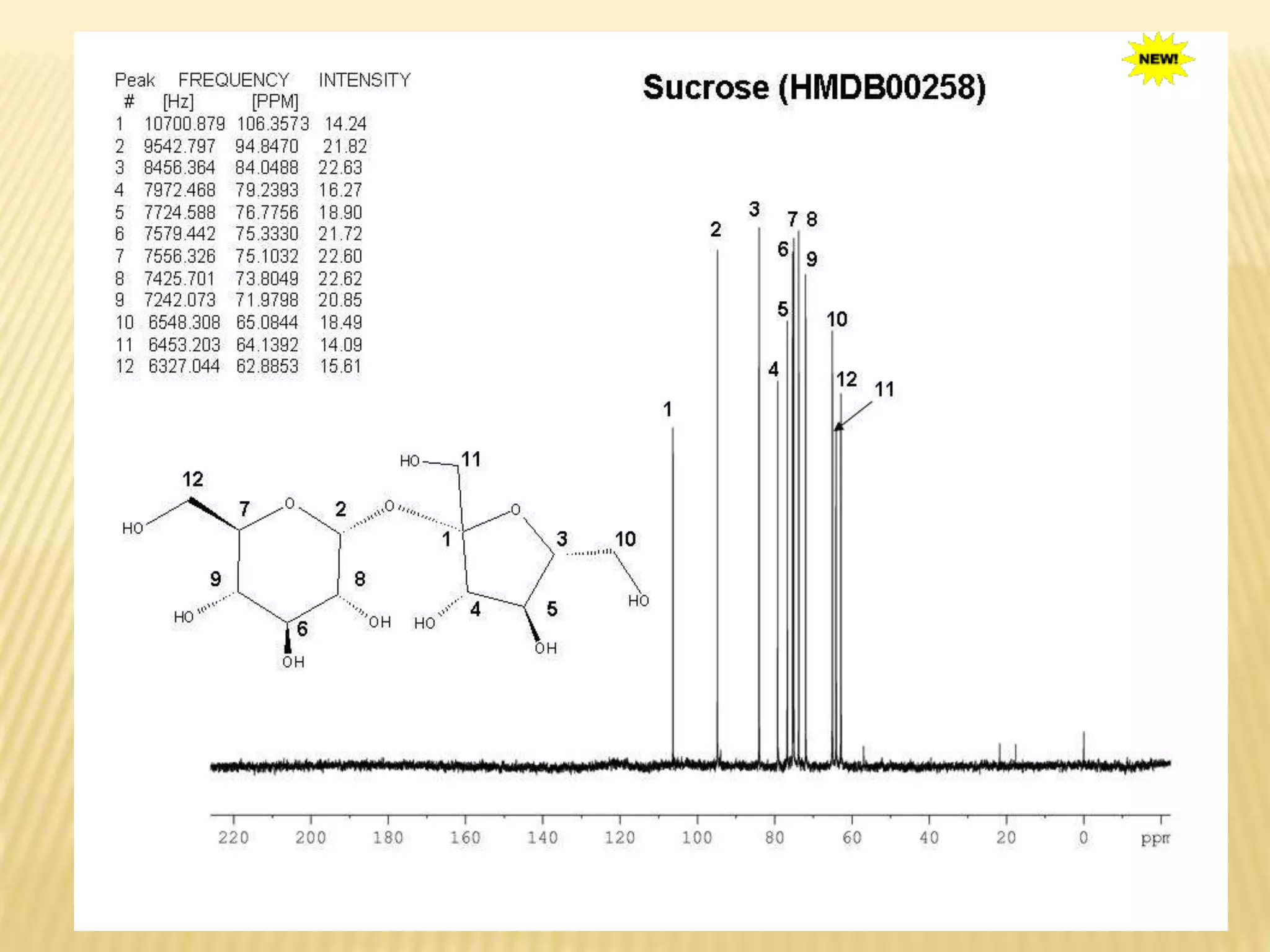
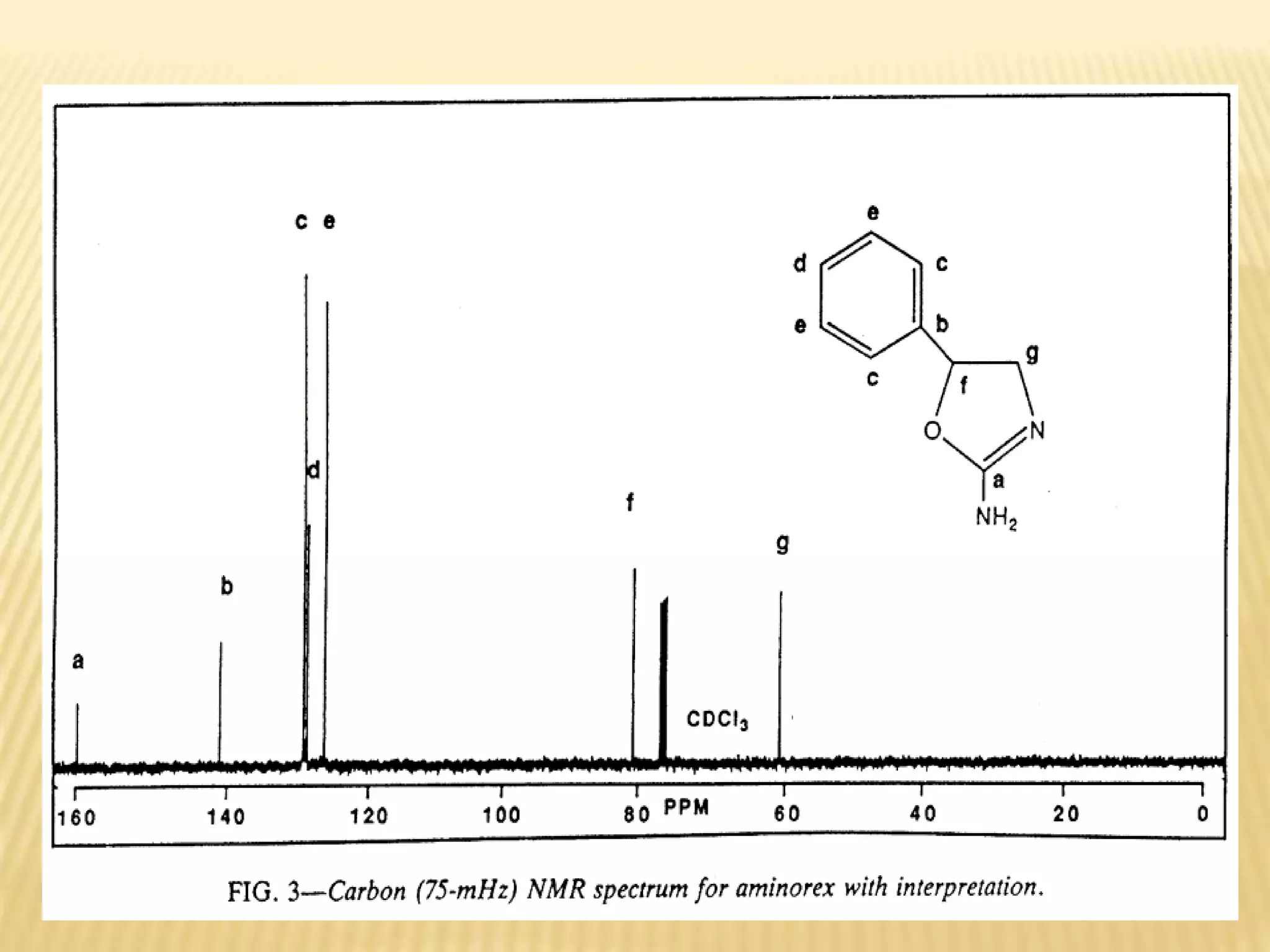
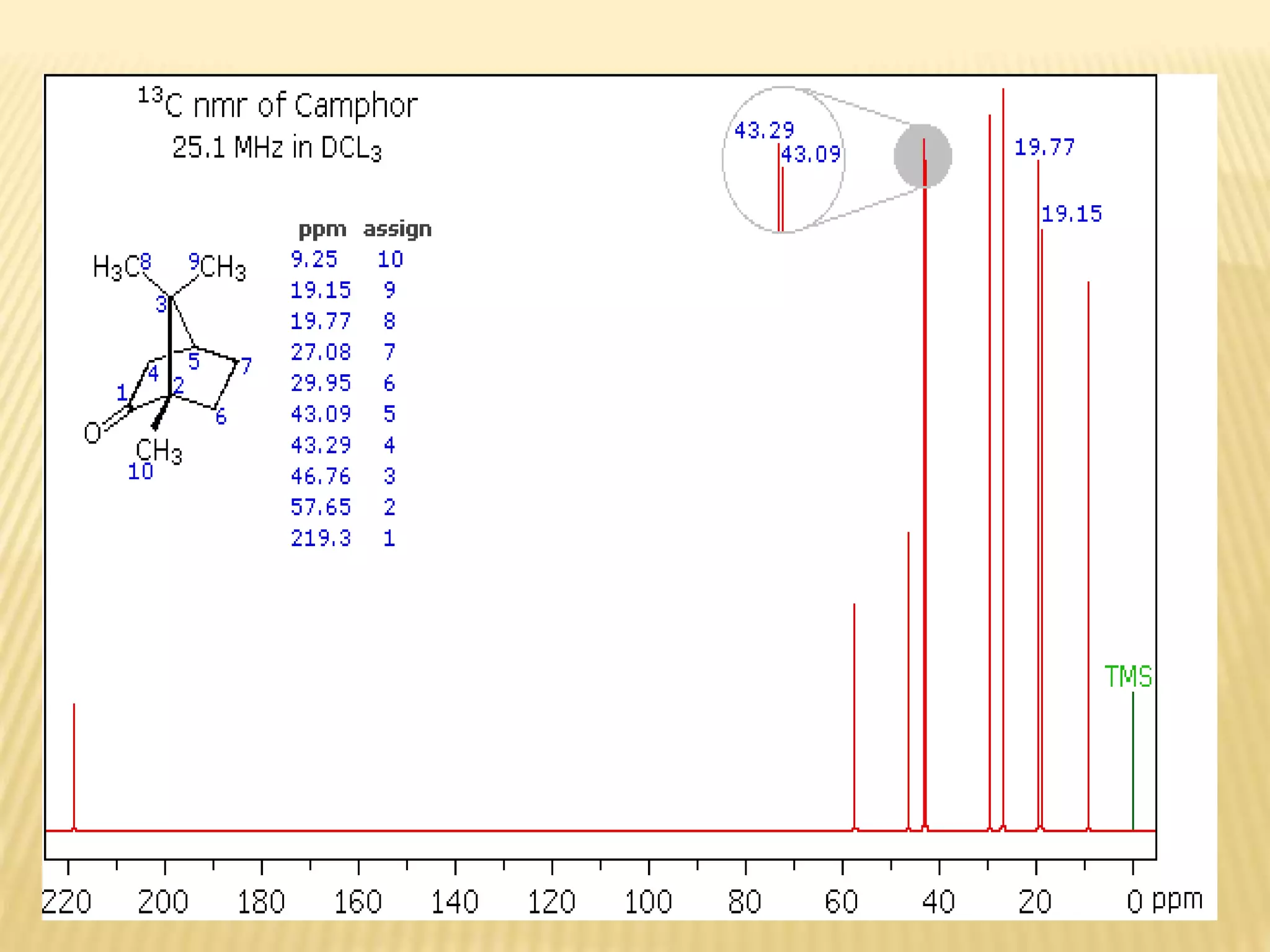
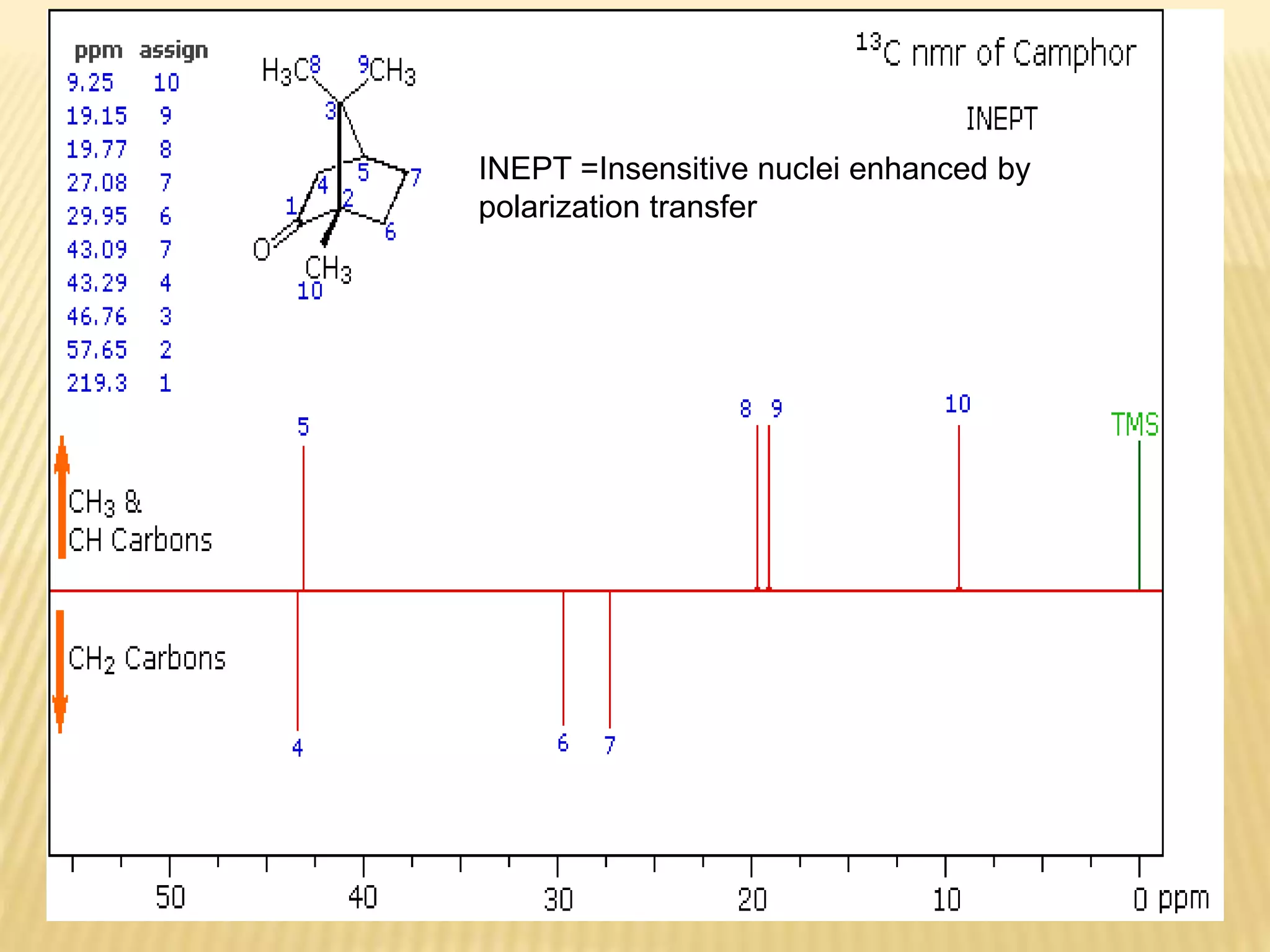
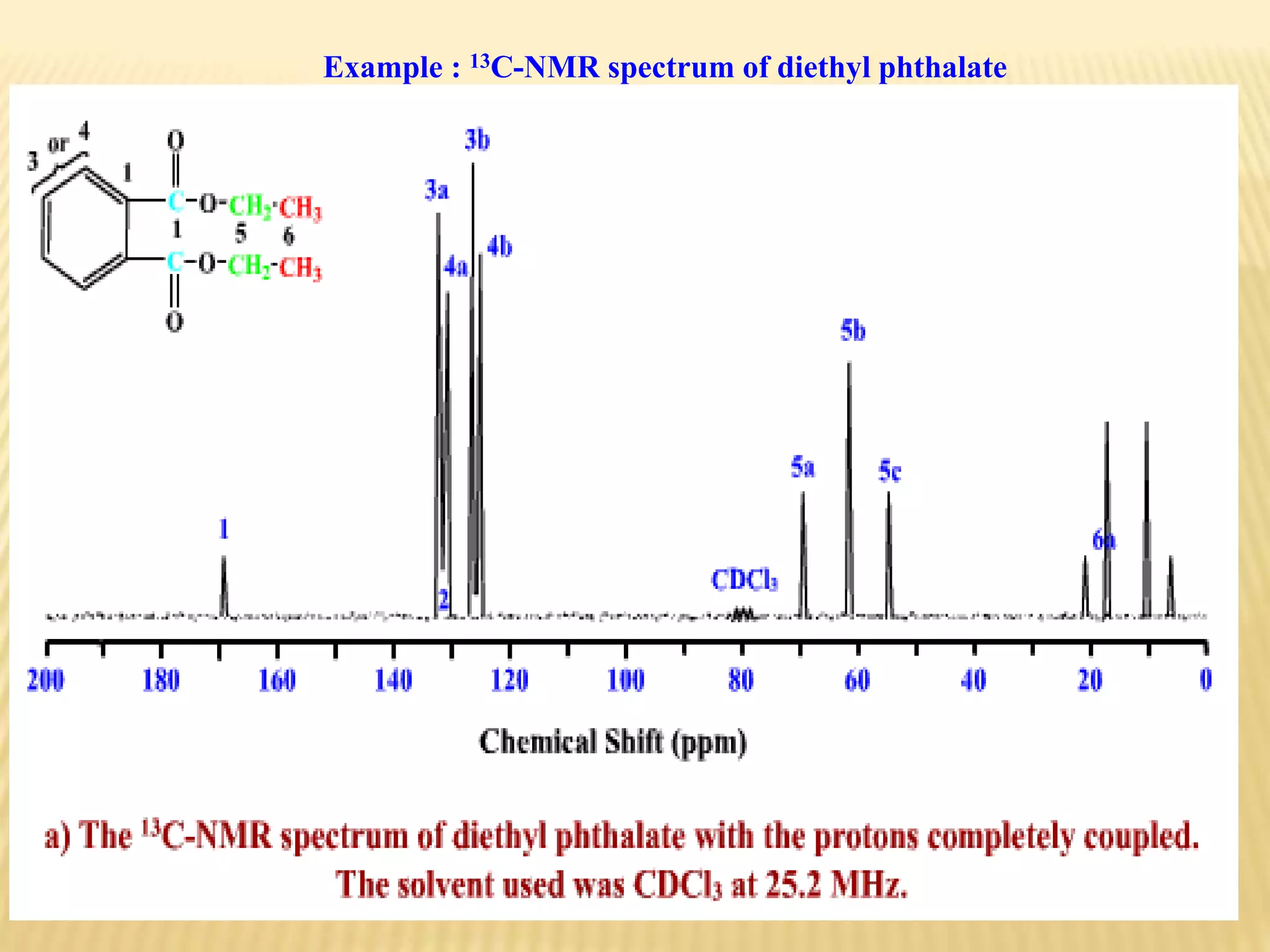
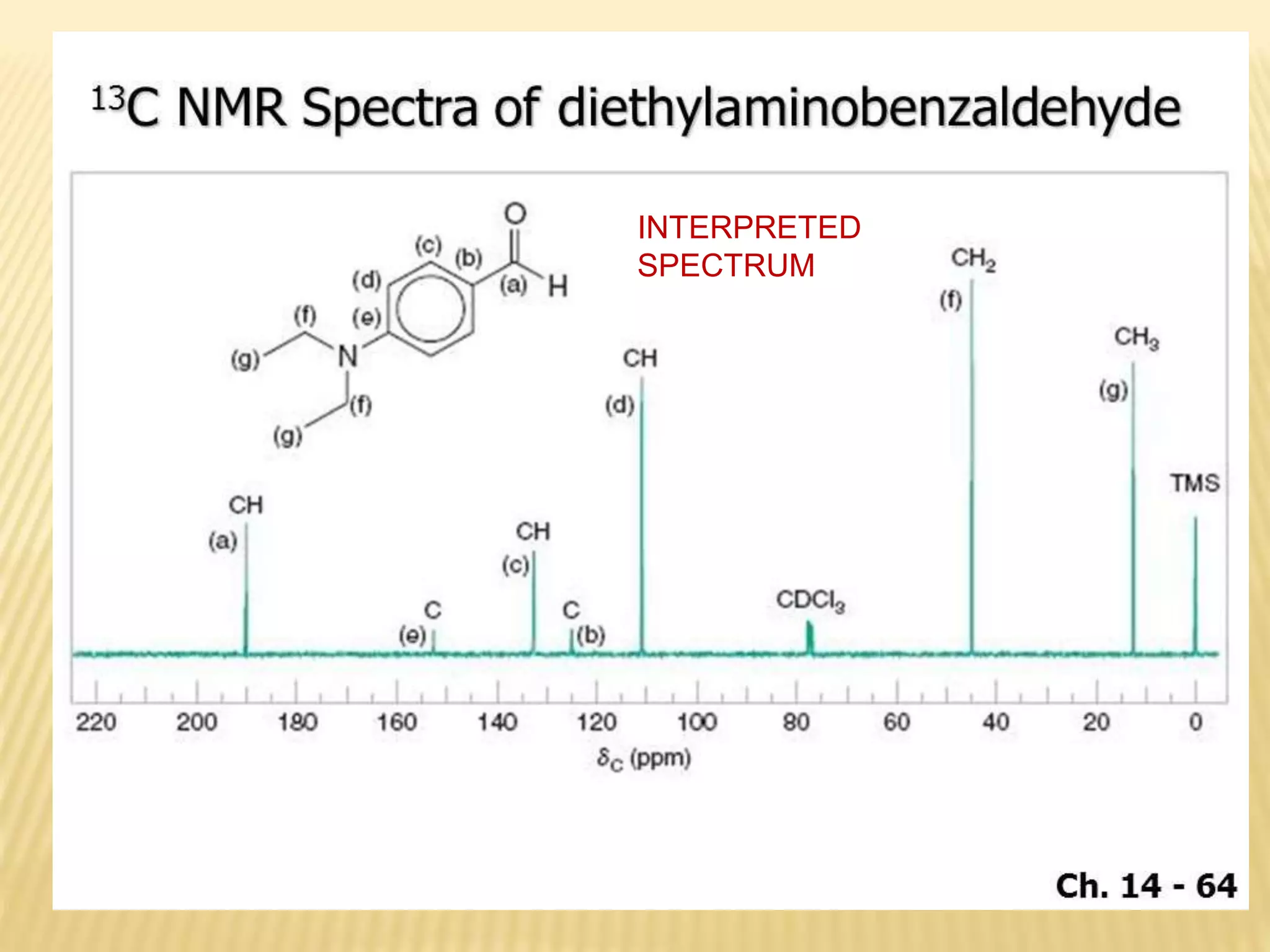
