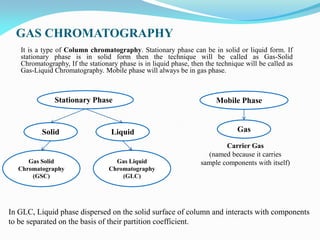
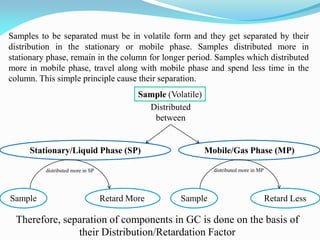
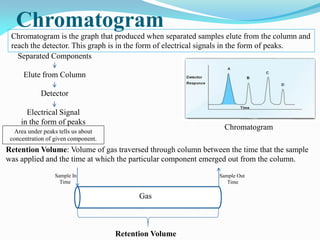
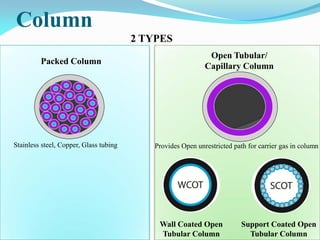
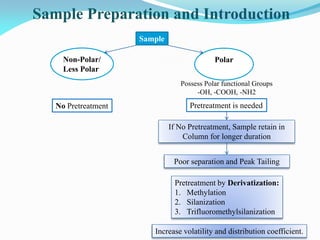
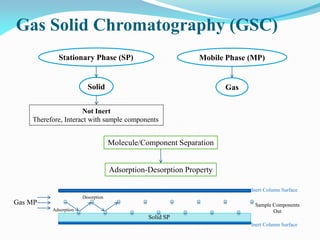
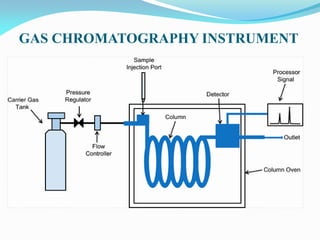
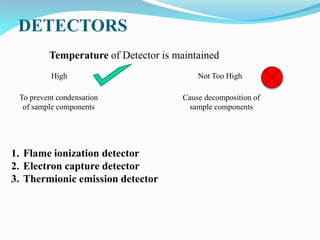
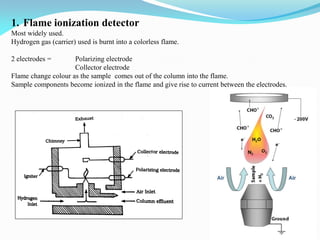
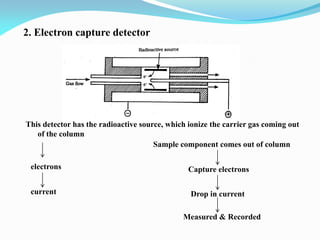
Gas chromatography is a type of chromatography that uses a mobile gas phase to transport sample components through a column containing a stationary liquid or solid phase. The separation of components is based on their distribution between the mobile gas phase and stationary phase. There are two main types - gas-solid chromatography where the stationary phase is a solid, and gas-liquid chromatography where the stationary phase is a liquid coated on an inert solid support. Common applications of gas chromatography include separation and analysis of organic and inorganic compounds, study of reaction rates and mechanisms, and determination of molecular properties.