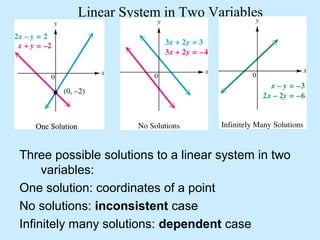
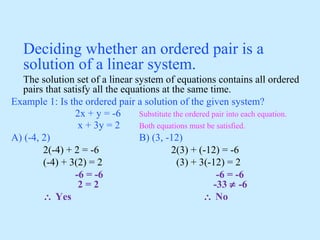
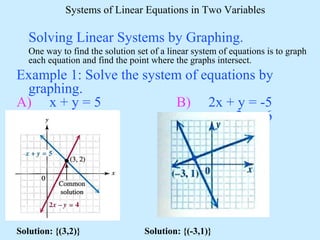
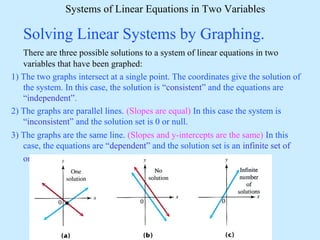
There are three possible solutions to a system of linear equations in two variables:
One solution: the graphs intersect at a single point, giving the solution coordinates.
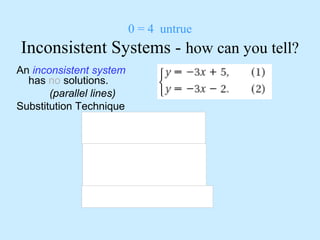
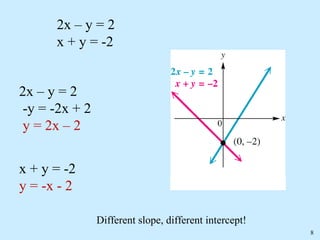
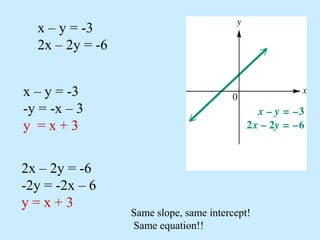
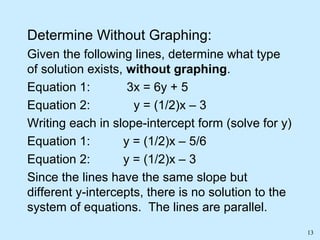
No solution: the graphs are parallel lines, making the system inconsistent.
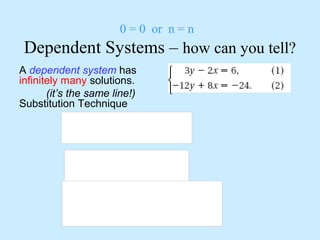
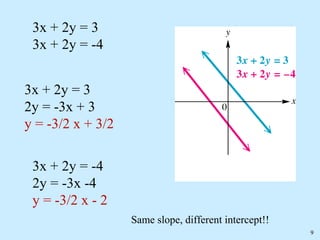
Infinitely many solutions: the graphs are the same line, making the equations dependent.
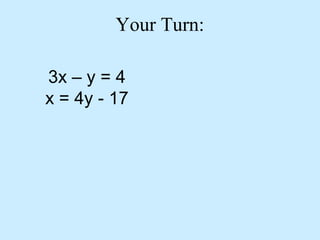
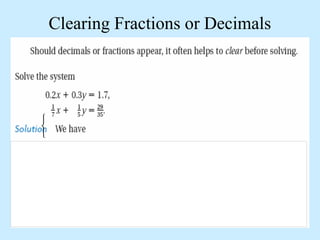
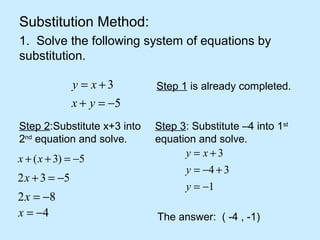
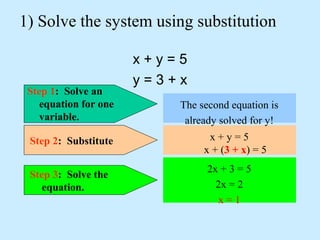
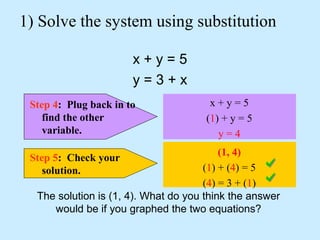
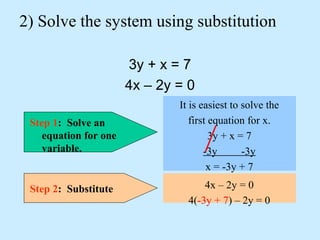
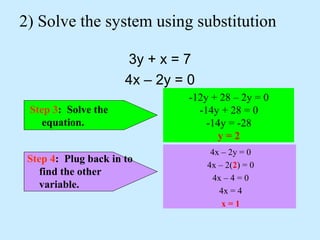
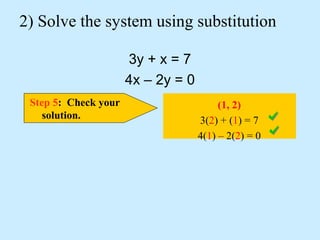
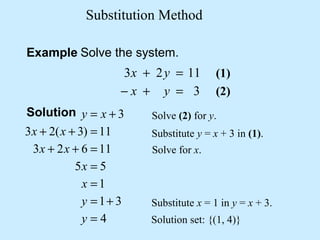
The substitution method for solving systems involves: 1) solving one equation for a variable, 2) substituting into the other equation, 3) solving the new equation, and 4) back-substituting to find the remaining variable.










![Systems of Linear Equations in Two Variables
Solving Linear Systems of two variables by
Method of Substitution.
Example 7:
Solve the system :
y = -2x + 2
-2x + 5(-2x + 2) = 22 -2x - 10x + 10 = 22
-12x = 12
x = -1 2(-1) + y = 2
y = 4
Solution Set: {(-1,4)}
1 1 1
2 4 2
2
1 1 1
rewrite as 4[ ] 2 2
2 4 2
: 2 2
-2 5 2
5 2
2
2
x y
x y
x y x y
Solve x y
x y
⇒ + = ⇒ + =
+
+
=
+
=
=
=
+
−](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/solvingsystemsoflinearequations-130926104114-phpapp01/85/Solving-systems-of-Linear-Equations-27-320.jpg)