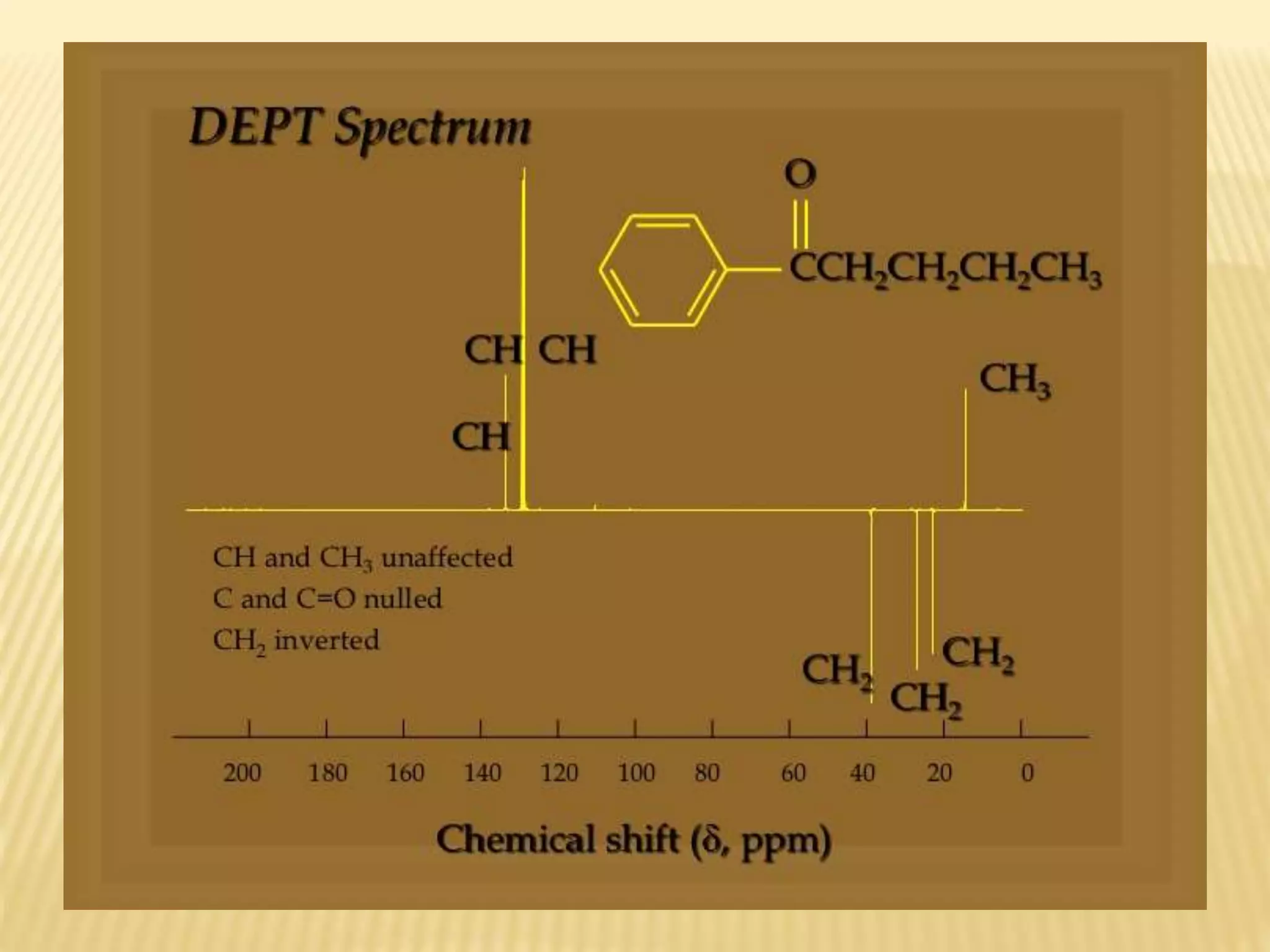
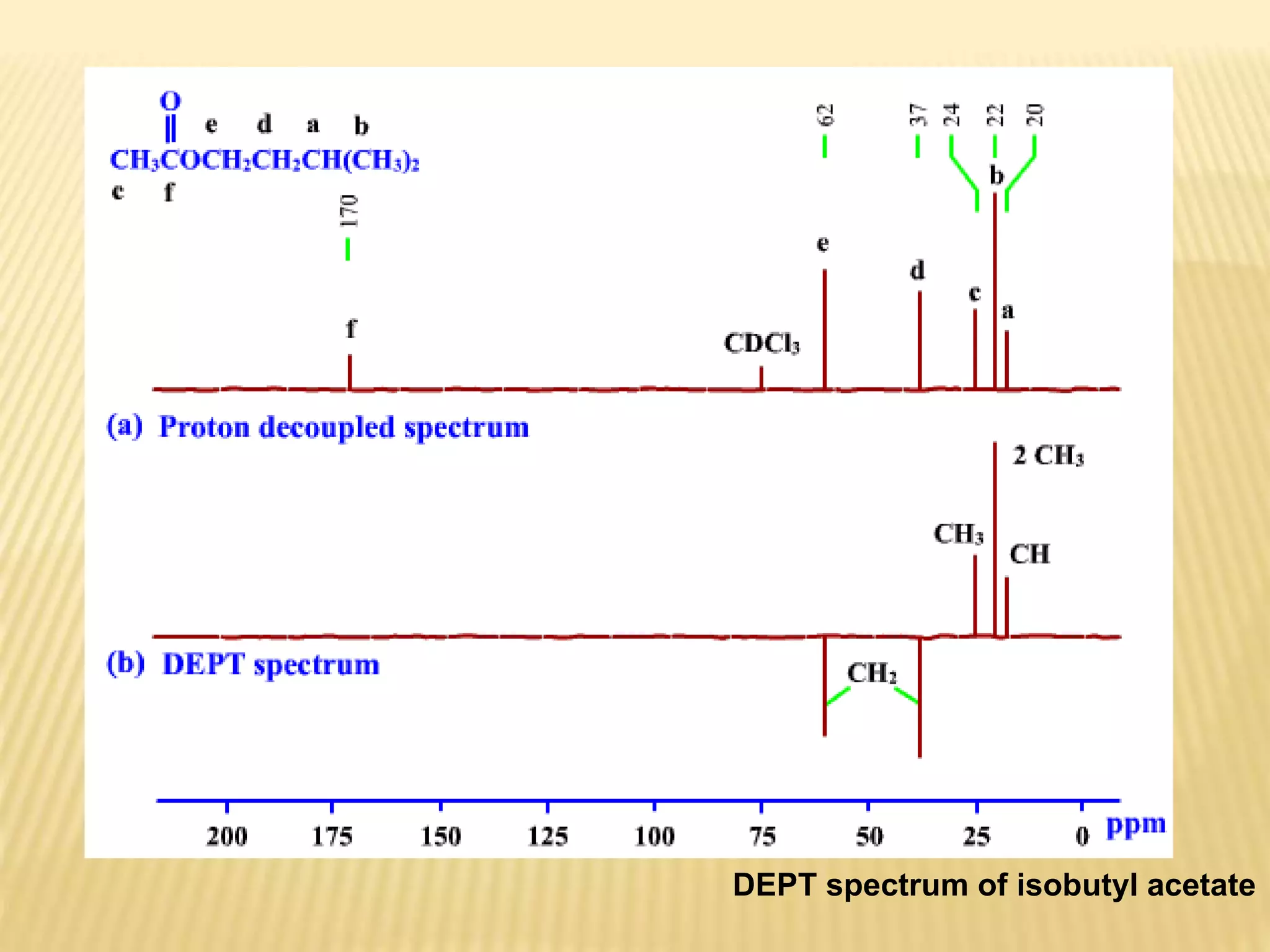
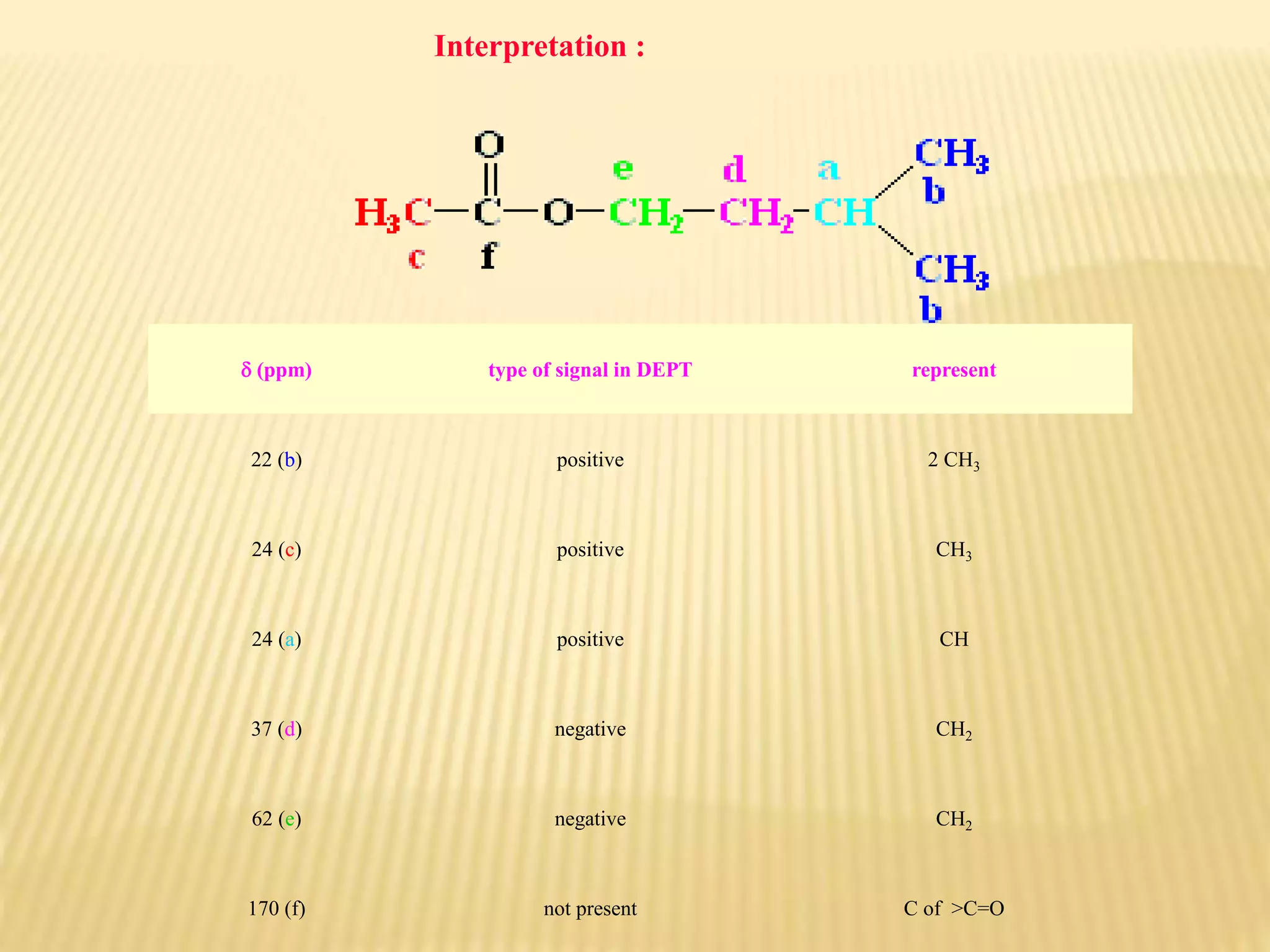
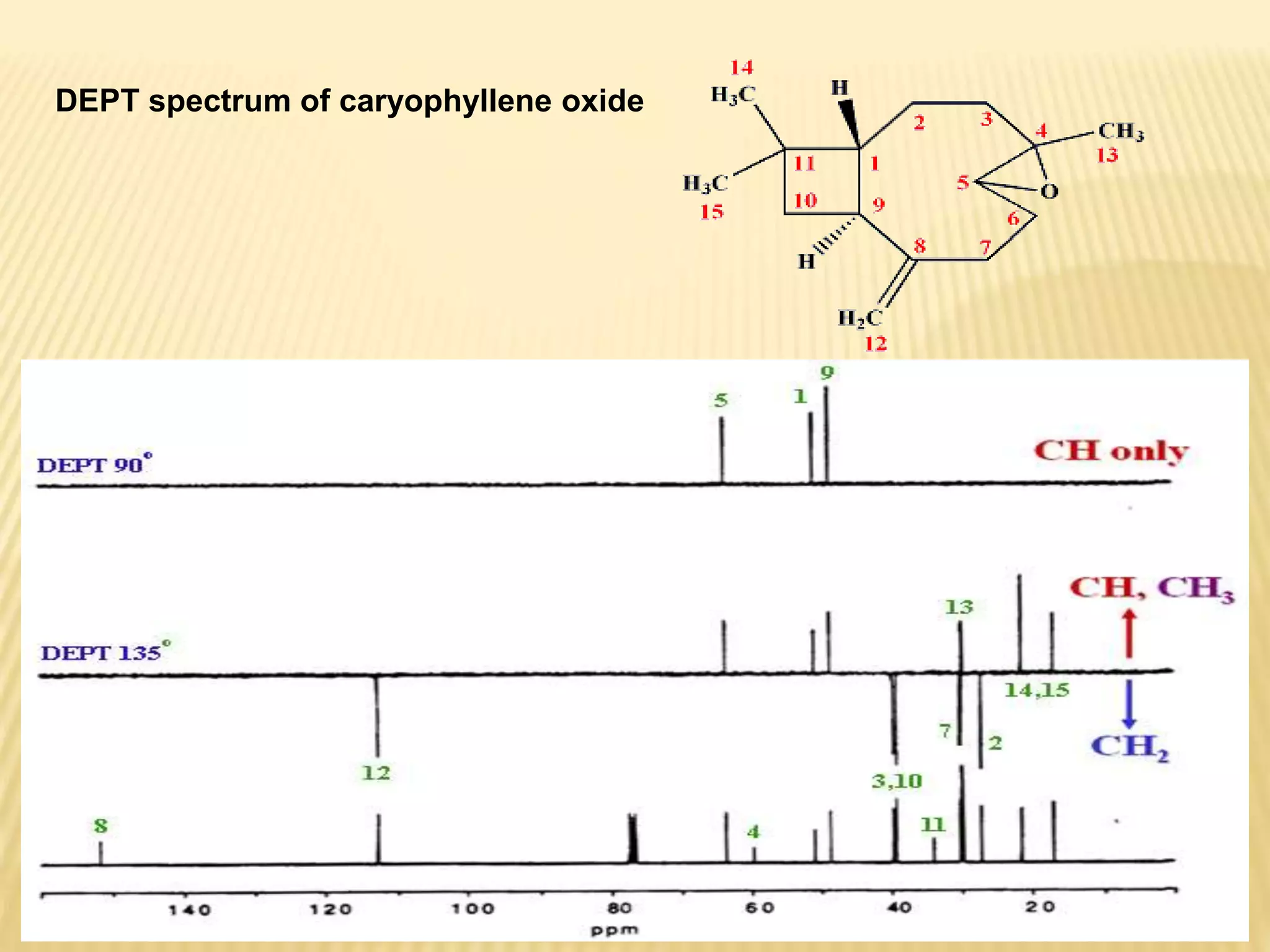
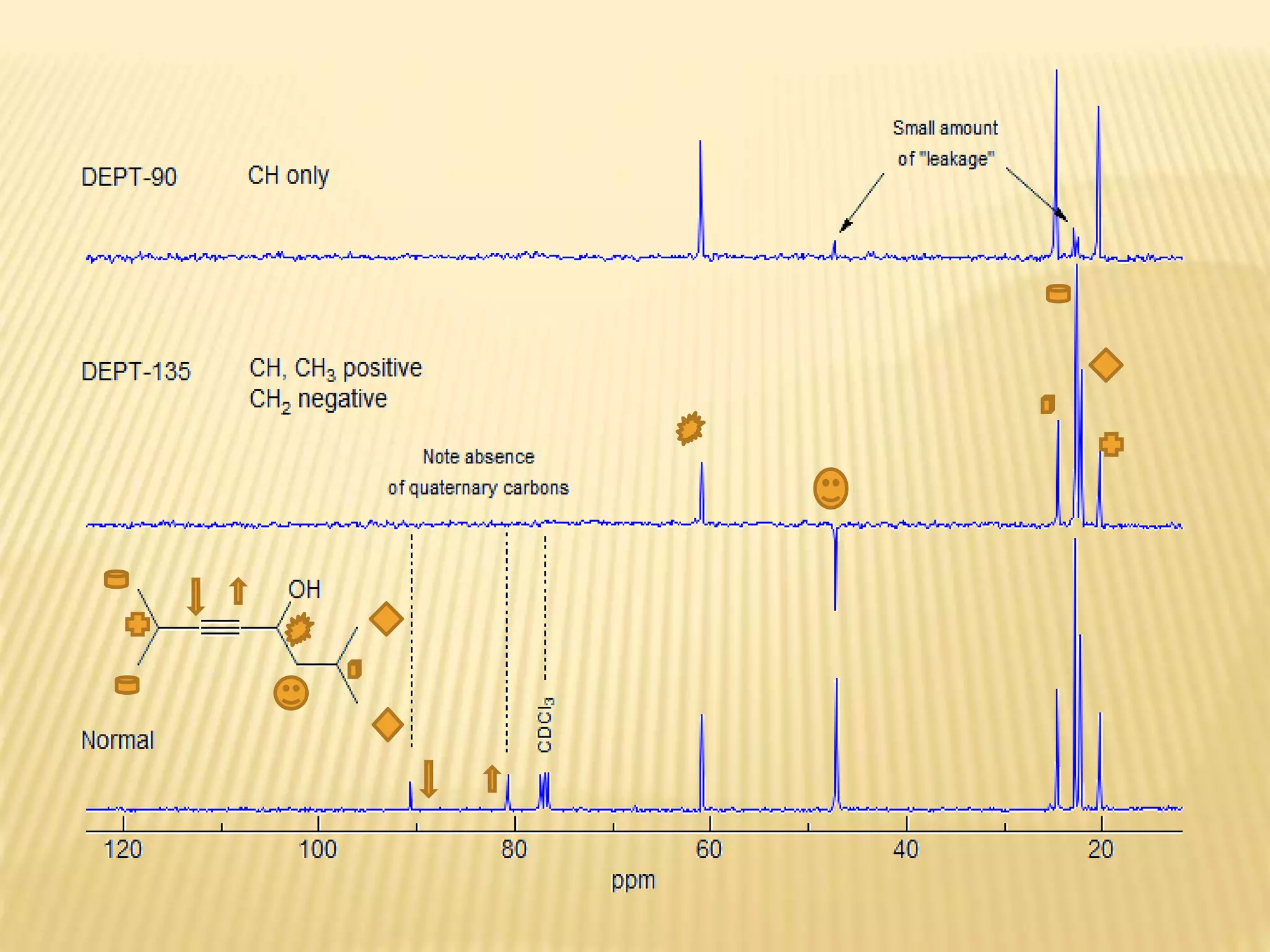
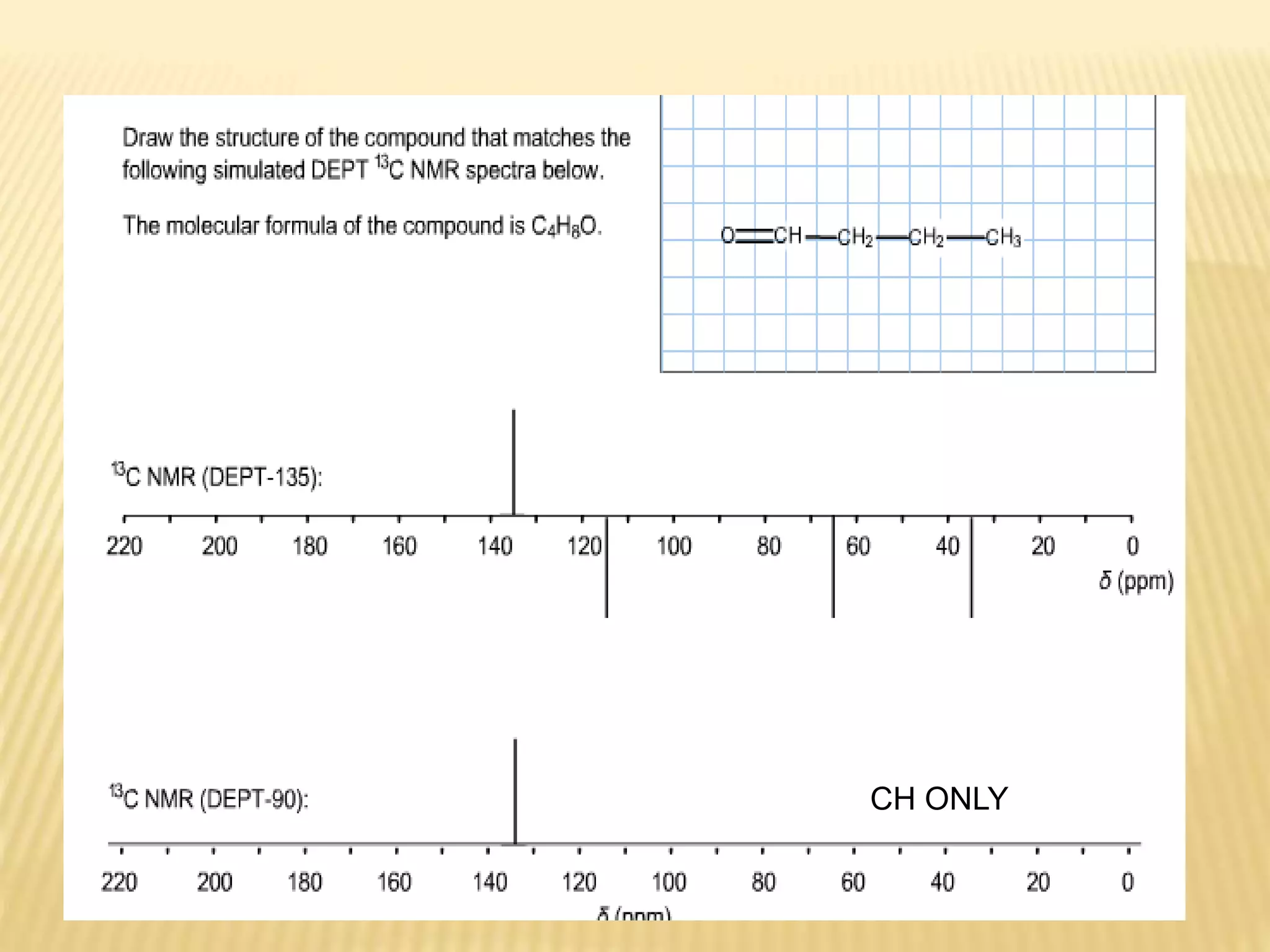
