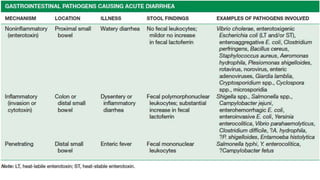
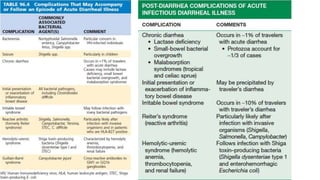
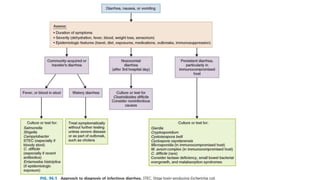
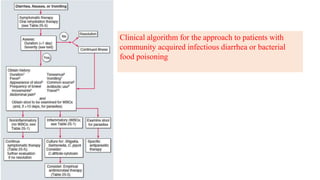
Gastrointestinal (GI) infections arise from various pathogens and can lead to significant morbidity and mortality, particularly in children under five in low-income countries. Symptoms can include diarrhea, vomiting, and systemic issues, with critical outbreaks often linked to contaminated food or water. The interplay of risk factors such as nutrition, age, and the intestinal microbiome influences susceptibility and severity of infections.



























![Prophylaxis
There are three GI infections for which vaccines have shown efficacy and are
approved for use.
A pentavalent rotavirus vaccine was recommended for routine use in infants in the
United States in 2006, with three doses given at 2, 4, and 6 months, respectively.
A monovalent rotavirus vaccine was recommended as an alternative in 2008, with
two doses given at 2 and 4 months.
For cholera, there are two killed whole-cell oral cholera vaccines that are
internationally licensed and prequalified by WHO.
One is a monovalent V. cholerae O1 vaccine, supplemented with the B subunit of
cholera toxin (manufactured as Dukoral [Valneva; Solna, Sweden]), and
the second is a bivalent V. cholerae O1 and O139 vaccine without supplemental B
subunit (manufactured as either Shanchol or Euvichol [SBL Vaccines; Shantha
Biotec, Hyderabad, India]).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gastrointestinalinfections-201110064005/85/Gastrointestinal-infections-40-320.jpg)
![Prophylaxis
In addition to these two killed whole-cell vaccines, a live-attenuated
monovalent oral cholera vaccine, CVD 103-HgR (manufactured as
Vaxchora [PaxVax; Redwood City, CA]), is licensed in the United States
and currently recommended for adult travelers to cholera endemic areas.
There are two current approaches to typhoid vaccination:
an oral, live-attenuated Ty21a vaccine, which is given in three doses and
produces approximately 50% protective efficacy over the subsequent 3
years, and
a parenteral Vi (virulence) polysaccharide vaccine, which is given in one
dose and produces approximately 60% protective efficacy over the
subsequent 2 years](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gastrointestinalinfections-201110064005/85/Gastrointestinal-infections-41-320.jpg)