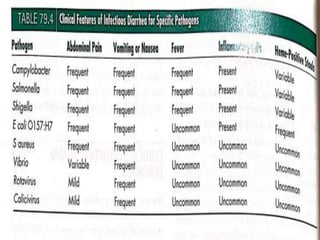
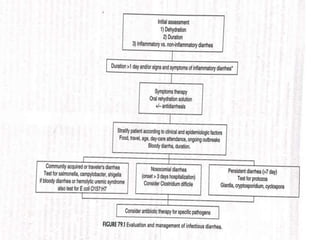
Gastrointestinal infections pose significant health risks, primarily dehydration, particularly affecting children under 5 and the elderly. Rehydration through oral rehydration therapy is essential for treatment, and infectious diarrhea can be caused by various pathogens, including viruses, bacteria, and parasites. Diagnosis and treatment strategies vary based on the type and severity of diarrhea and the causative organism, with a focus on fluid replacement and targeted antimicrobial therapy as needed.