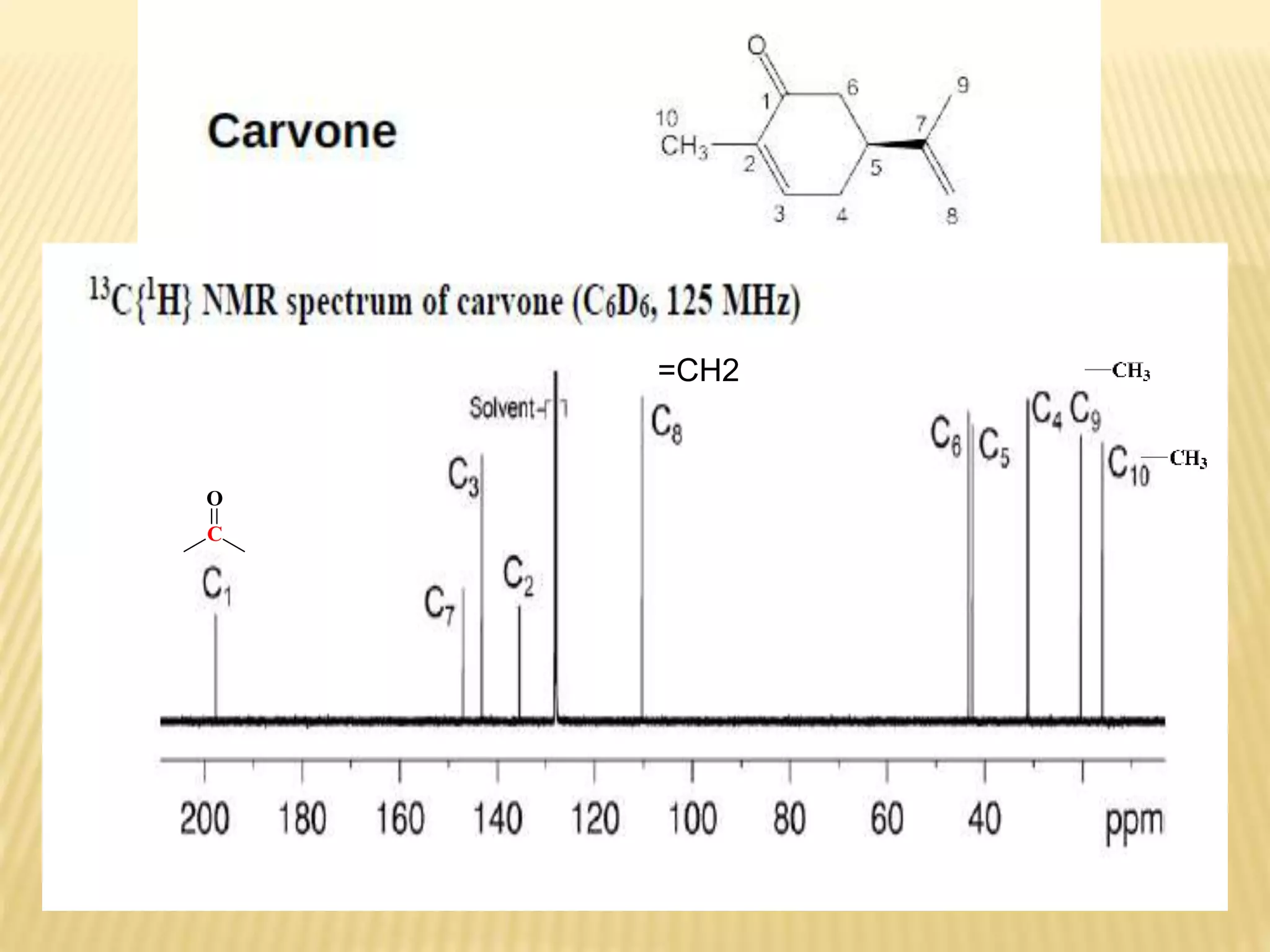
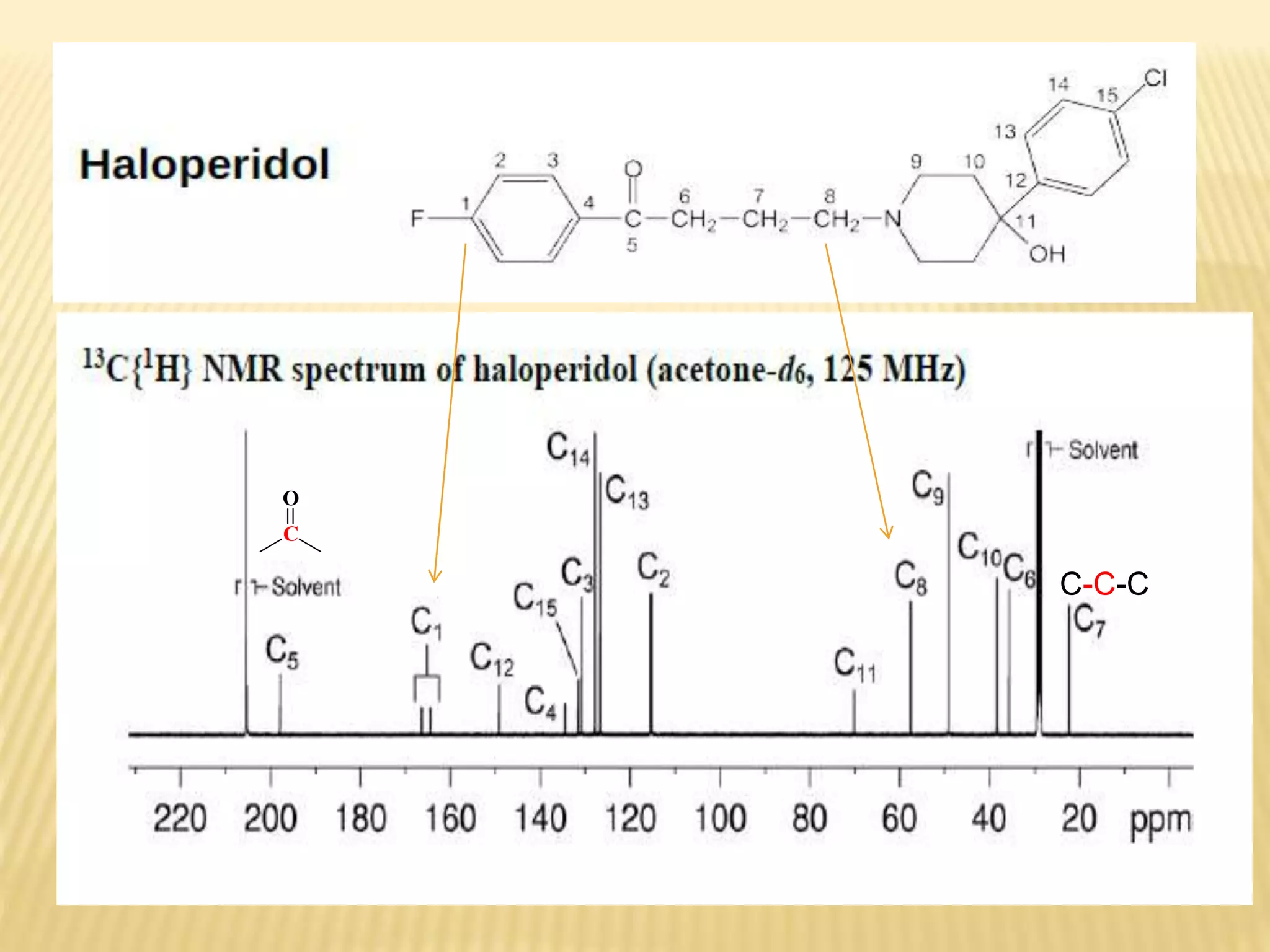
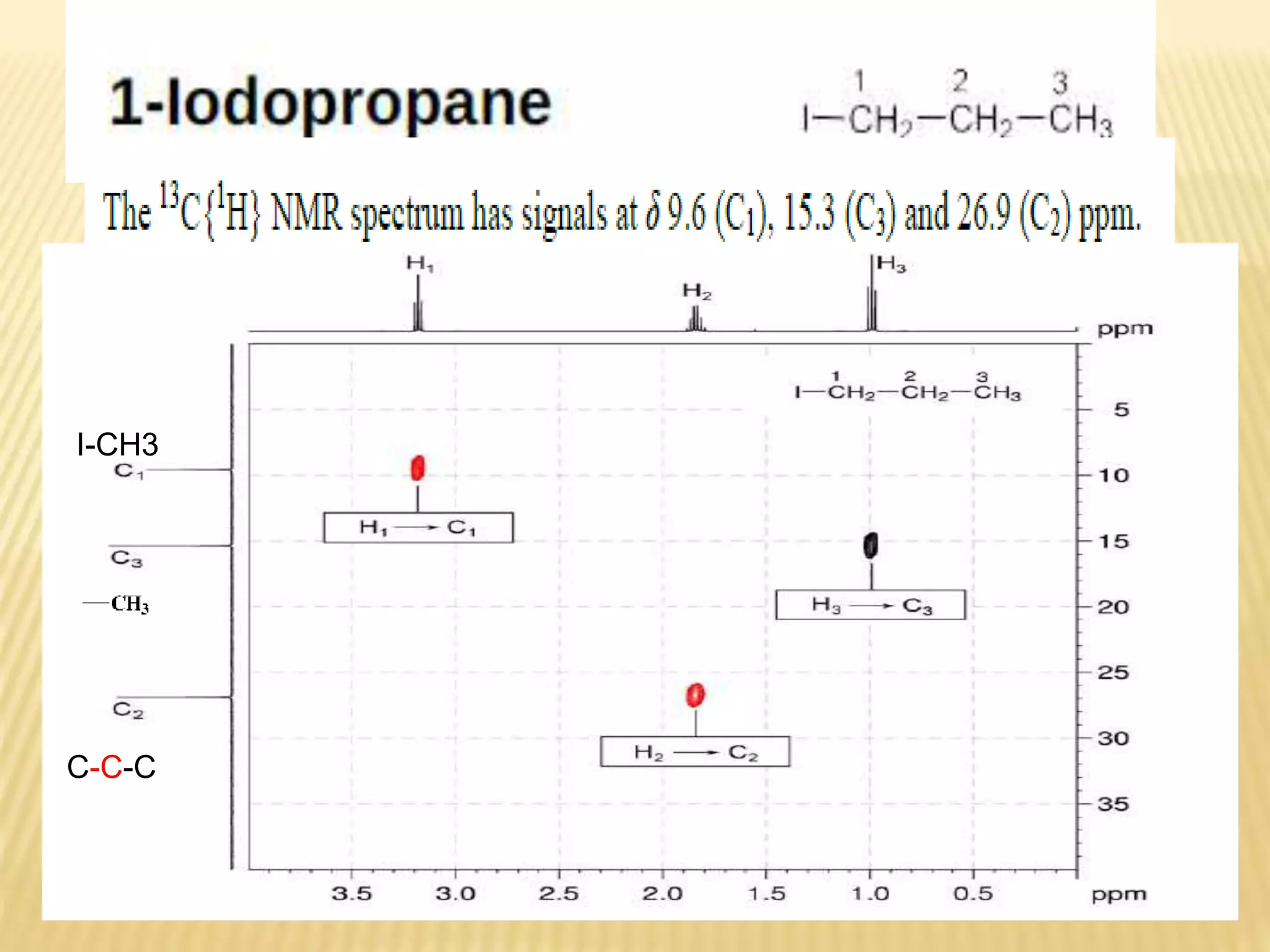
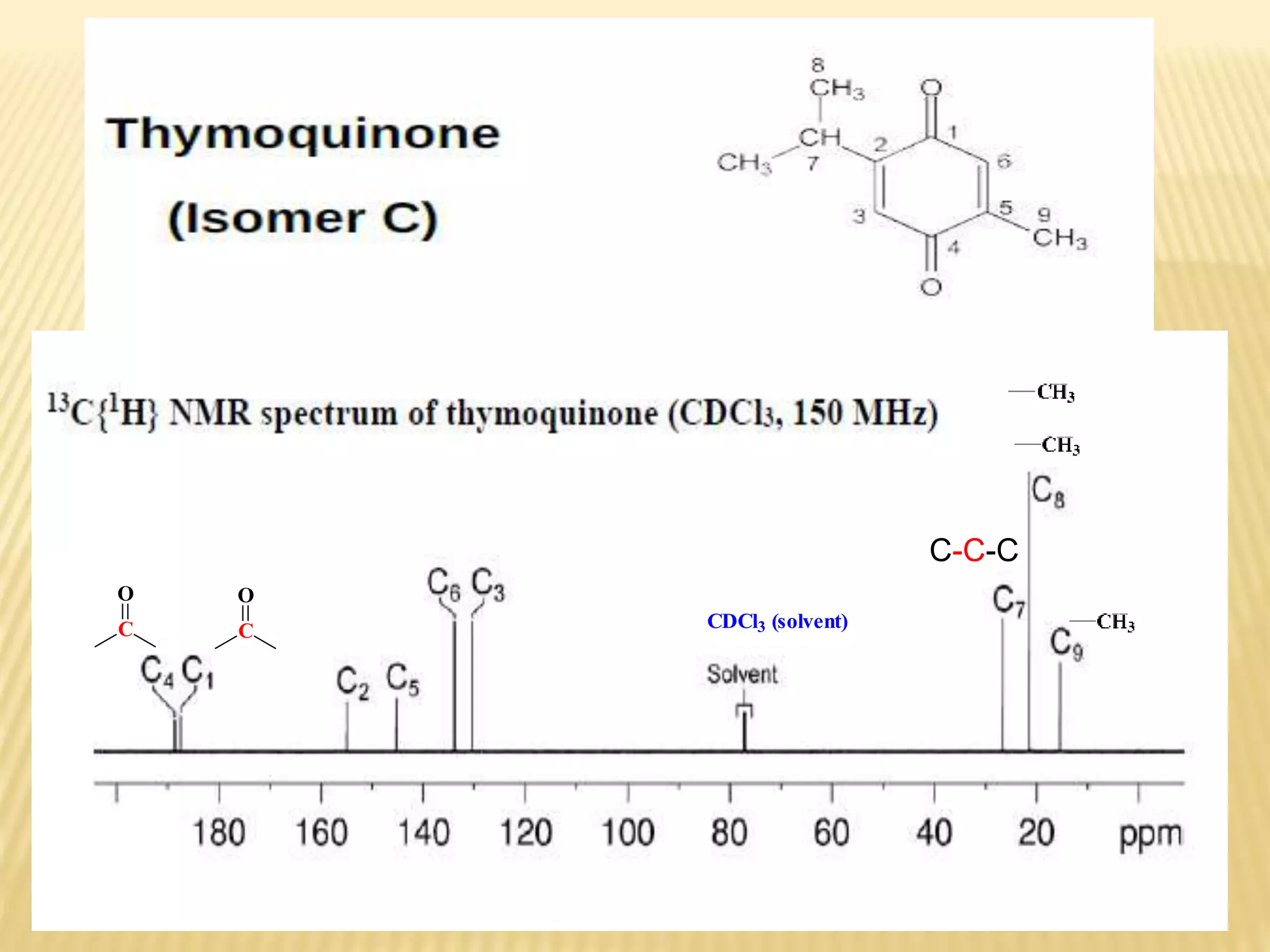
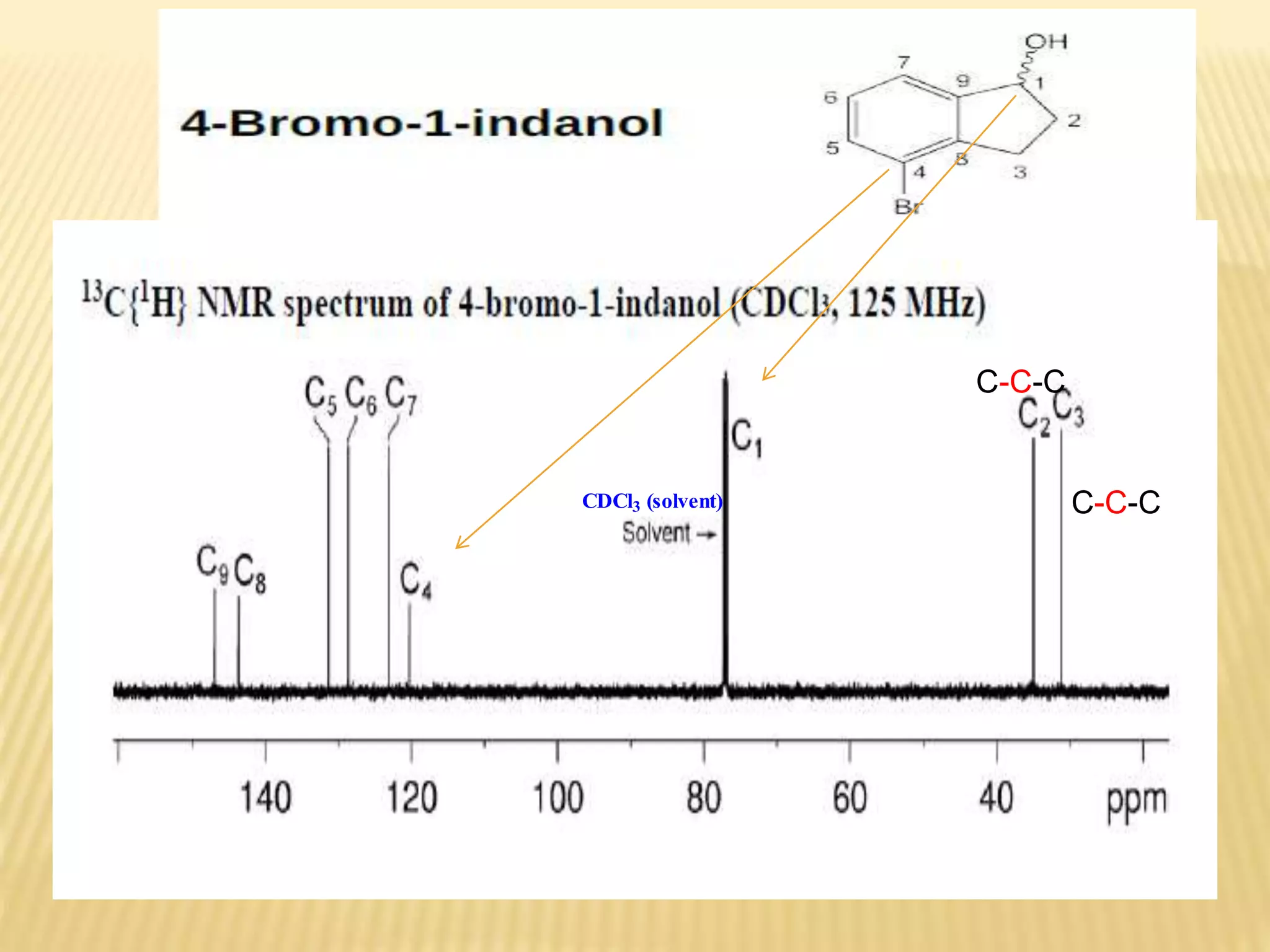
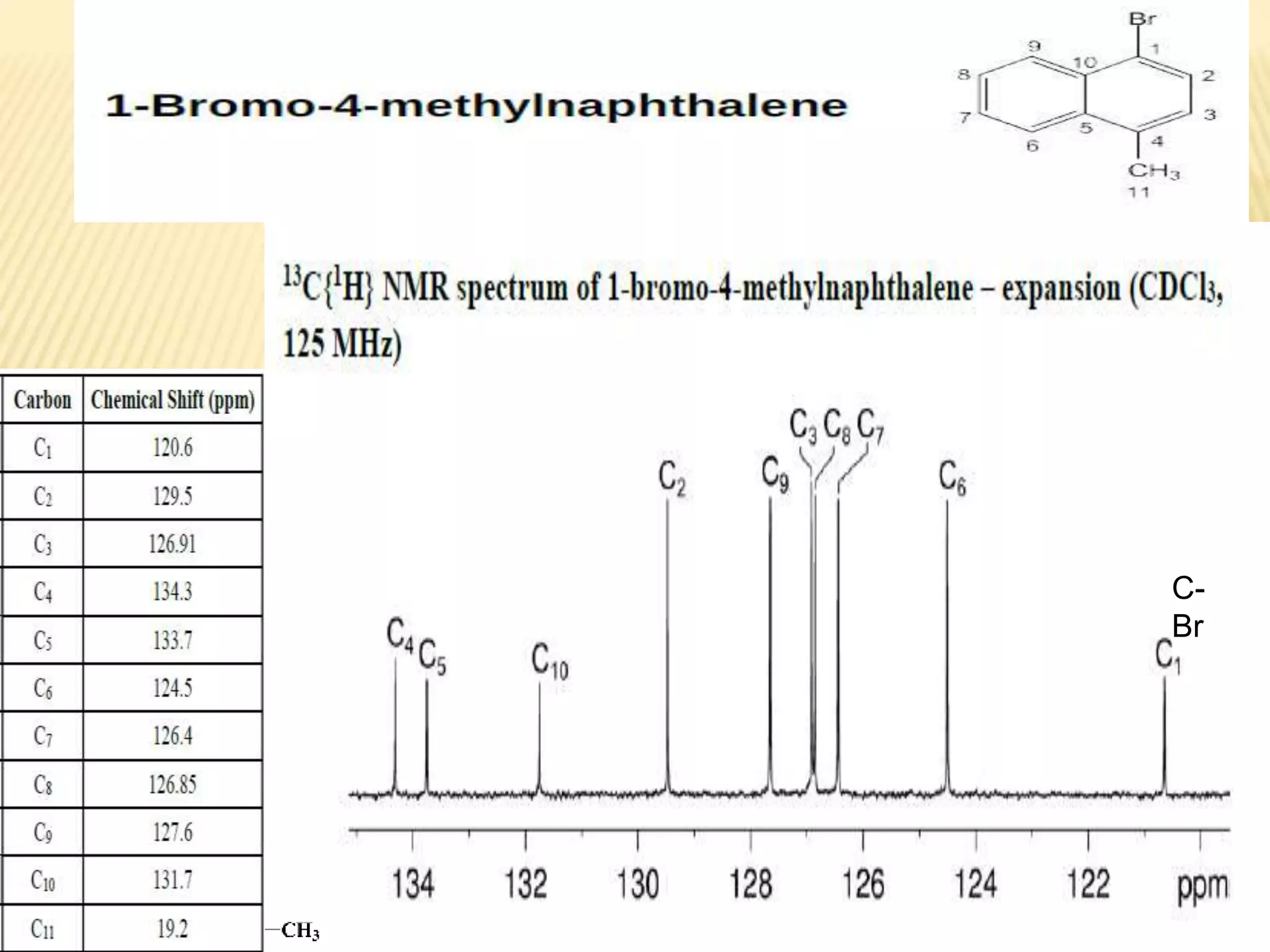
