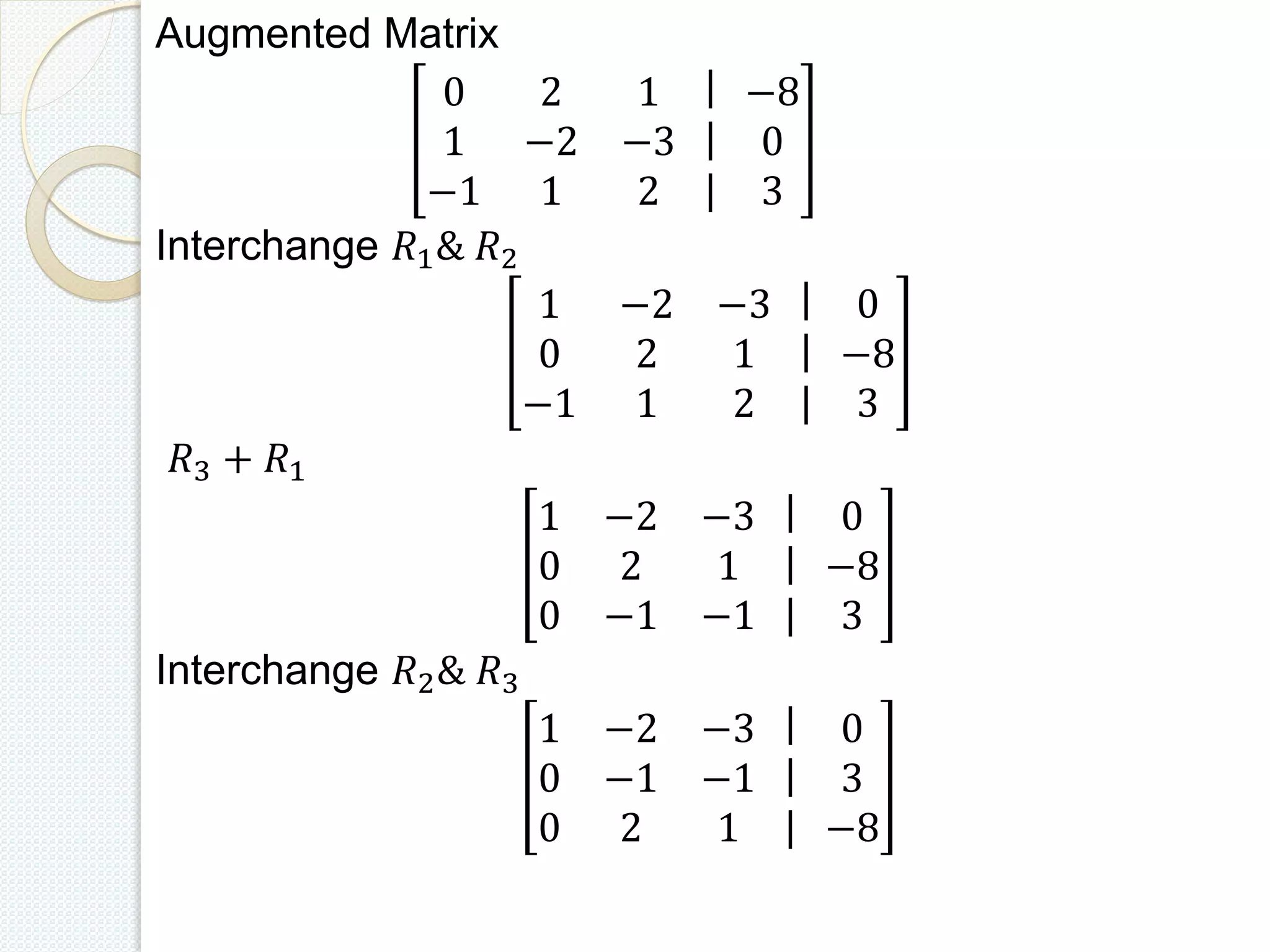
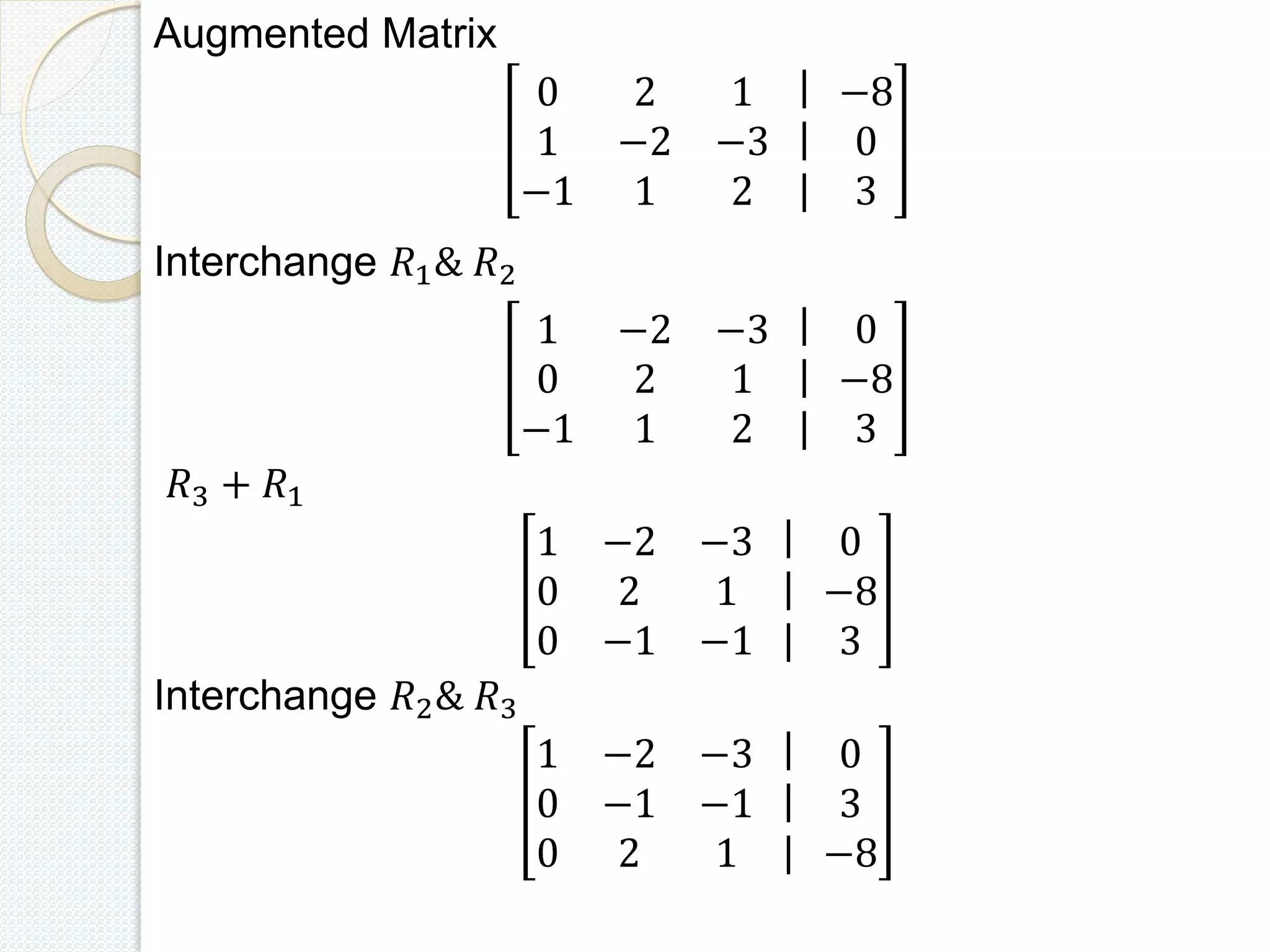
This document discusses methods for solving systems of linear equations, including the traditional method, matrix method, row echelon method, Gauss elimination method, and Gauss Jordan method. It provides examples working through solving systems of equations using Gauss elimination and Gauss Jordan. The key steps of each method like constructing the augmented matrix, row operations, and back substitution are demonstrated. Related fields where linear algebra is applied are also listed.
















