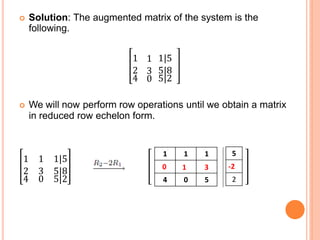
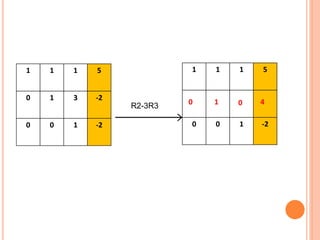
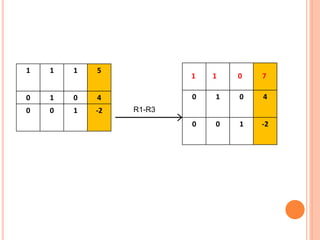
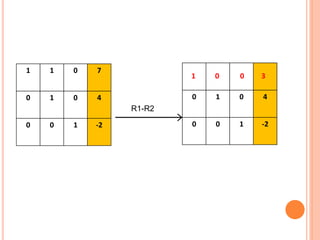
The document discusses the Gauss-Jordan elimination method for solving systems of linear equations. It involves transforming the augmented matrix of the system into reduced row echelon form using elementary row operations. The key steps are to turn the equations into an augmented matrix, use row operations to put the matrix in diagonal form with ones on the diagonal, and then divide elements to solve for the variables. An example problem demonstrates applying the Gauss-Jordan method to solve a system of three equations with three unknowns.


![HERE ARE THE STEPS TO GAUSS-JORDAN
ELIMINATION:
Turn the equations into an augmented matrix.
Use elementary row operations on matrix [A|b] to
transform A into diagonal form. Make sure there are
no zeros in the diagonal.
Divide the diagonal element and the right-hand
element (of b) for that diagonal element's row so
that the diagonal element is equal to one.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cp11gj1-220716120602-4ff3245c/85/Gauss-jordan-method-pptx-3-320.jpg)