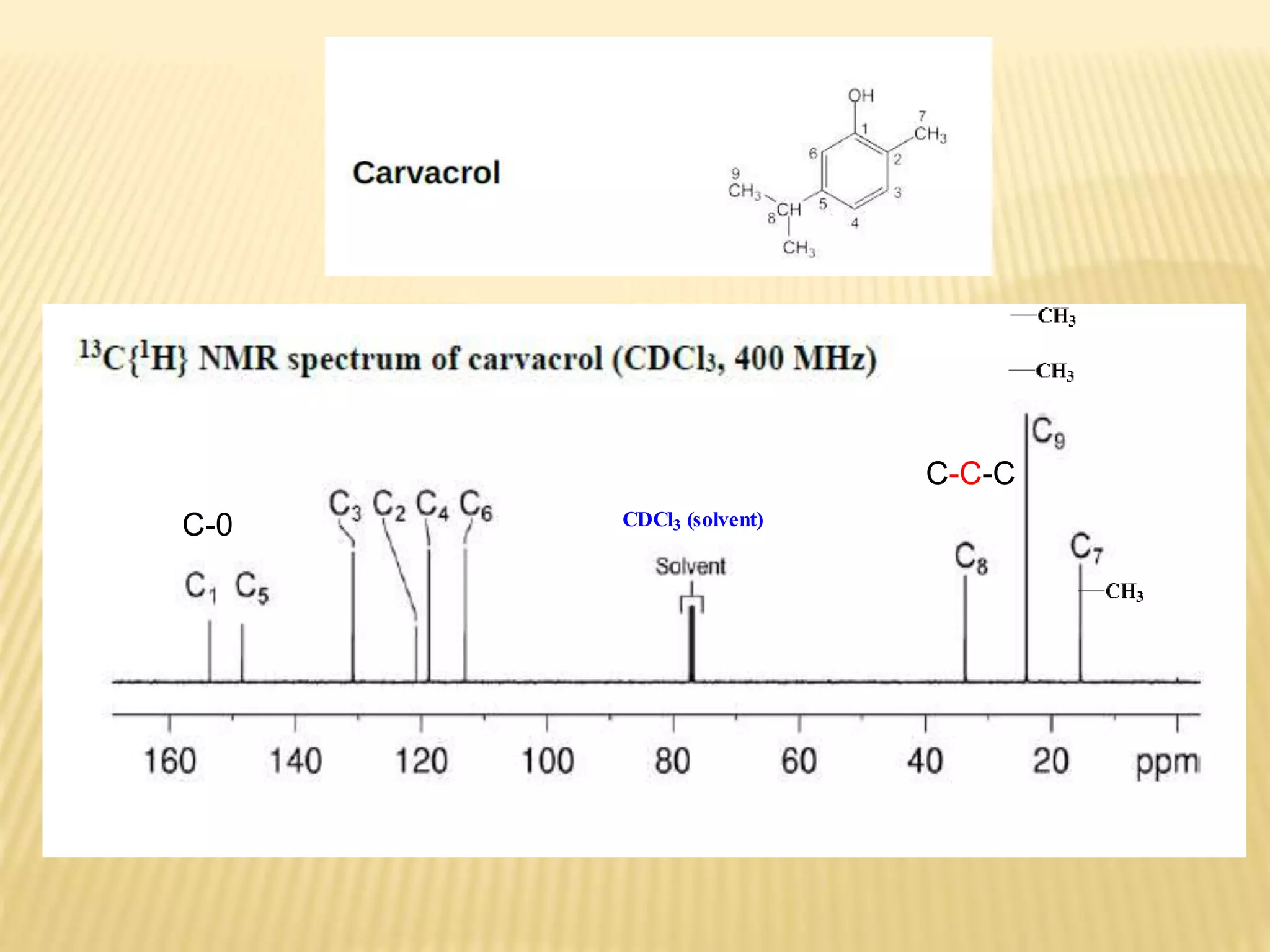
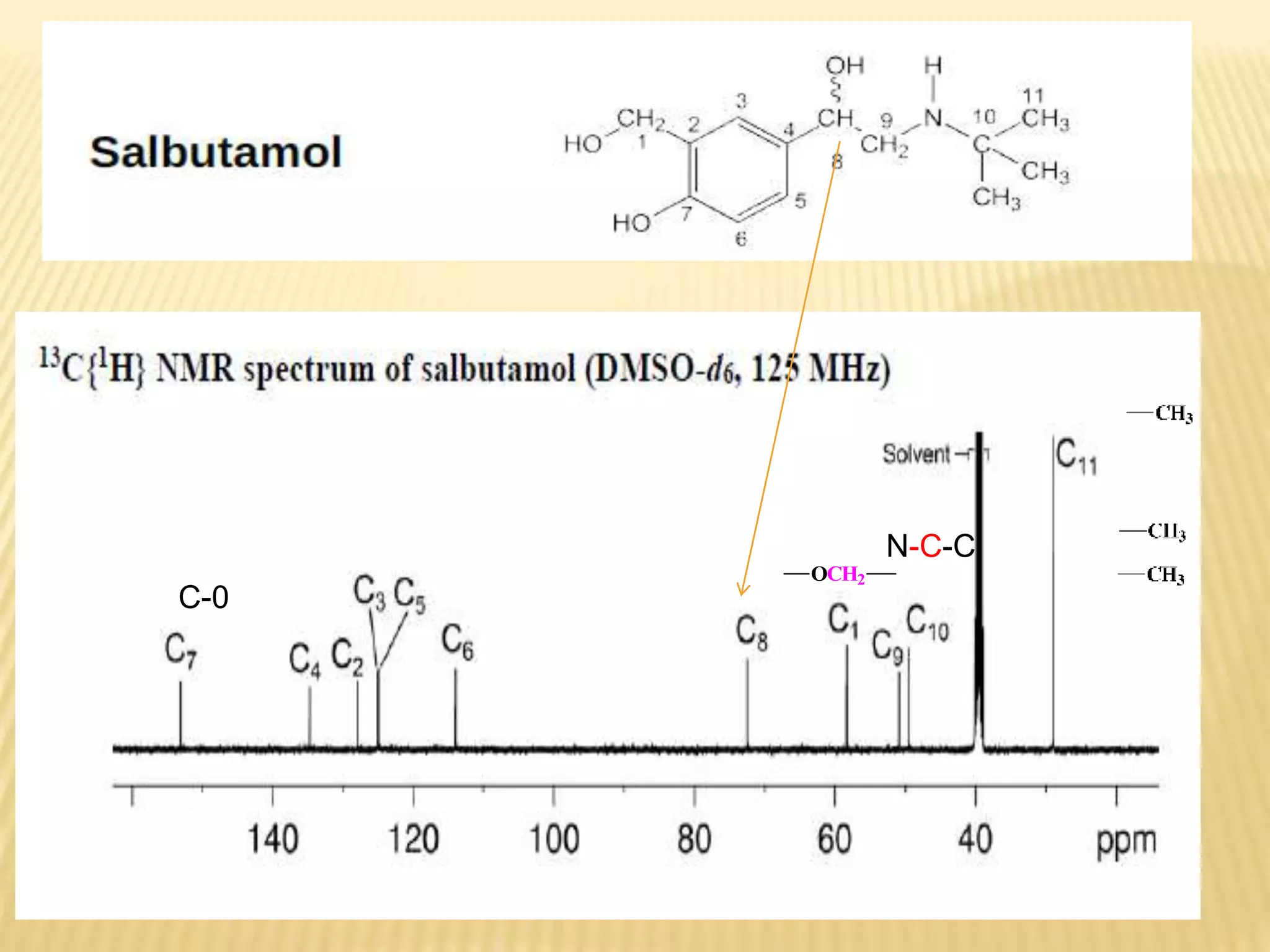
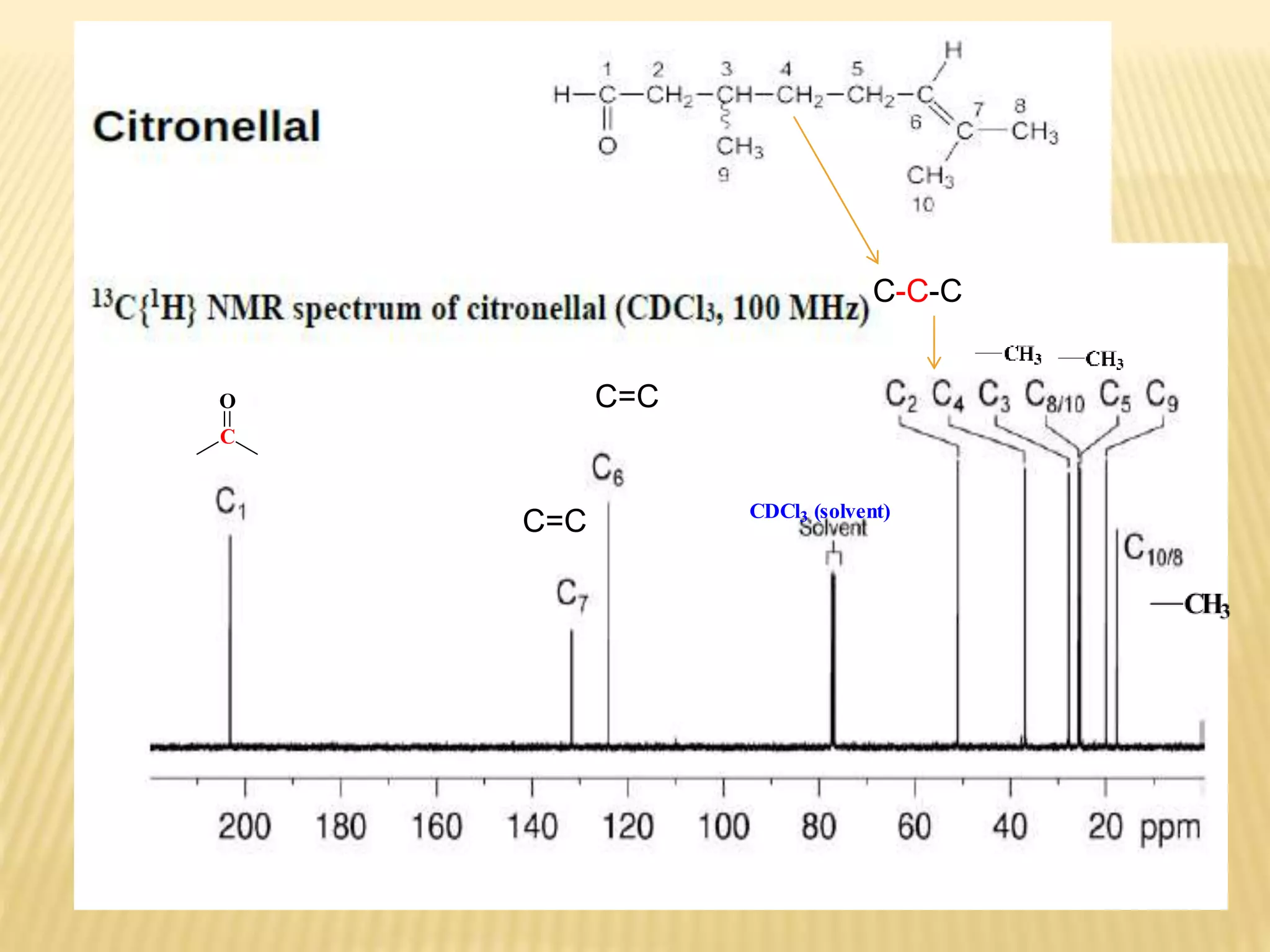
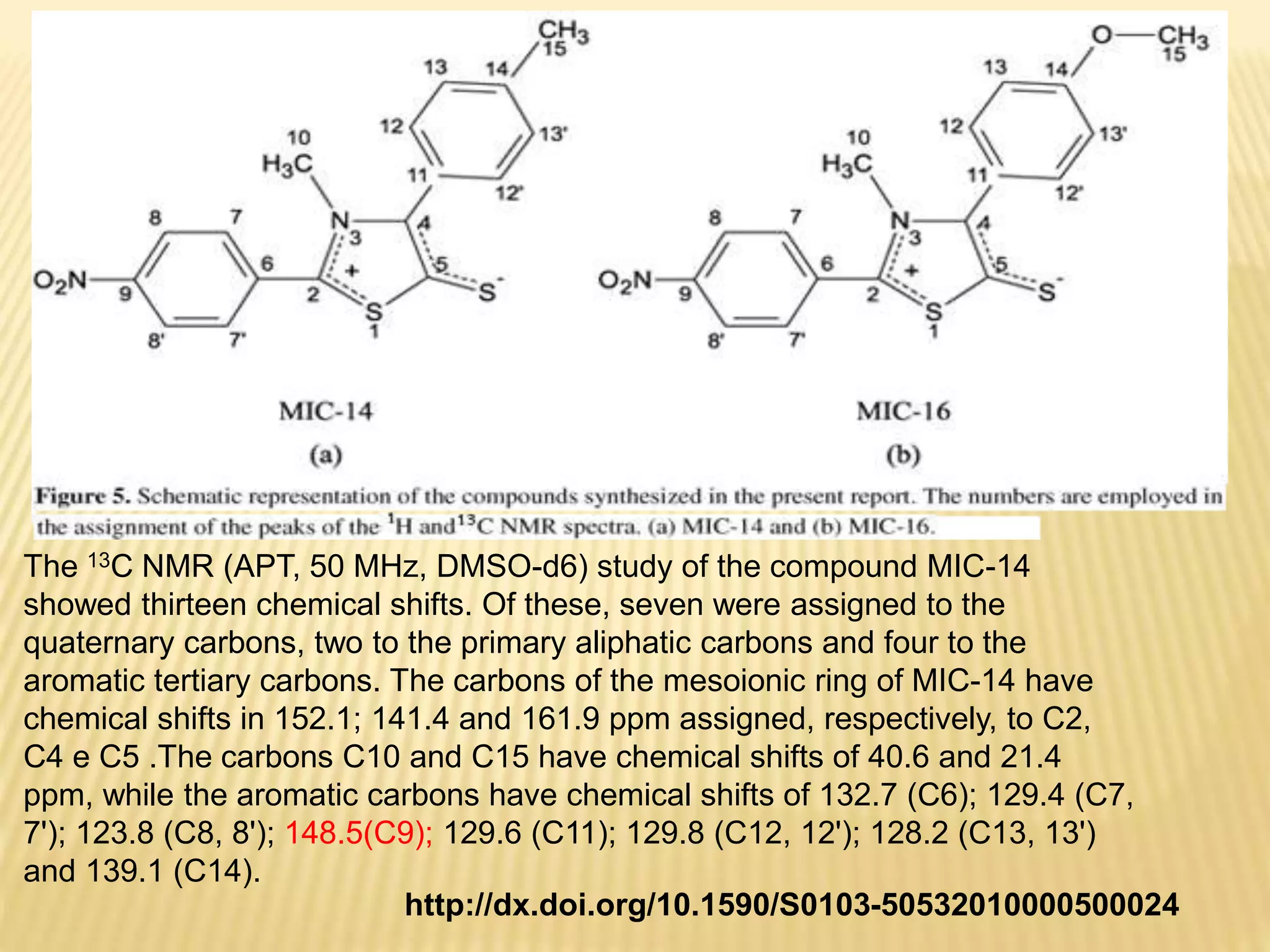
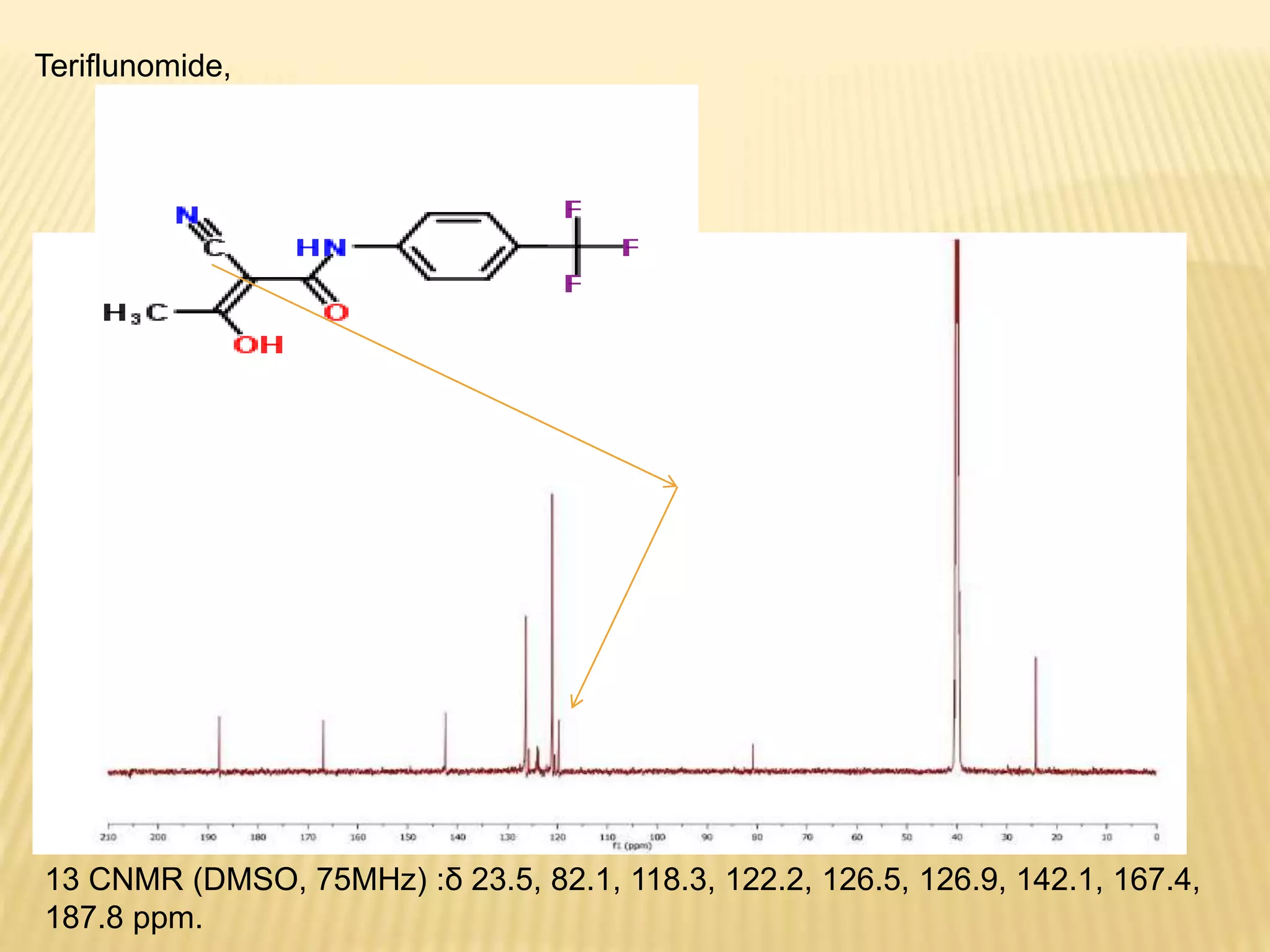
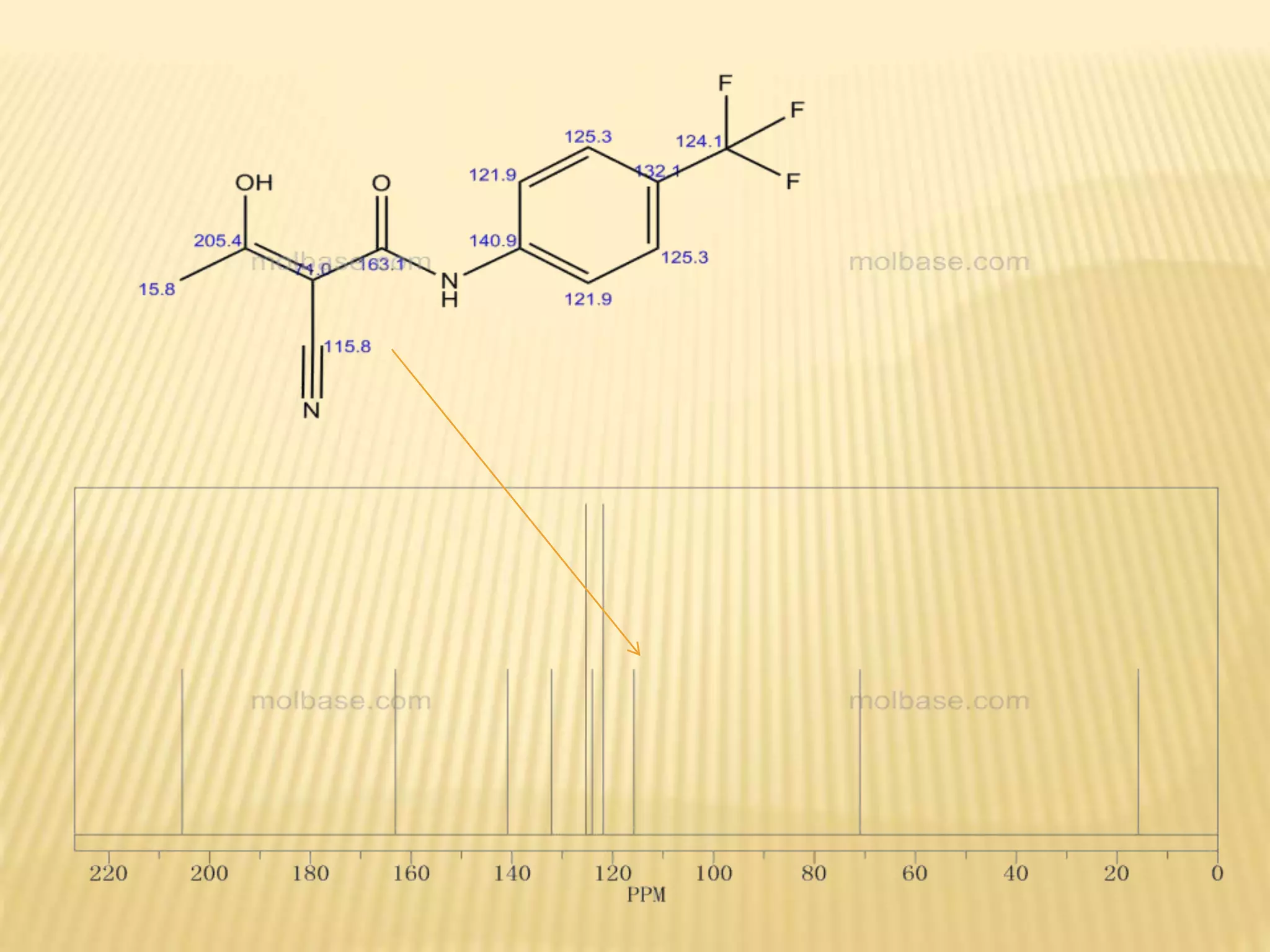