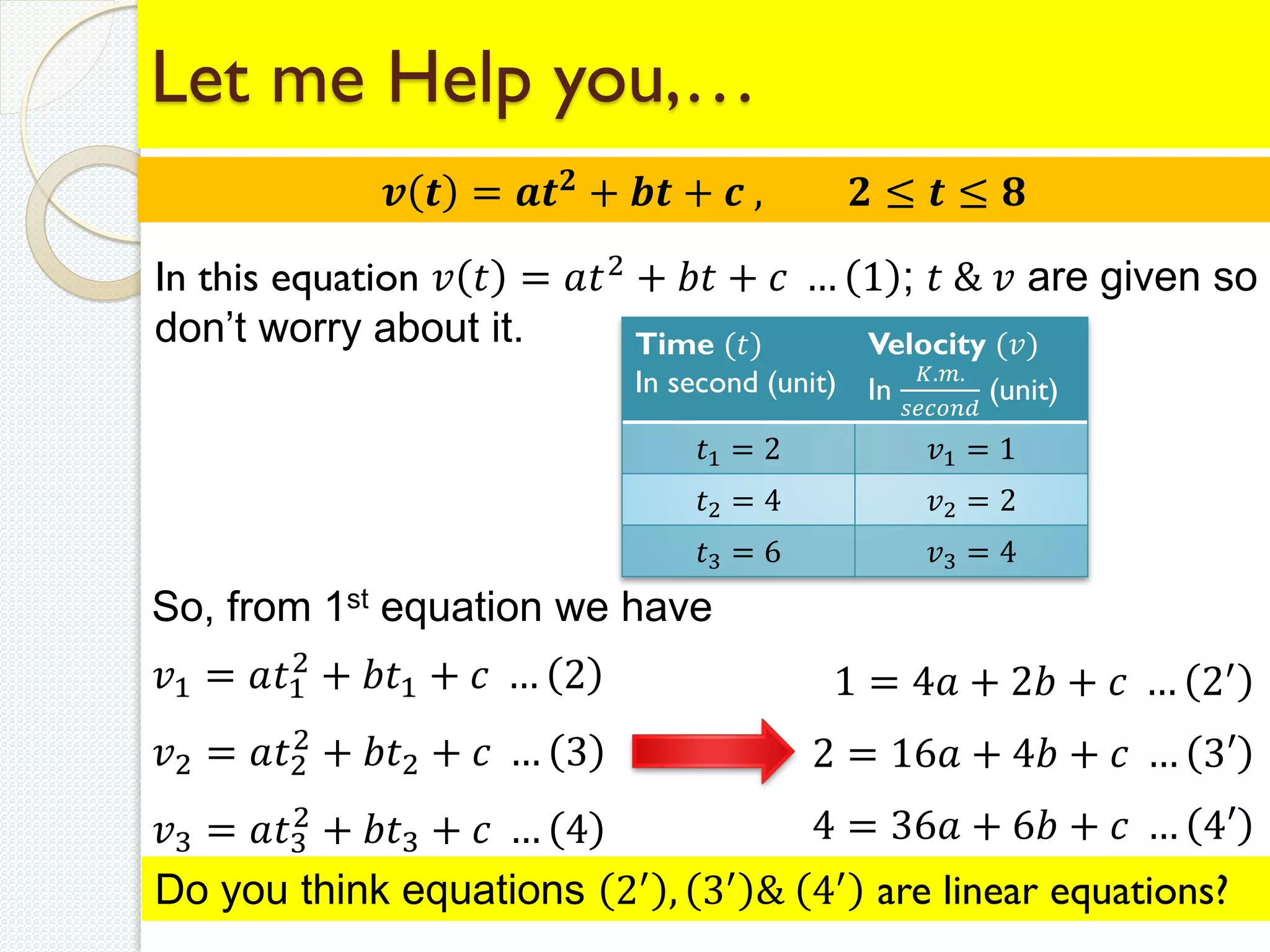

![From the above values 𝑎 = 0.125
𝑏 = −0.250
𝑐 = 1.000
& equation_(1) 𝑣 𝑡 = 𝑎𝑡2 + 𝑏𝑡 + 𝑐
we have
𝒗 𝒕 = 𝟎. 𝟏𝟐𝟓𝒕 𝟐
− 𝟎. 𝟐𝟓𝒕 + 𝟏 … 𝟓
Equation_(5) Shows the Rocket Velocity equation in the time interval
of [2 8] seconds.
Now can you answer for these:
Find The Velocity at 𝑡 = 5,7, 7.5 and 8 seconds.
From equation_(5) 𝑣 𝑡 = 0.125𝒕2 − 0.25𝒕 + 1
Put 𝑡 = 5 ⇒ 𝑣 5 = 0.125 × 𝟓2
− 0.25 × 𝟓 + 1 ⇒ 𝒗 𝟓 = 𝟐. 𝟖𝟕𝟓
𝒌𝒎
𝒔
𝑡 = 7 ⇒ 𝑣 7 = 0.125 × 𝟕2
− 0.25 × 𝟕 + 1 ⇒ 𝒗 𝟕 = 𝟓. 𝟑𝟕𝟓
𝒌𝒎
𝒔
𝑡 = 7.5 ⇒ 𝑣 7.5 = 0.125 × 𝟕. 𝟓2 − 0.25 × 𝟕. 𝟓 + 1 ⇒ 𝒗 𝟕. 𝟓 = 𝟔. 𝟏𝟓𝟔
𝒌𝒎
𝒔
𝑡 = 8 ⇒ 𝑣 8 = 0.125 × 𝟖2 − 0.25 × 𝟖 + 1 ⇒ 𝒗 𝟖 = 𝟕. 𝟎𝟎
𝒌𝒎](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gausseliminationgaussjordanmethodppt-170319070213/75/Gauss-elimination-Gauss-Jordan-method-23-2048.jpg)