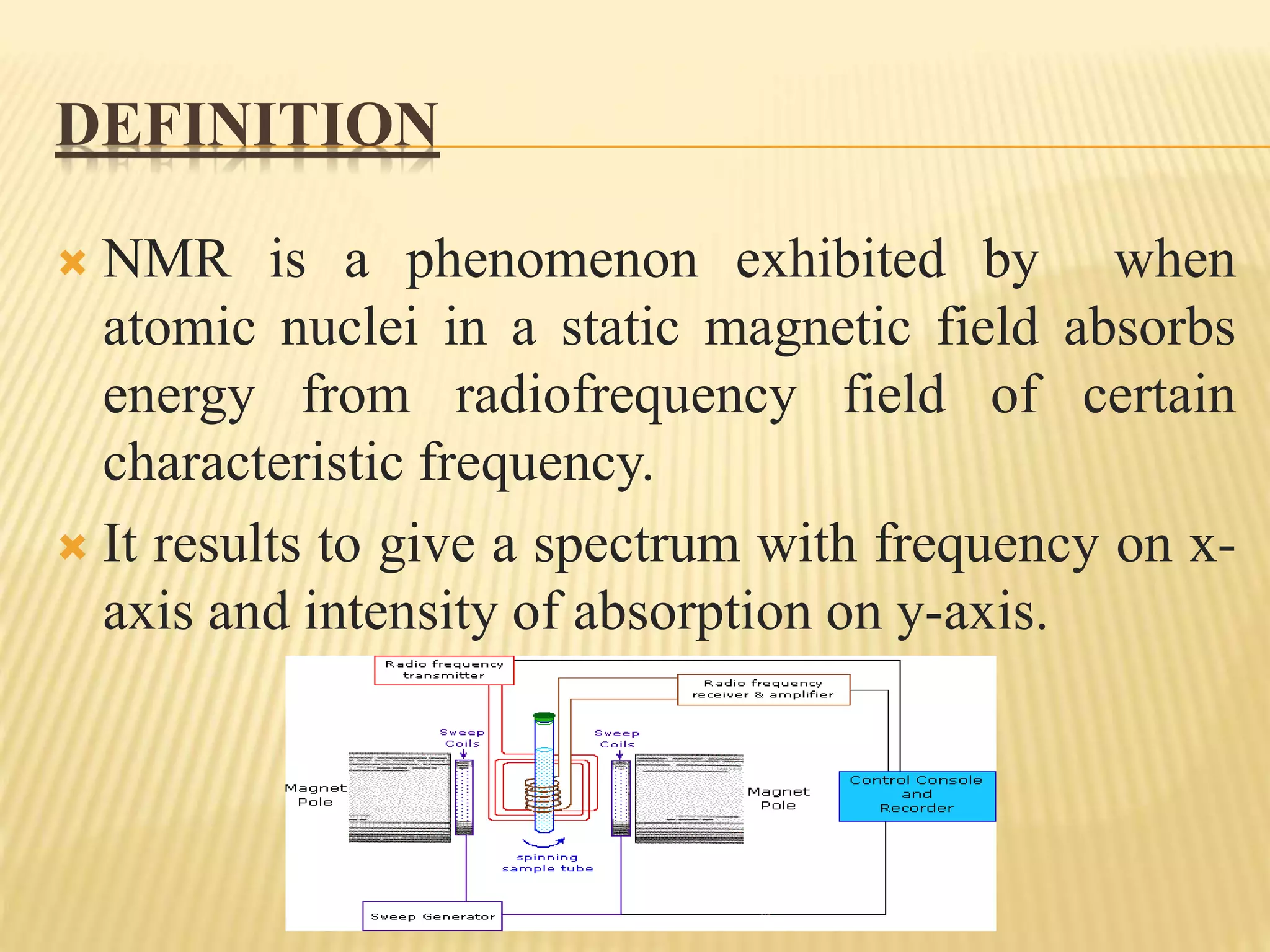
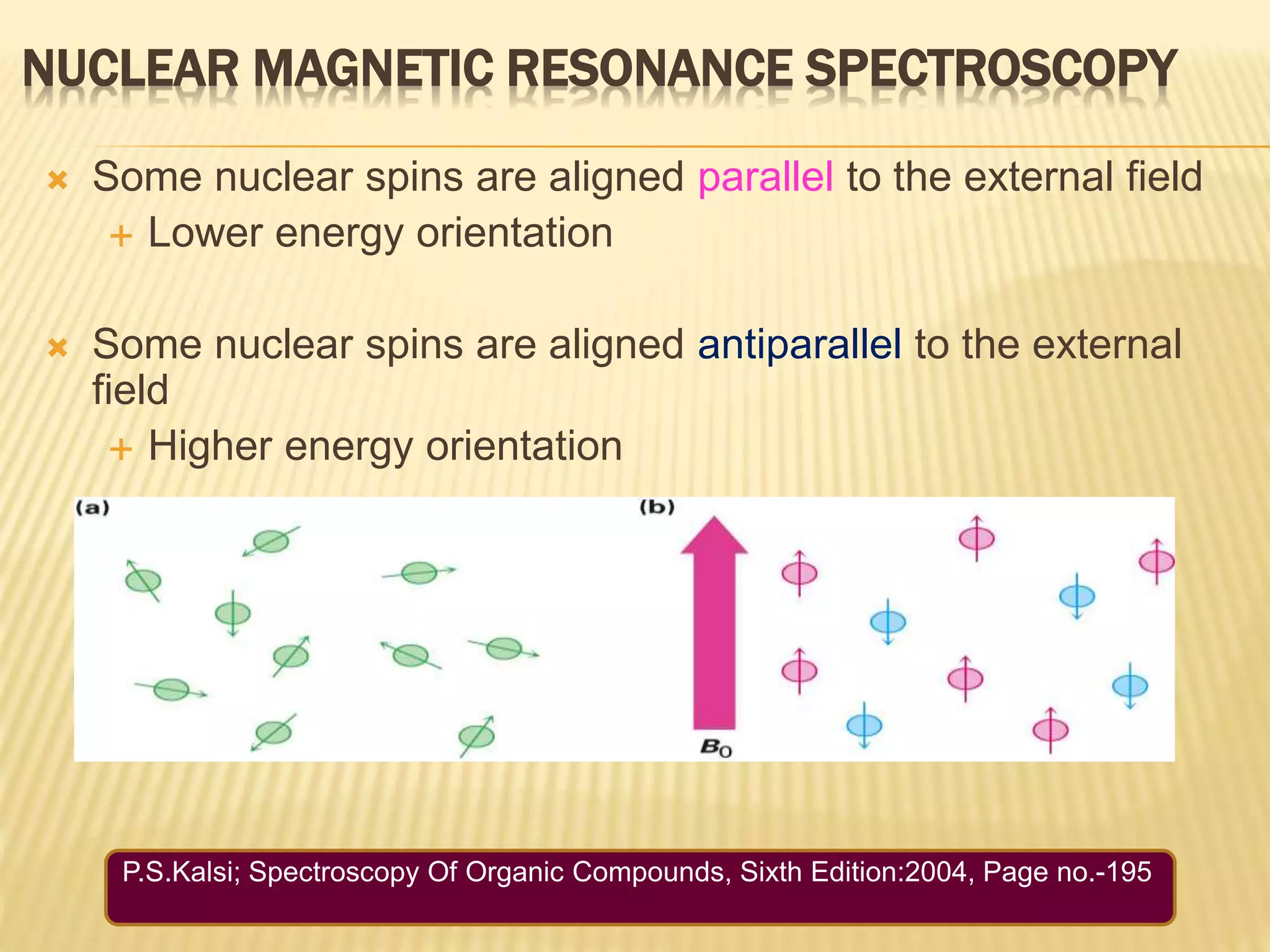
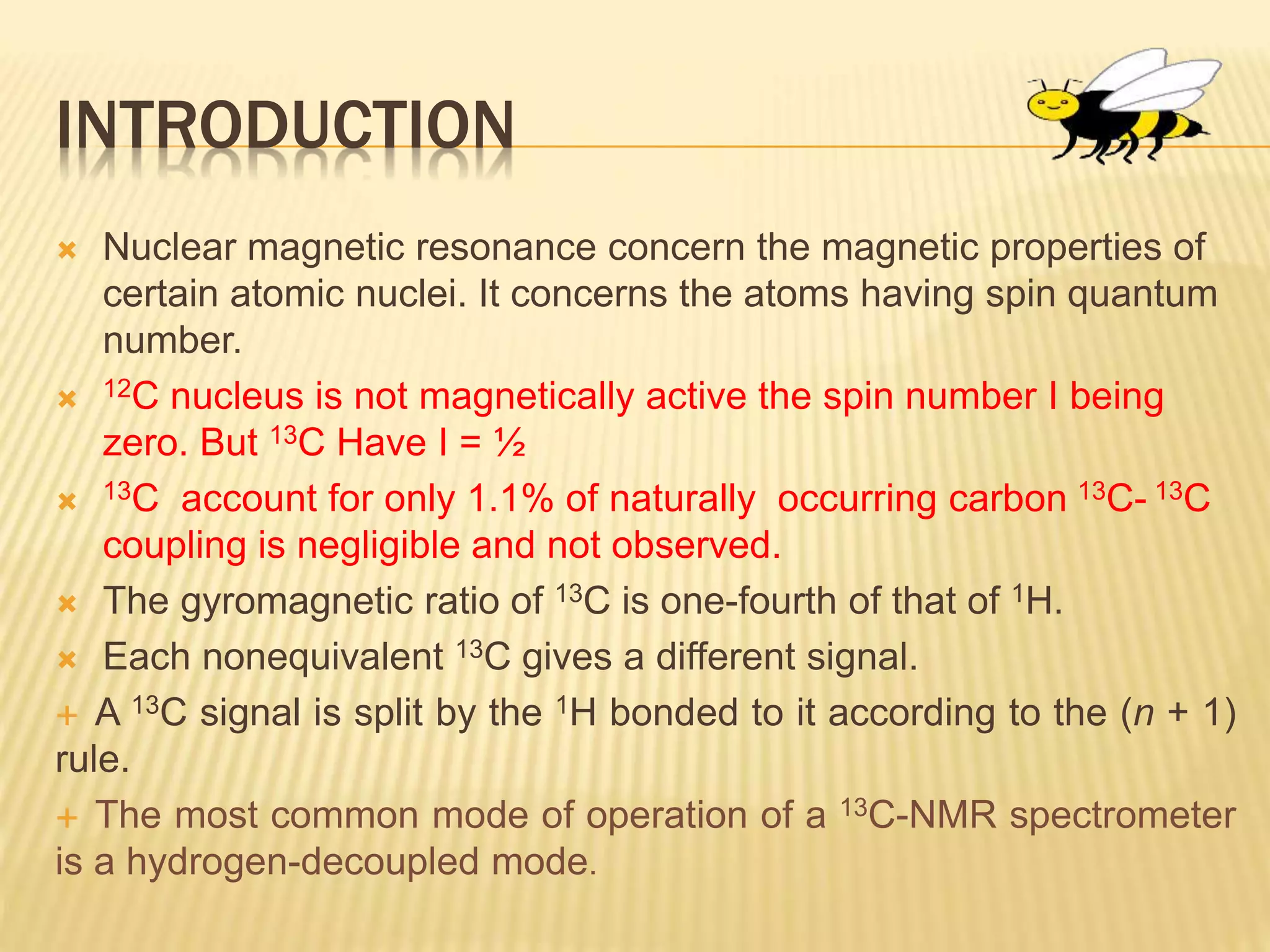
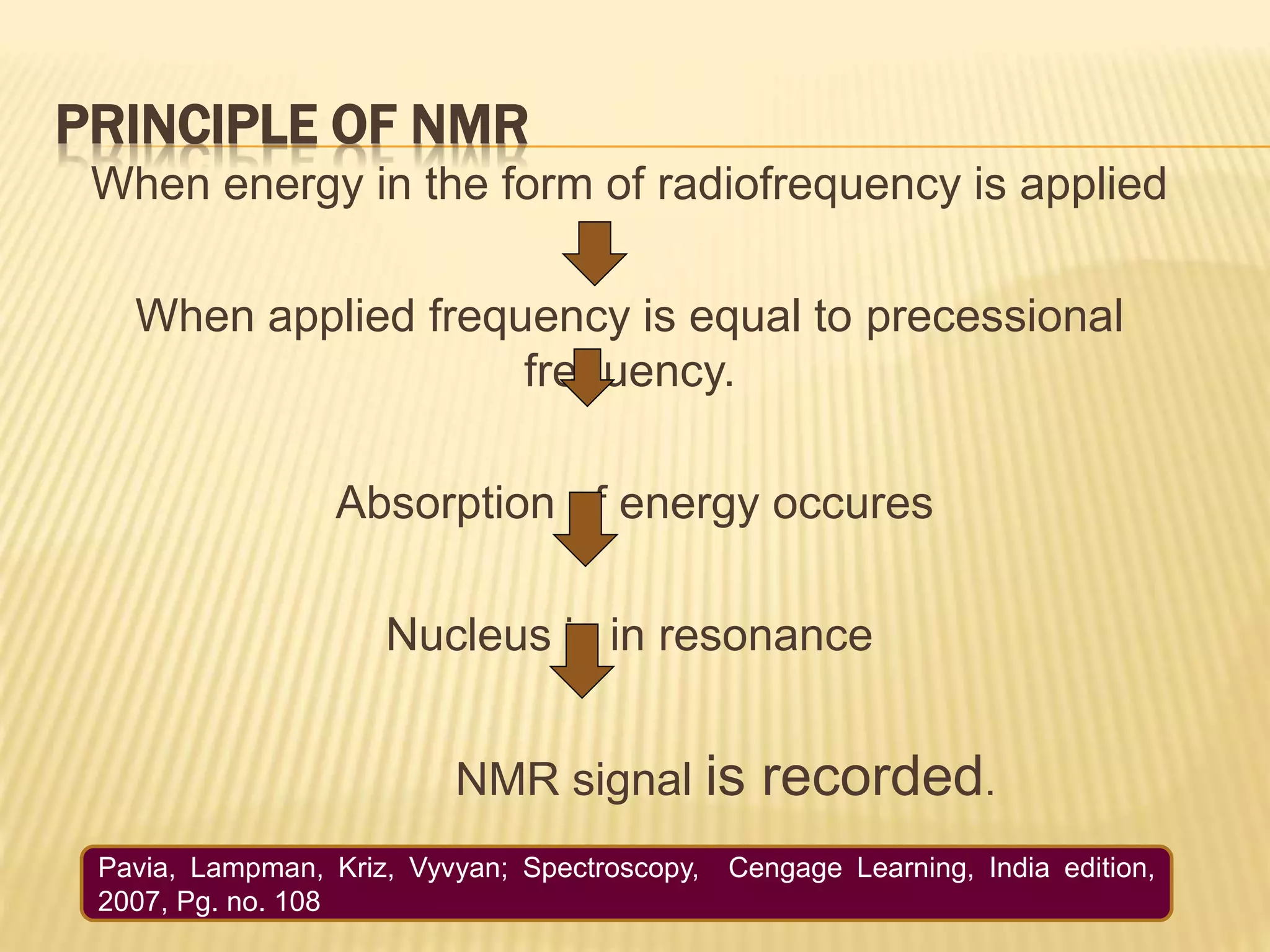
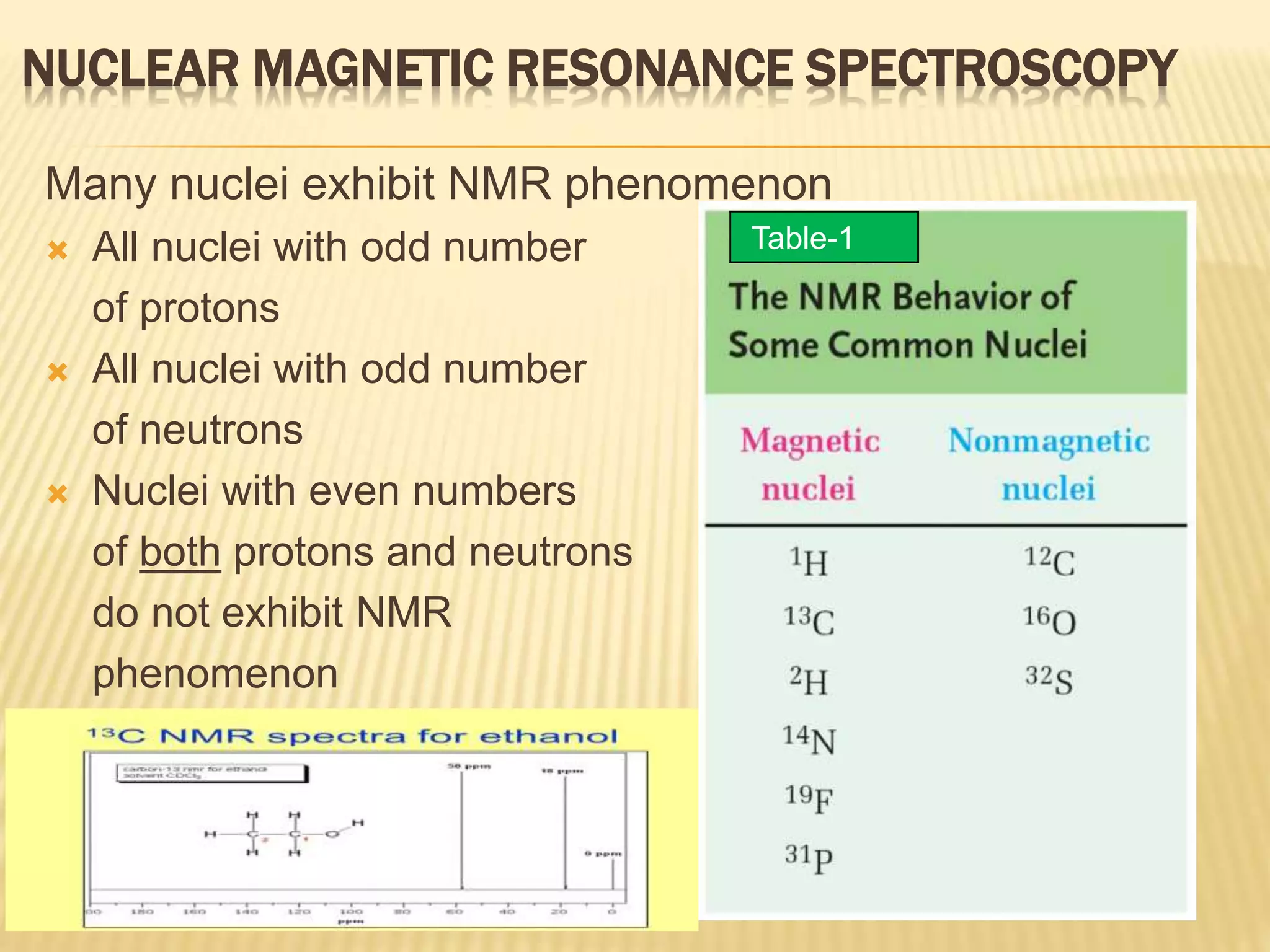
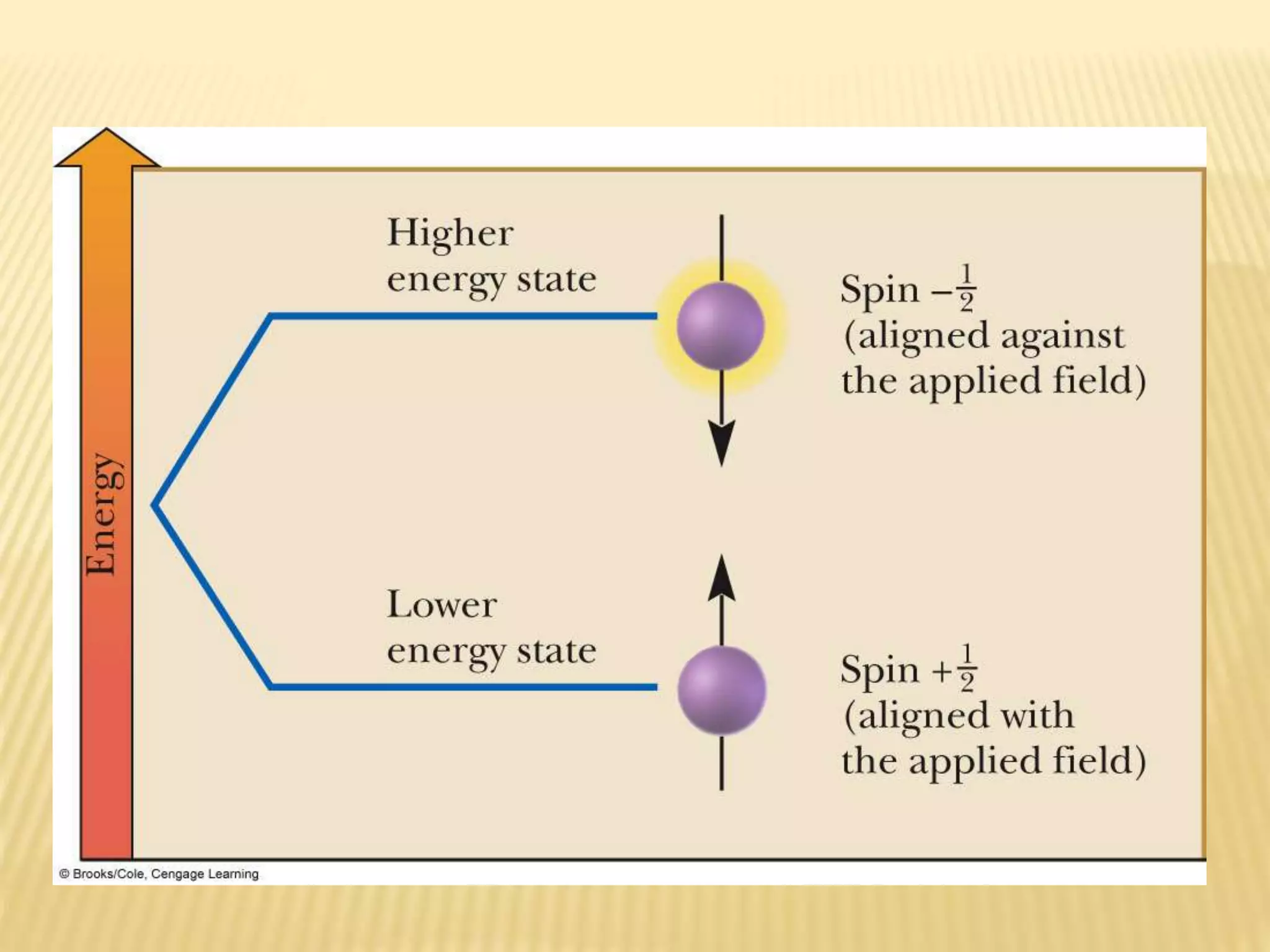
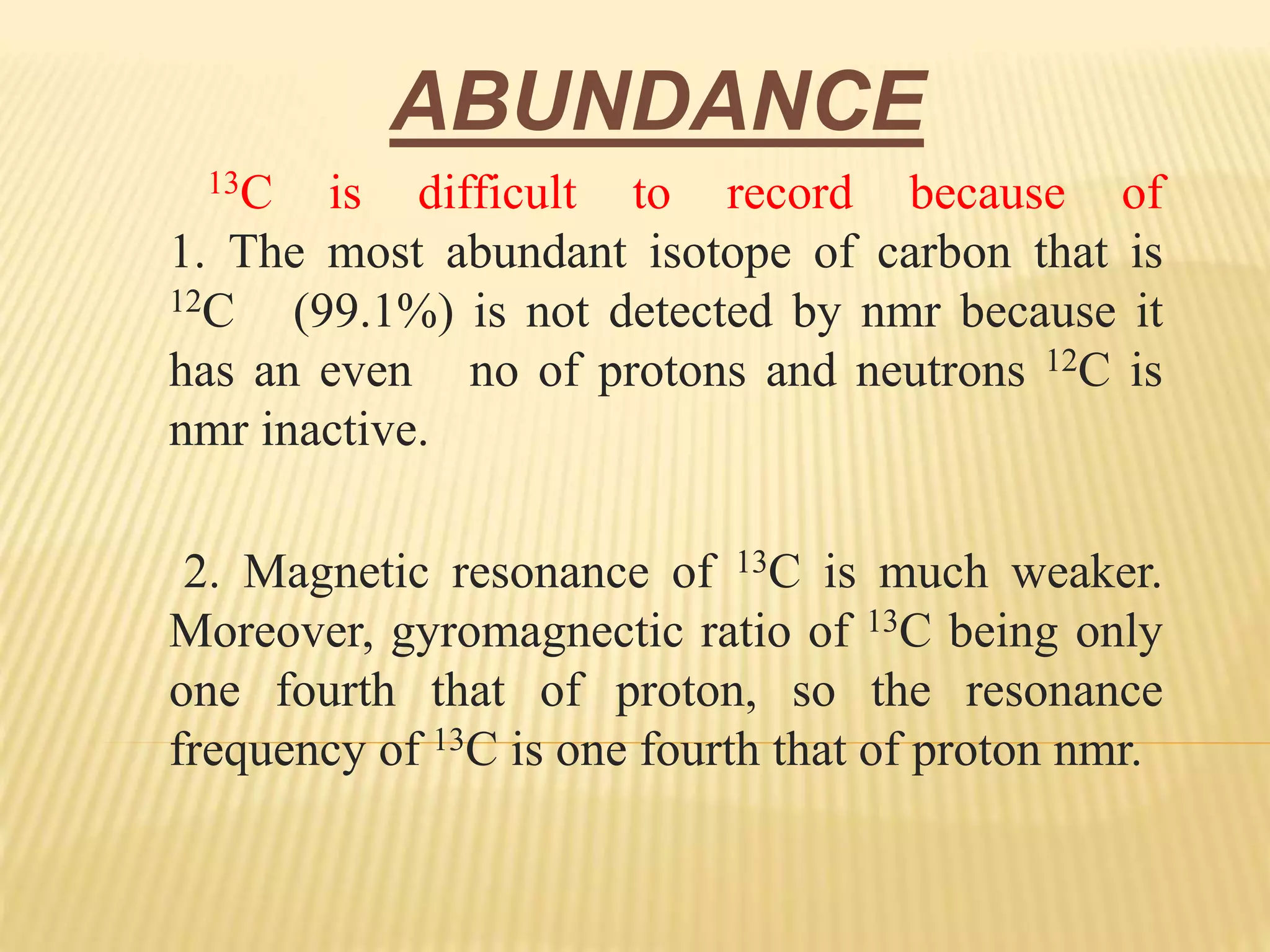
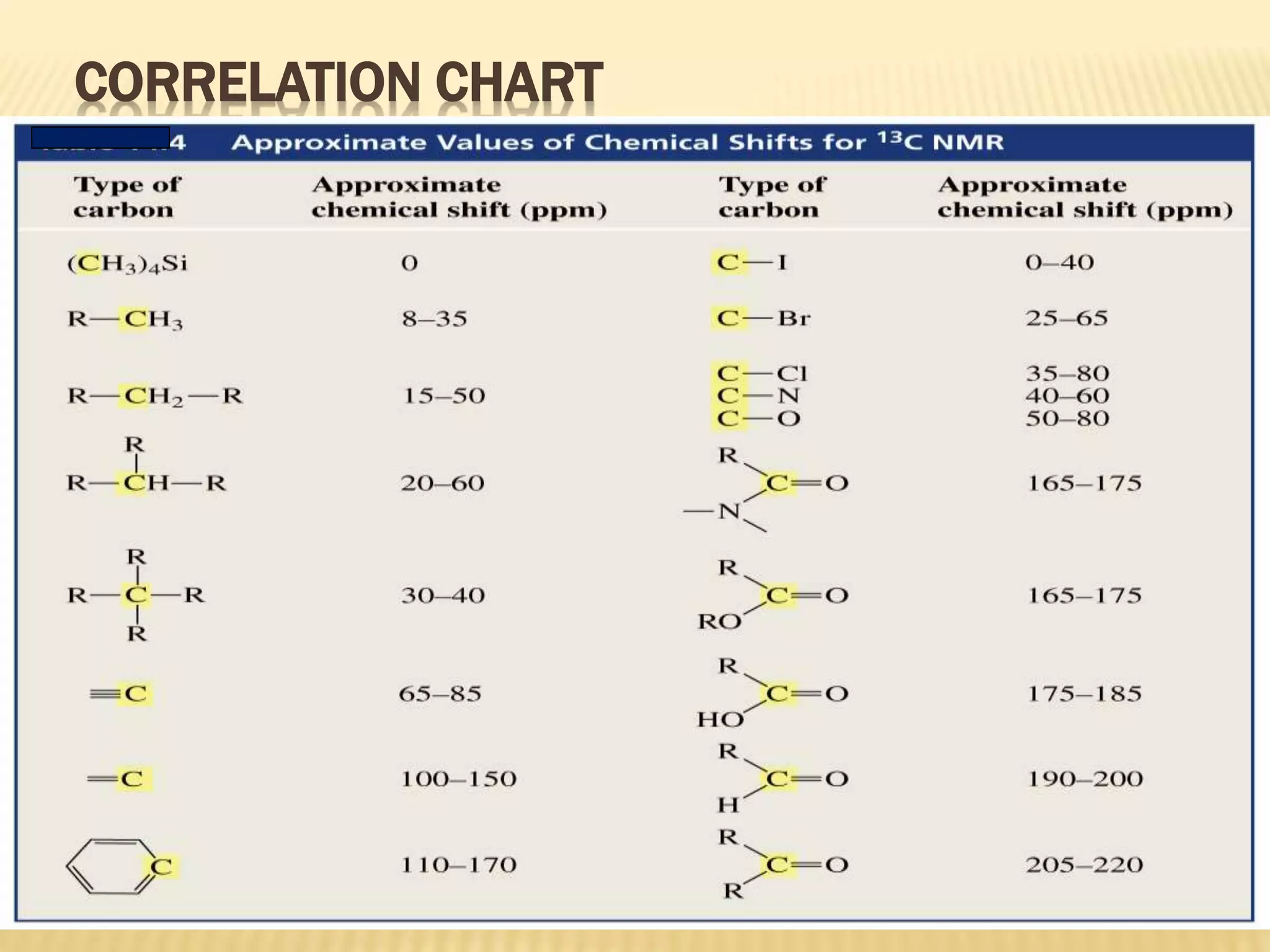
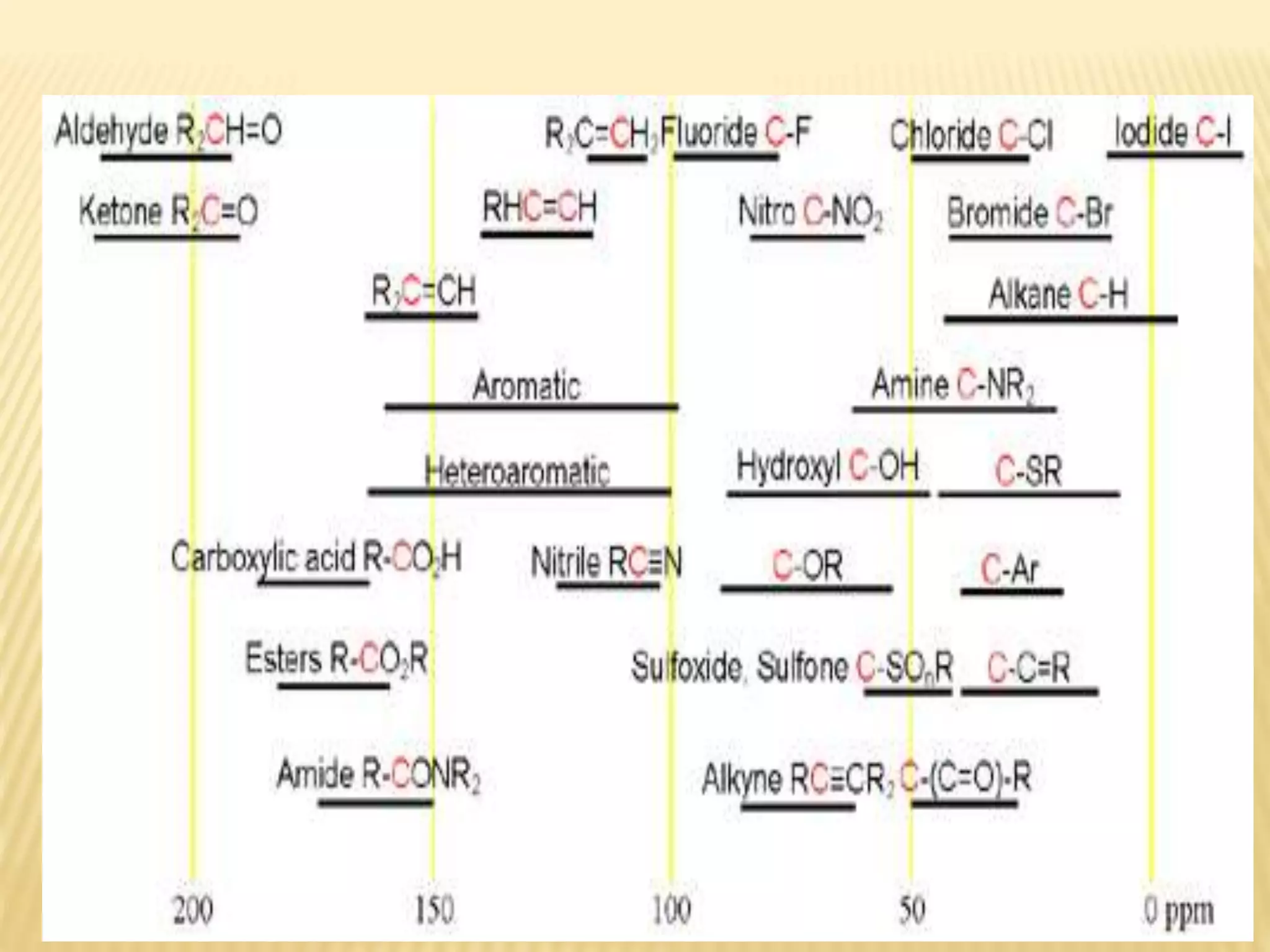
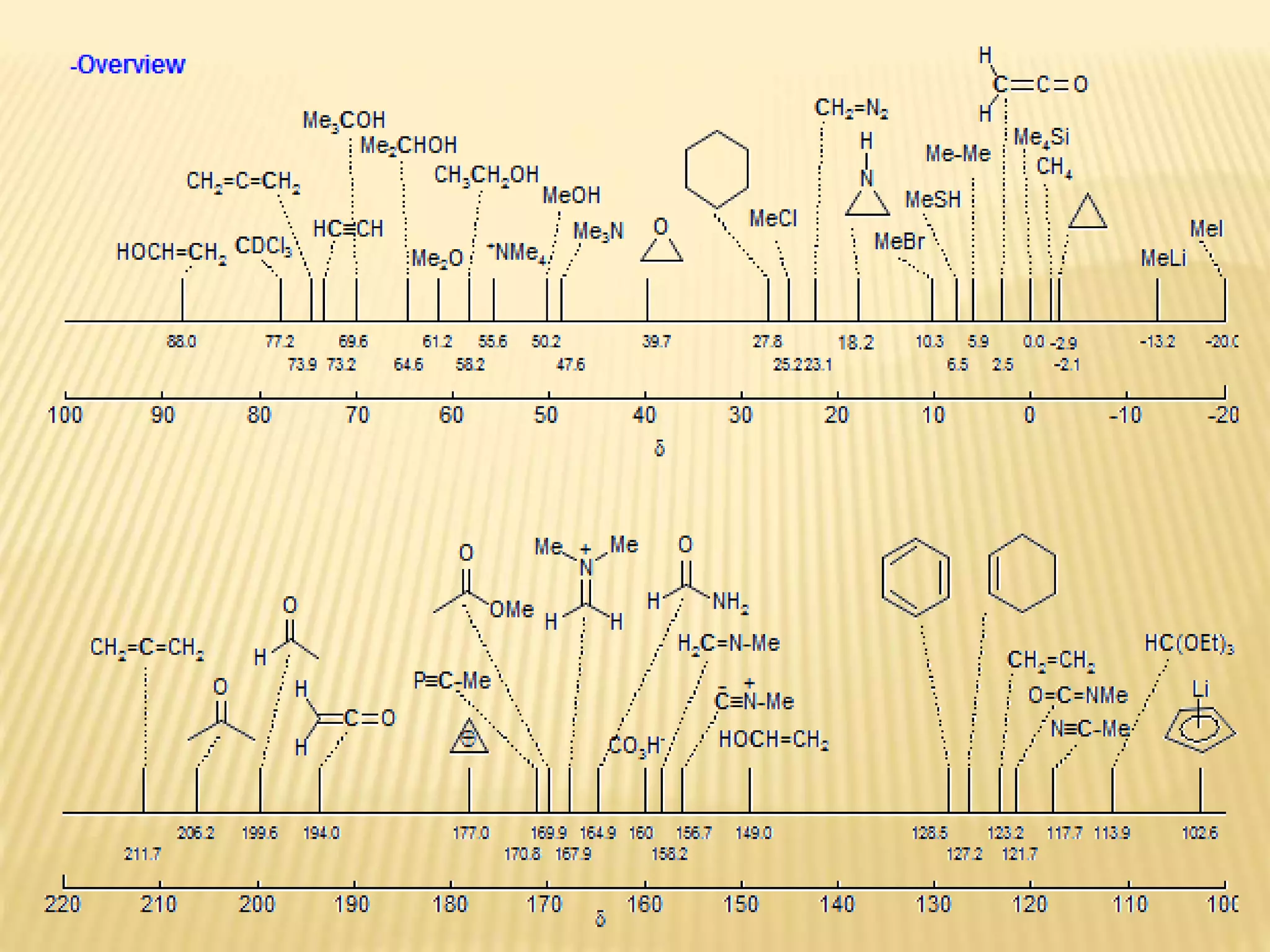
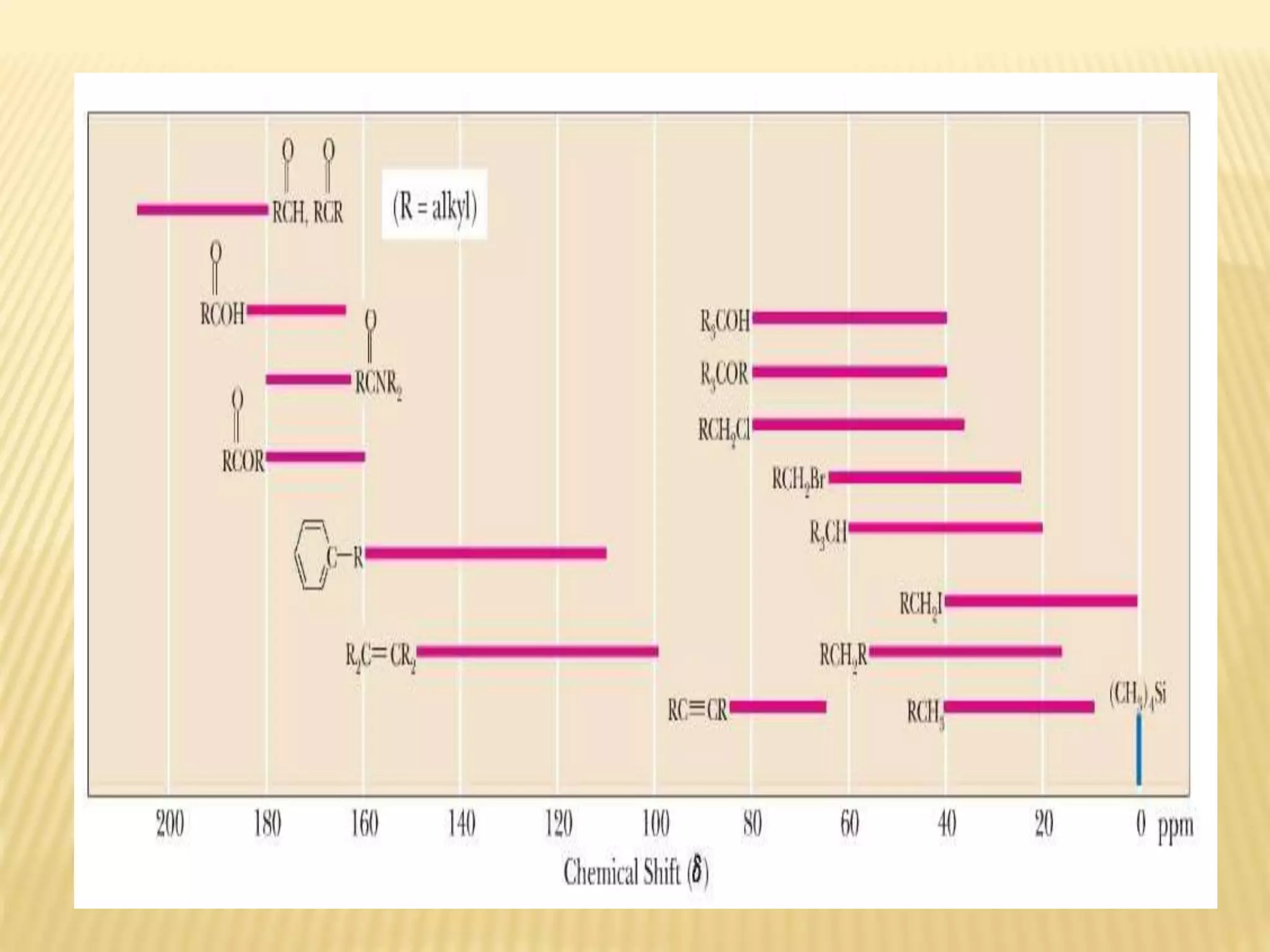
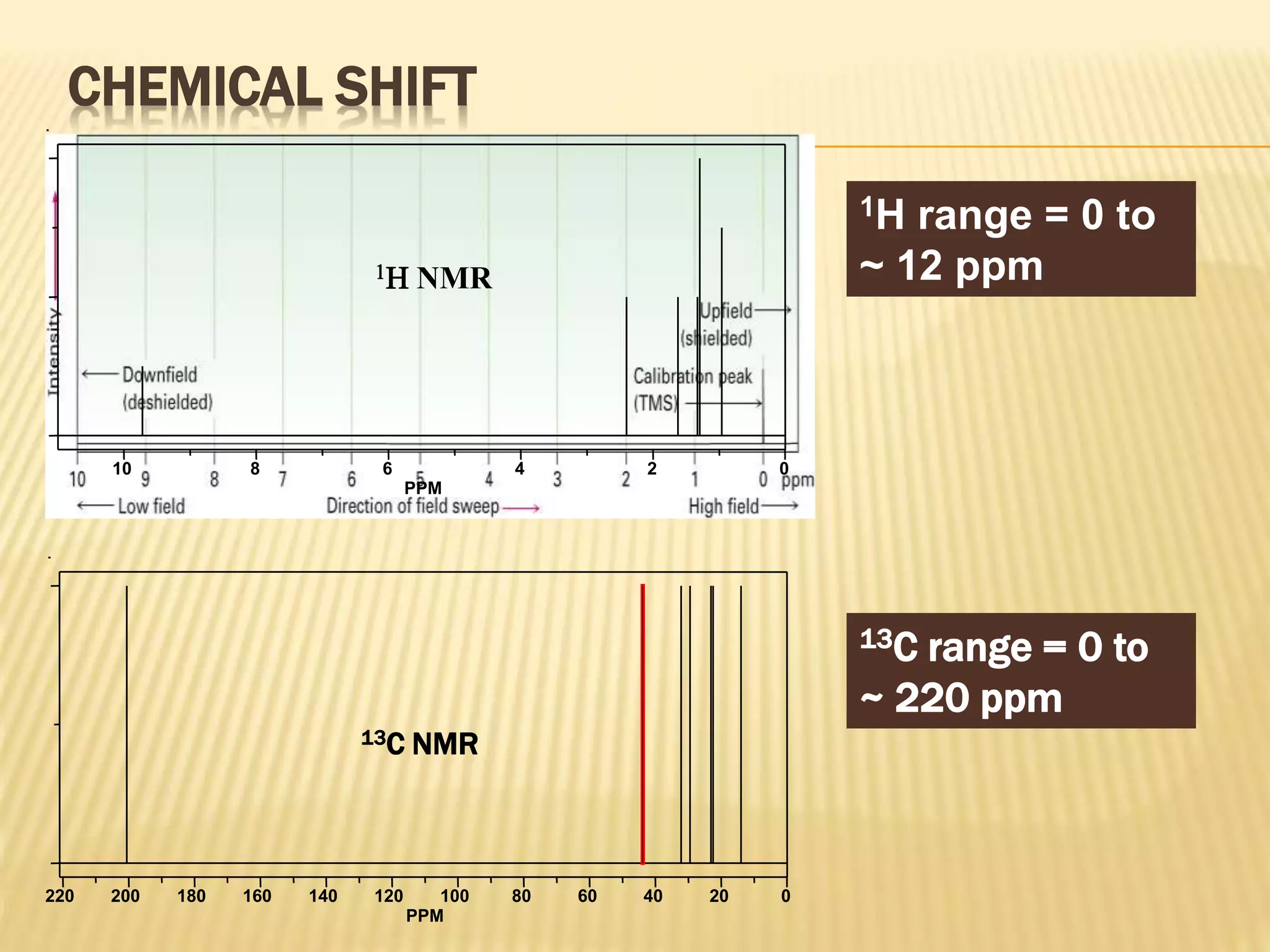
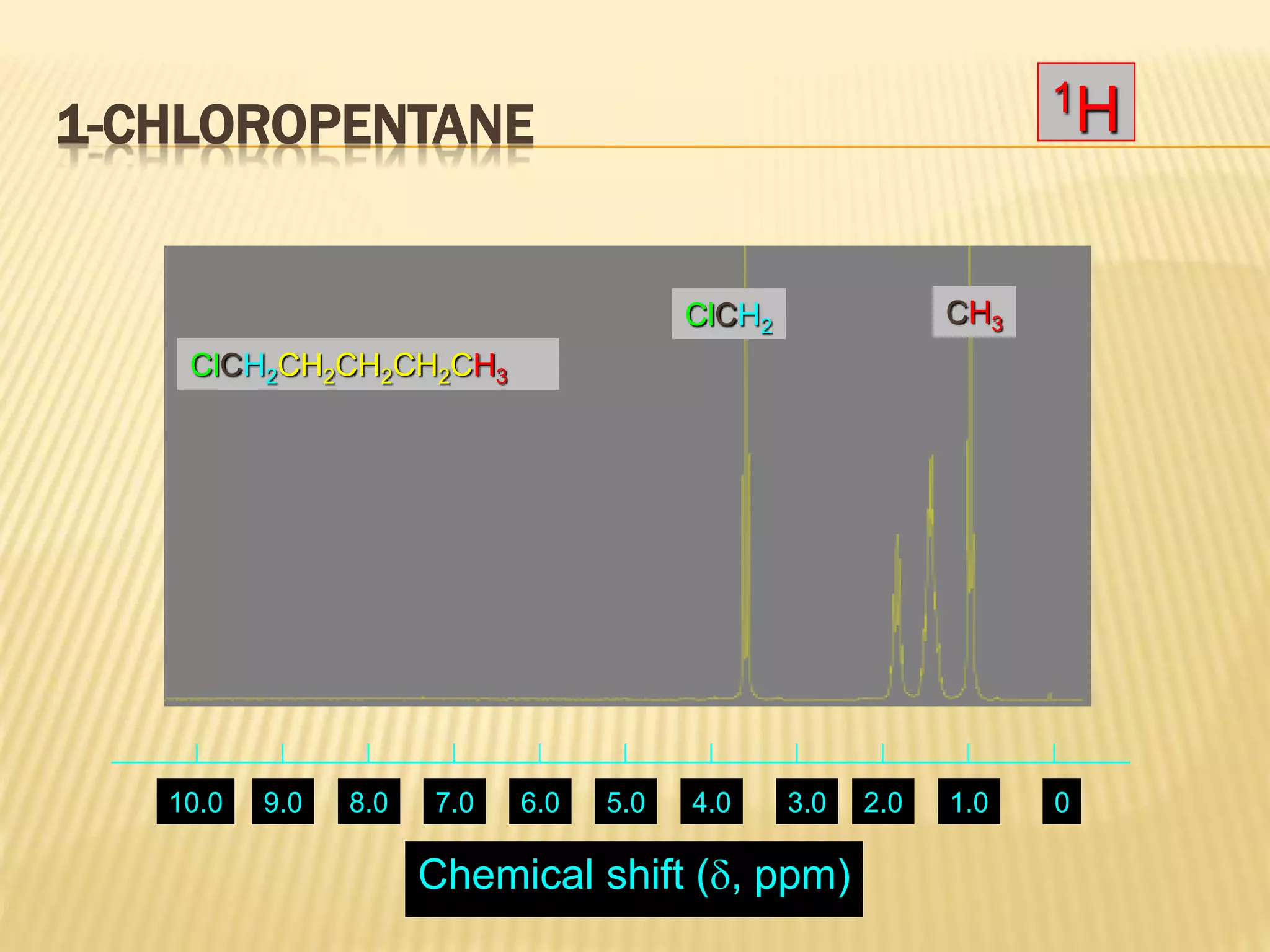
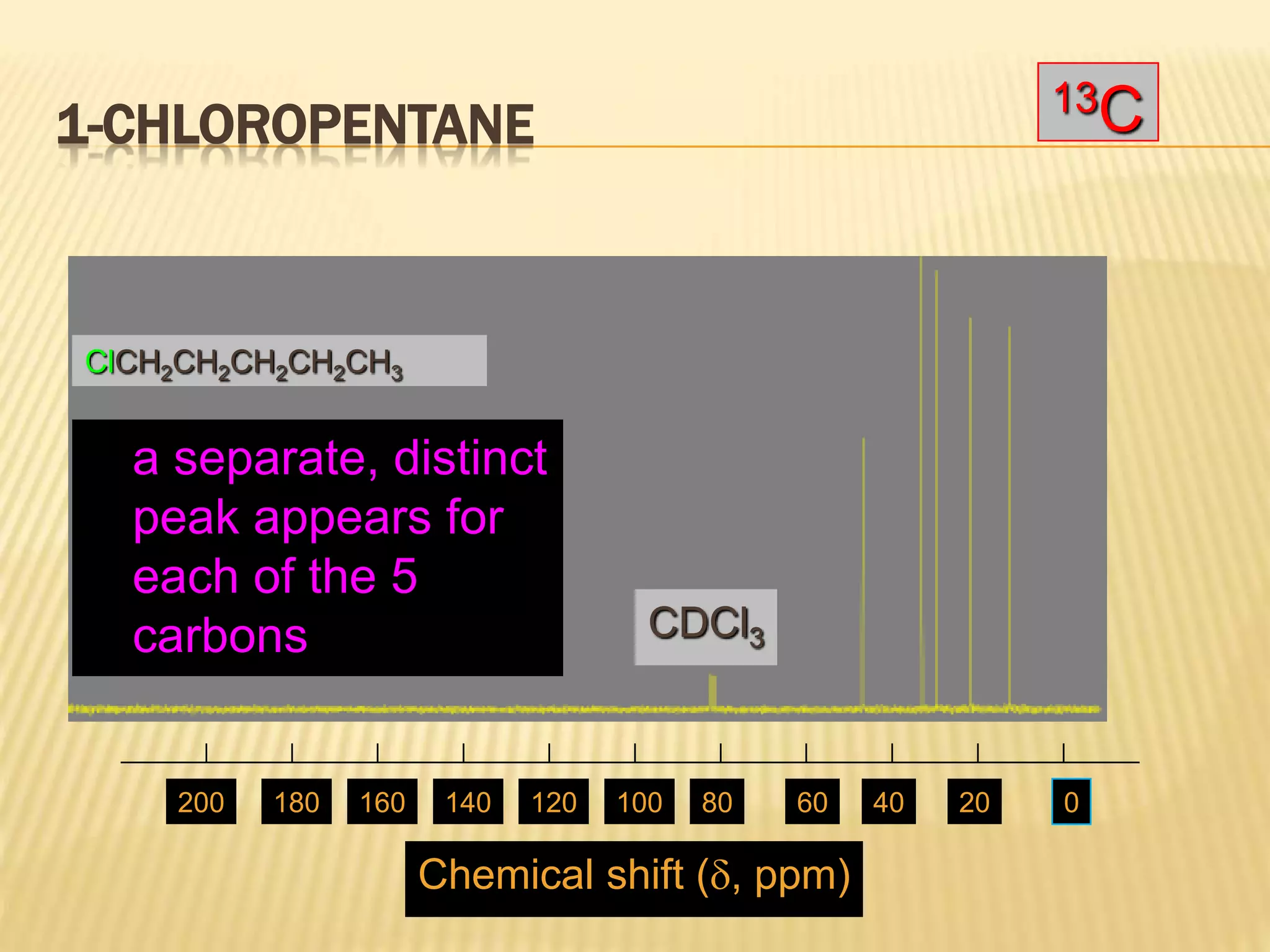
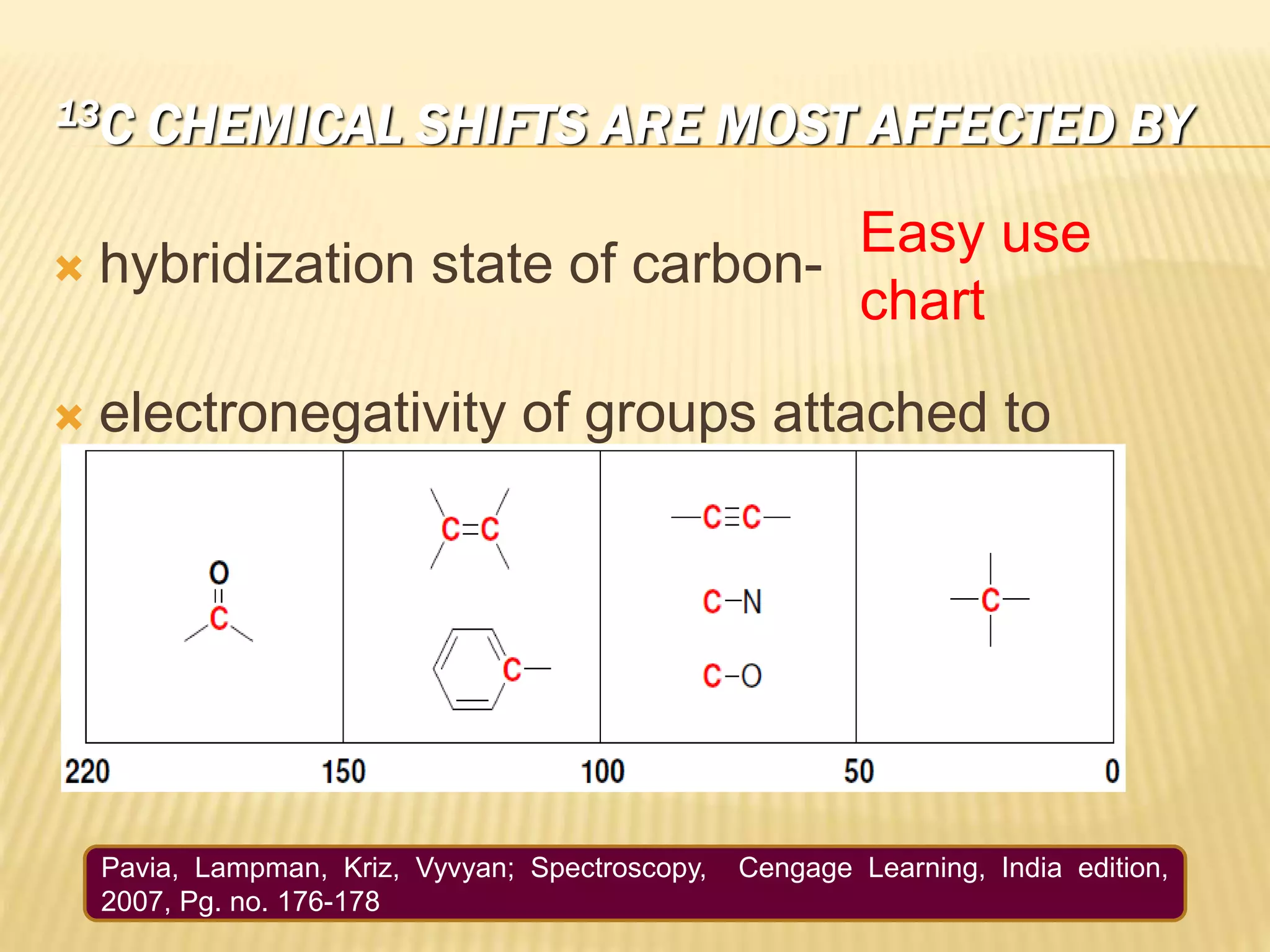
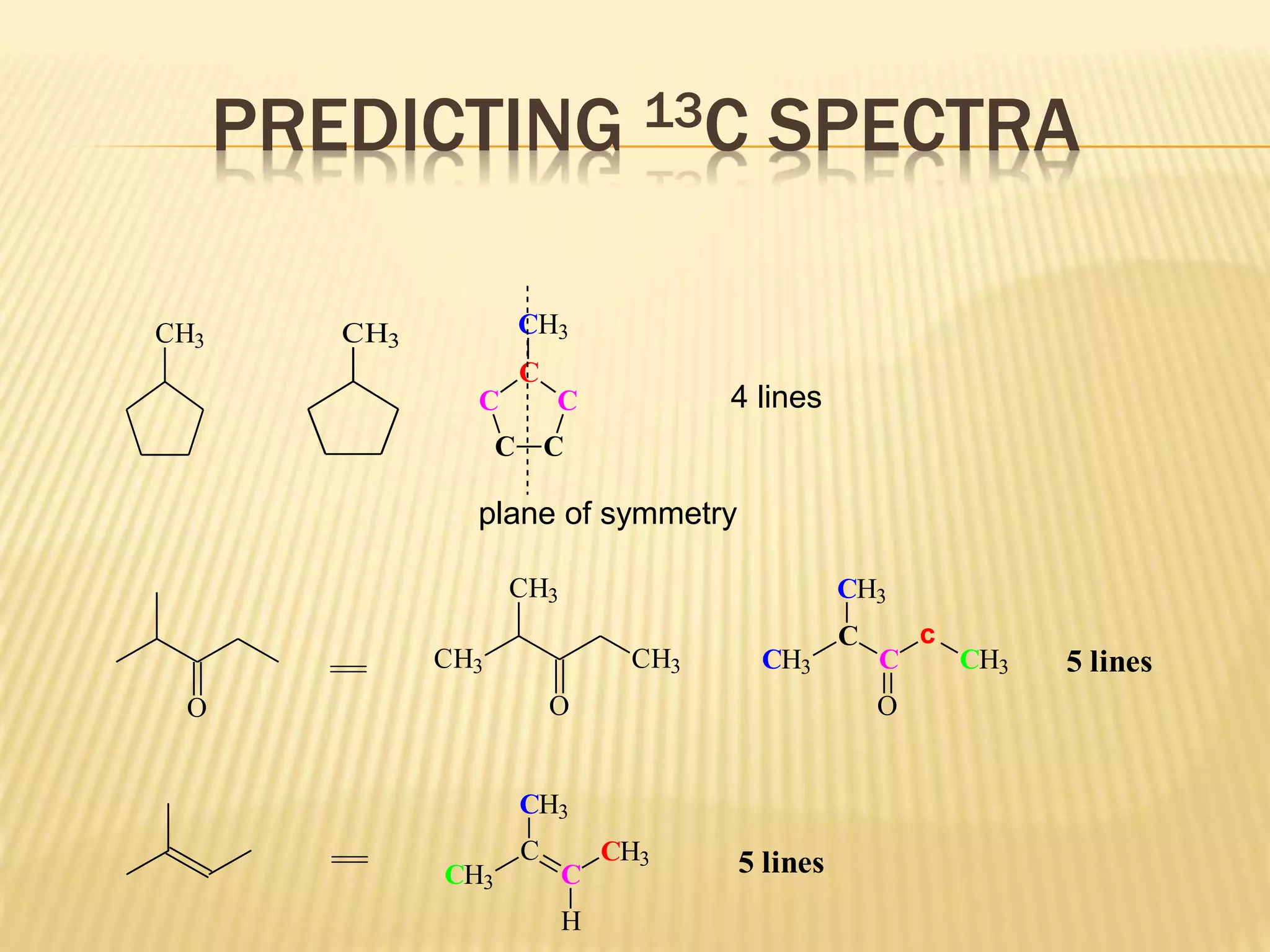
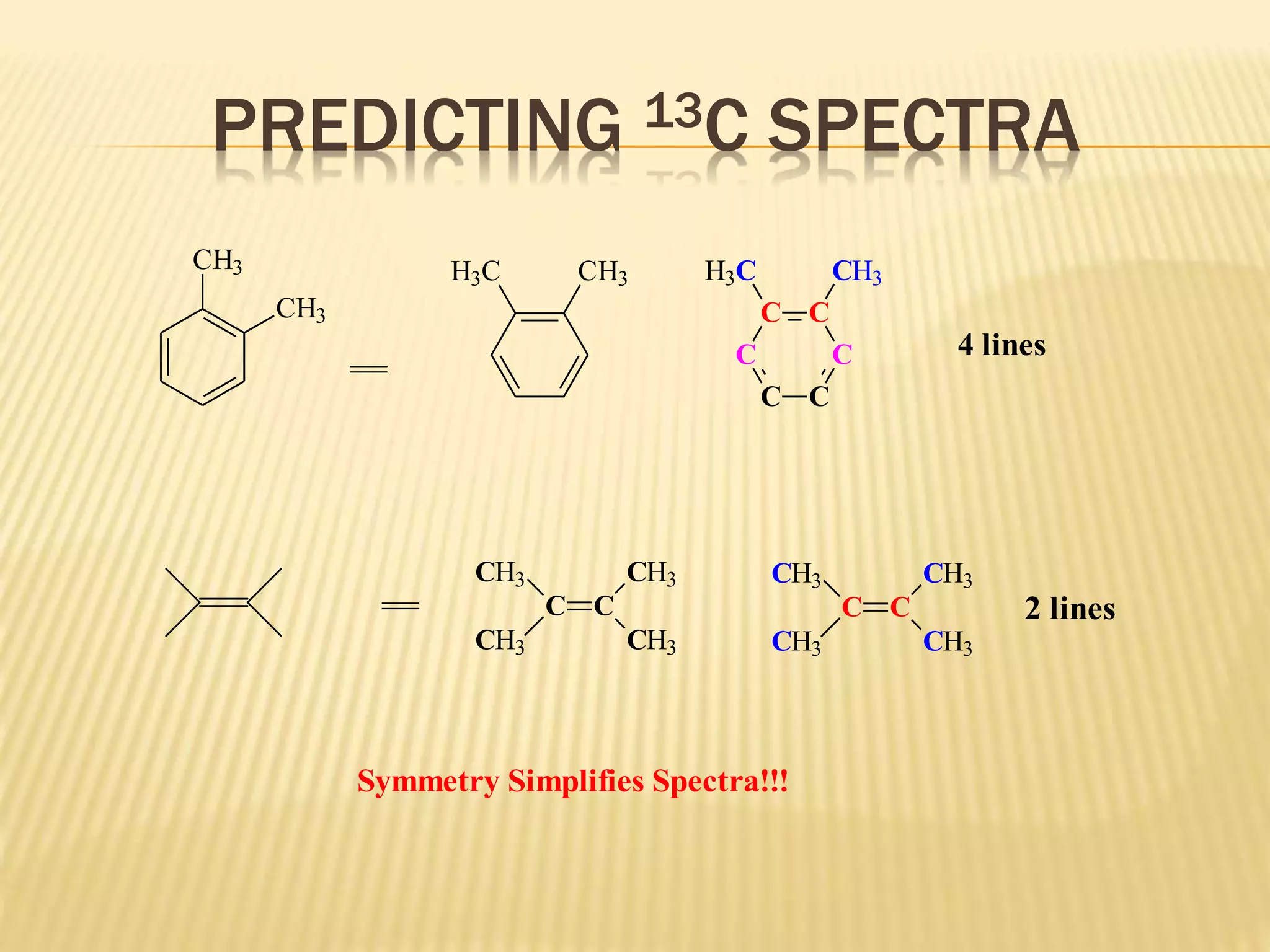
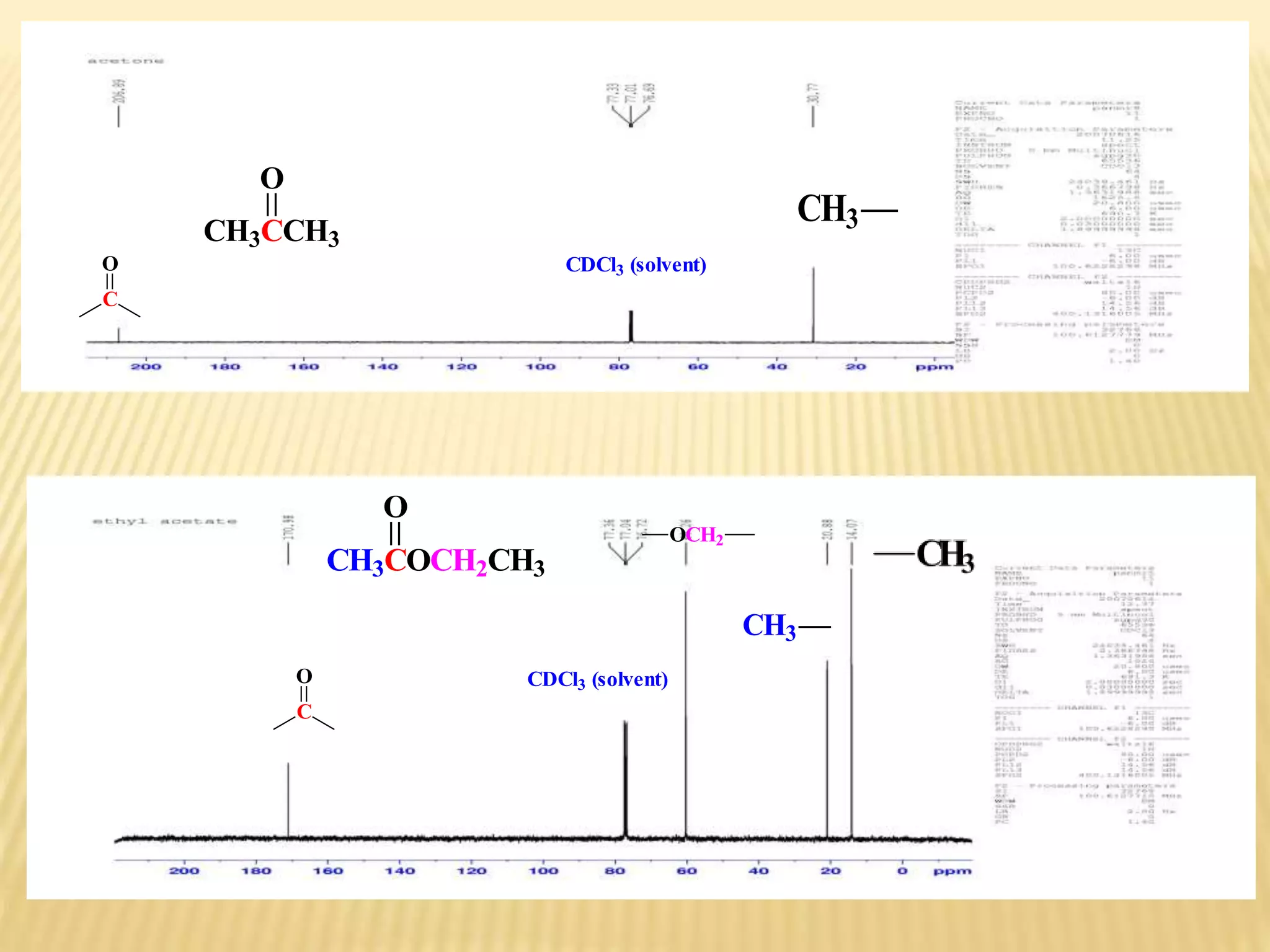
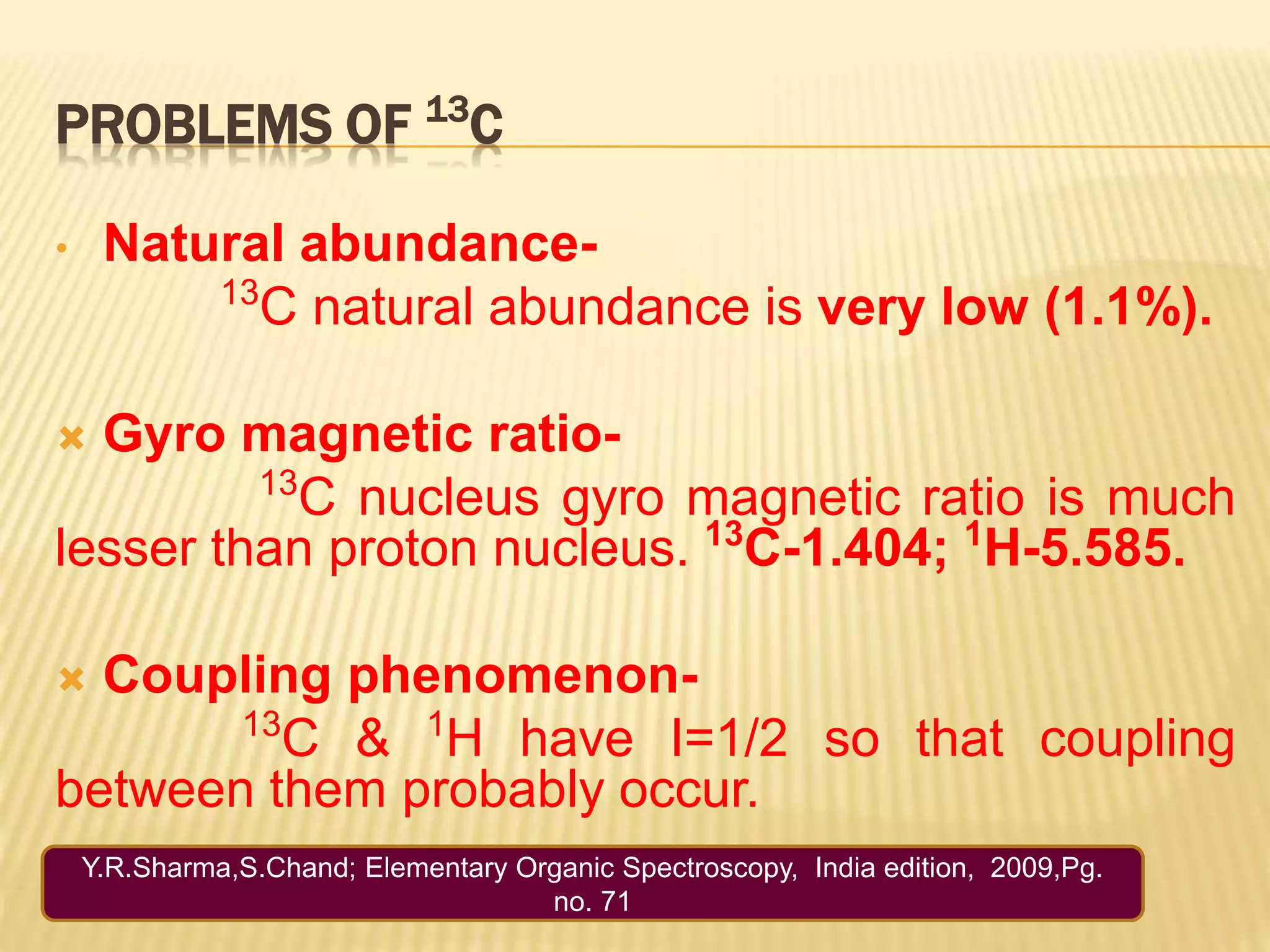
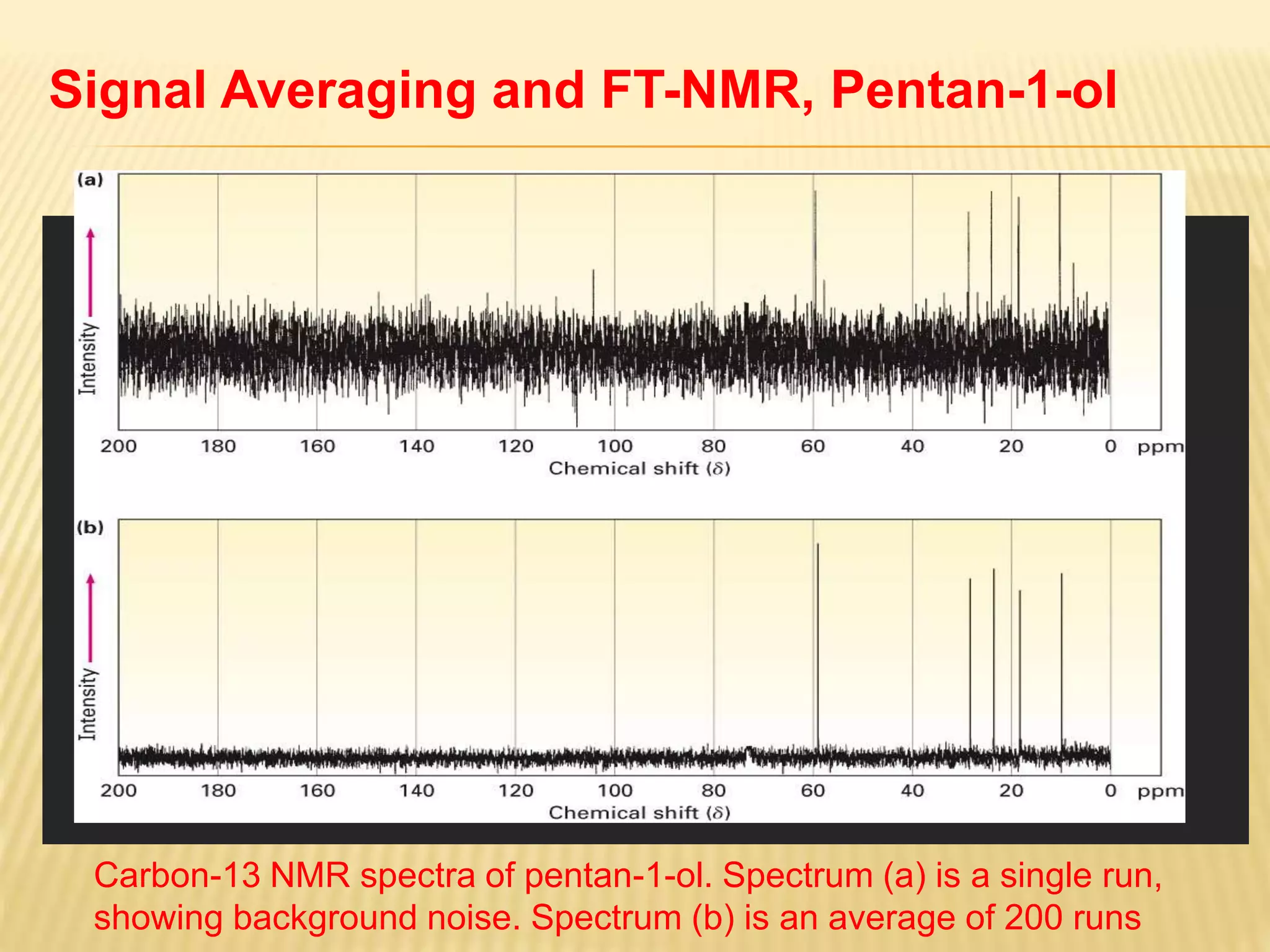
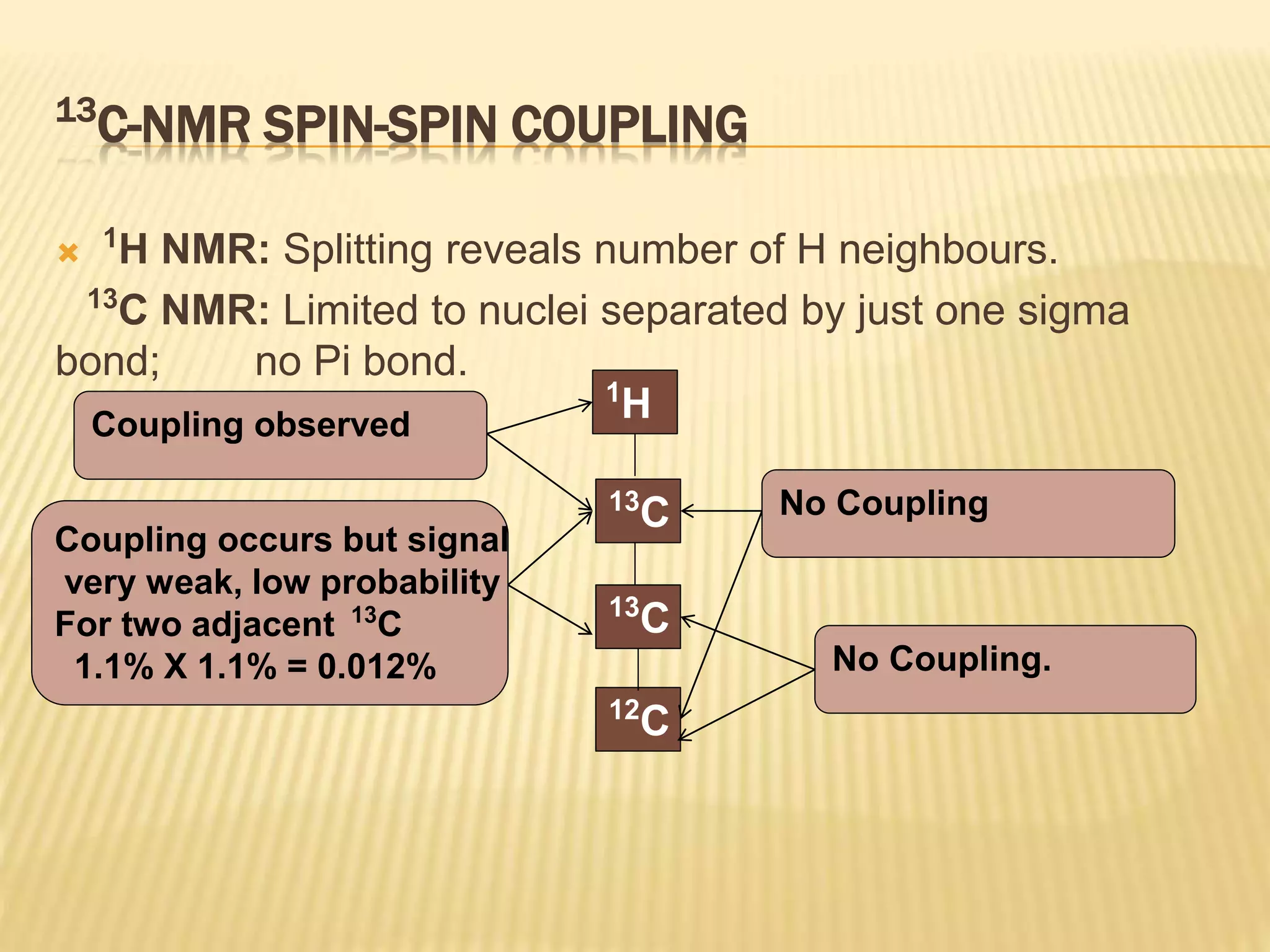
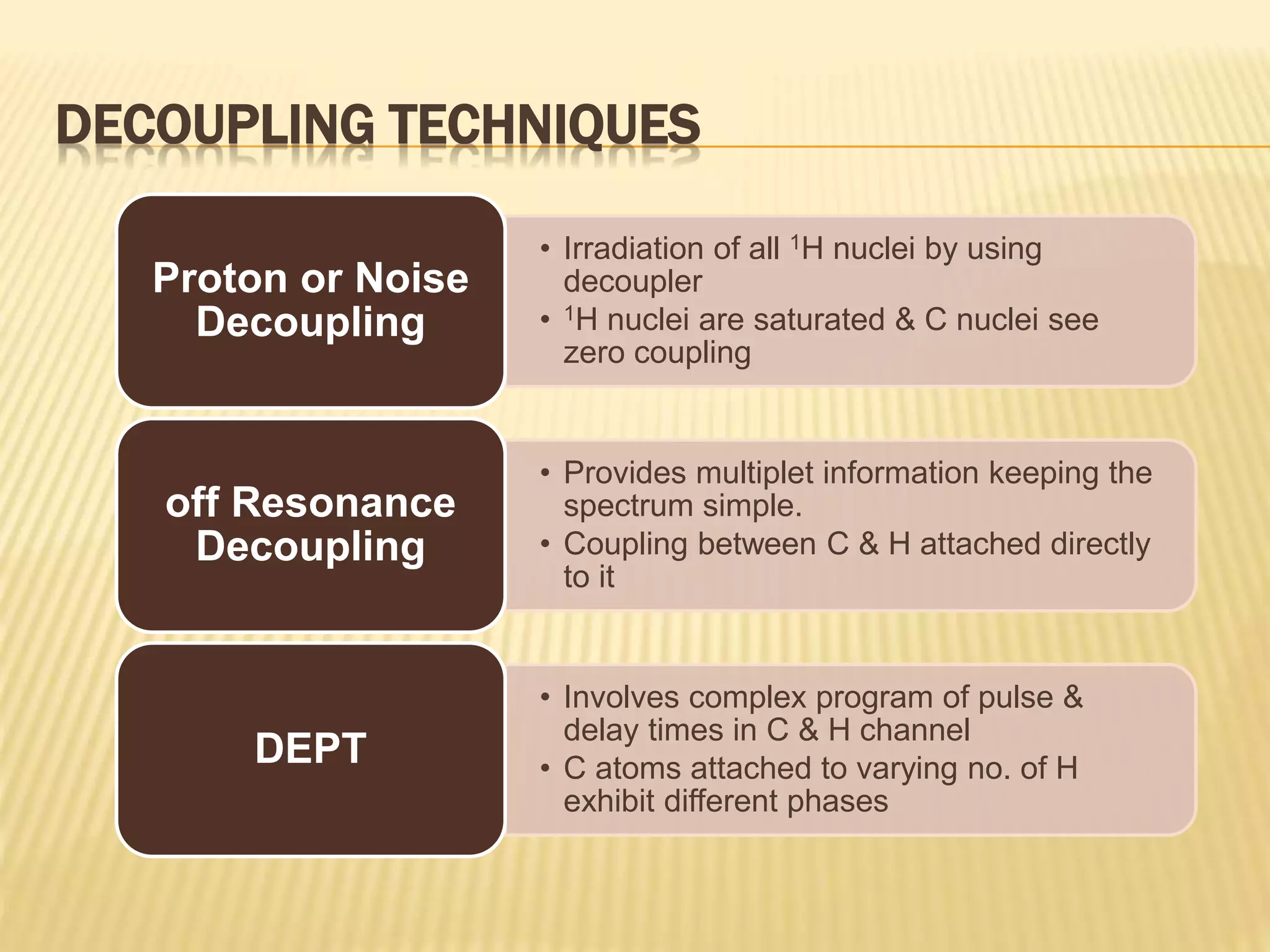
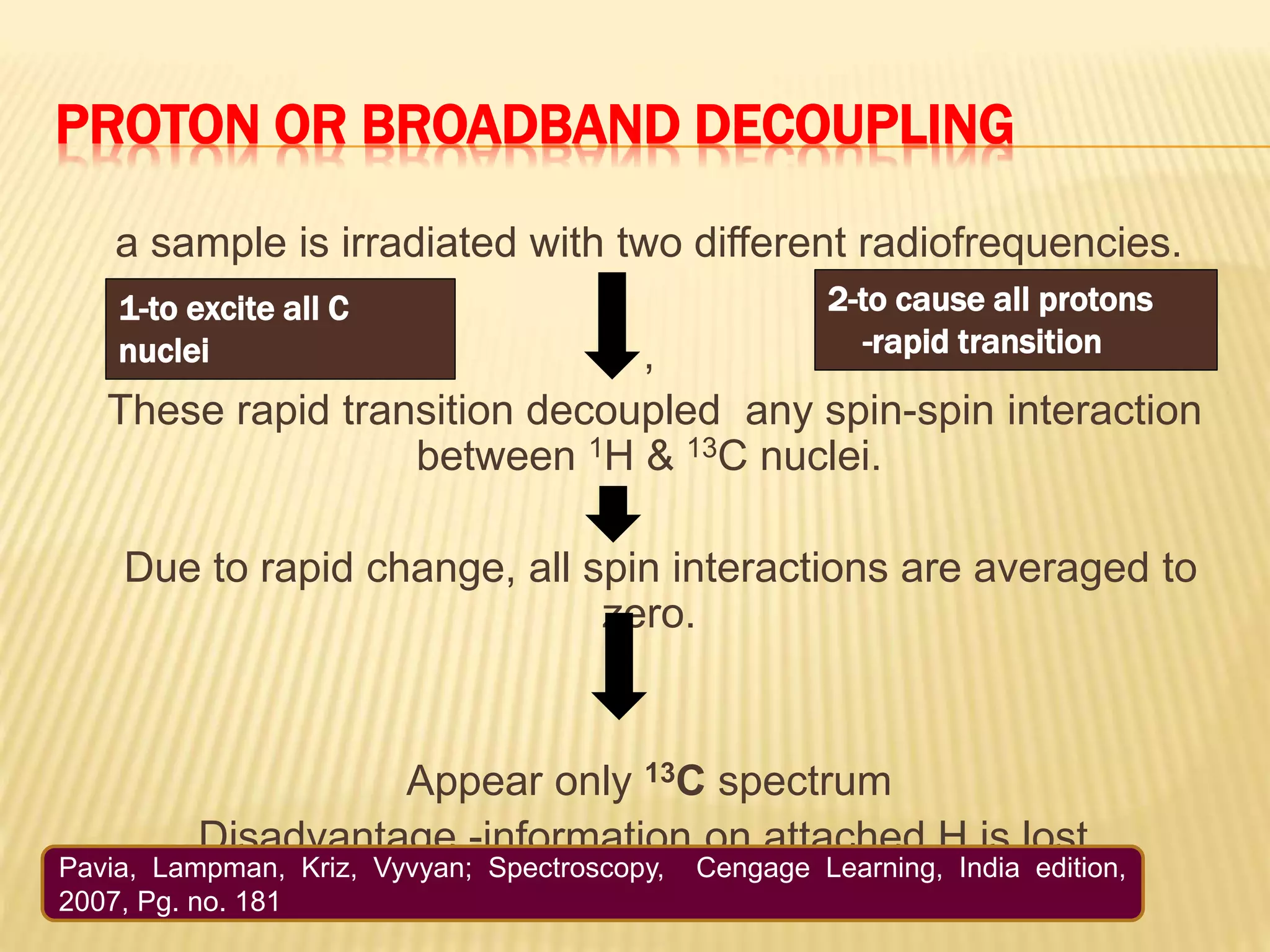
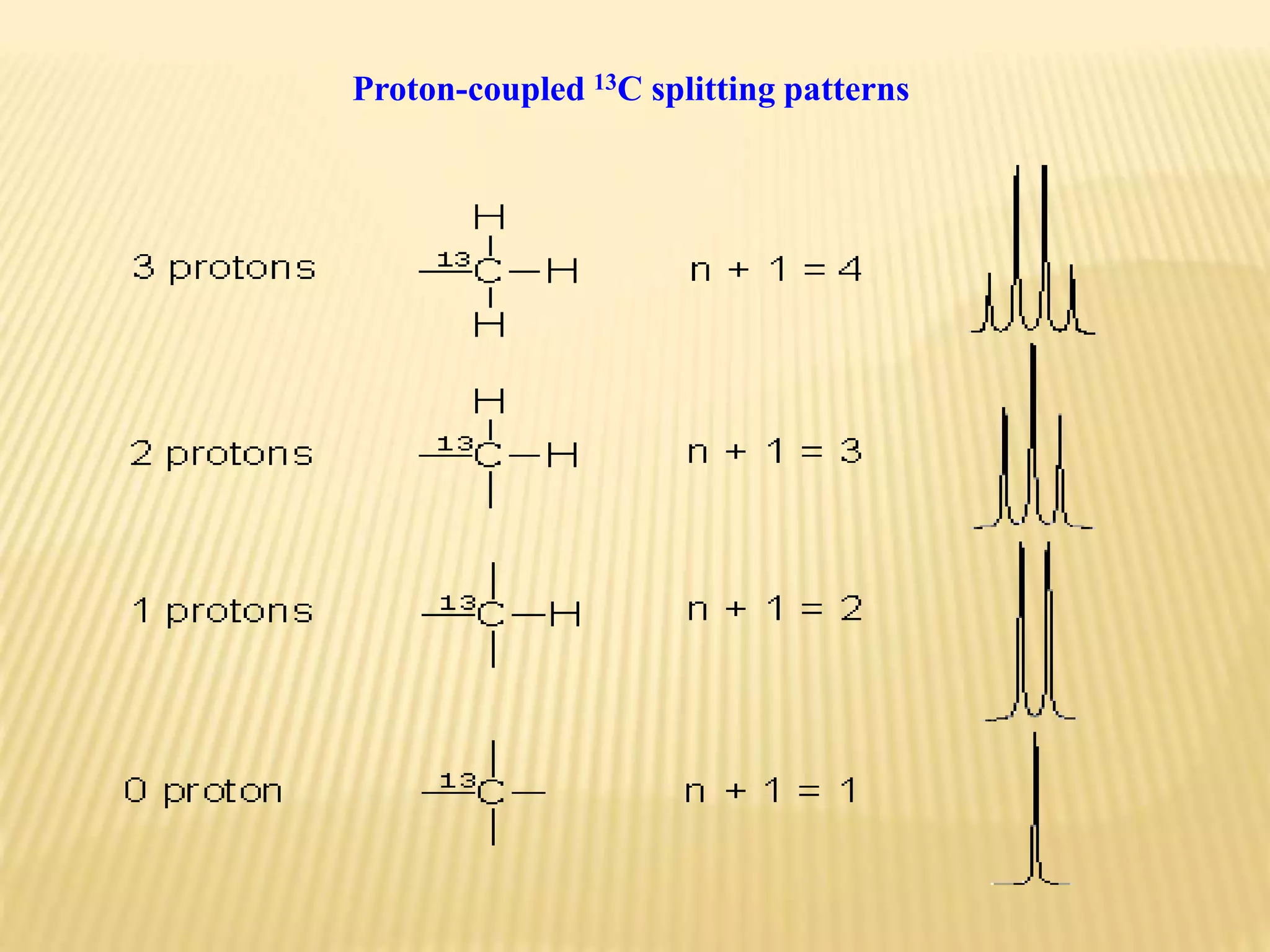
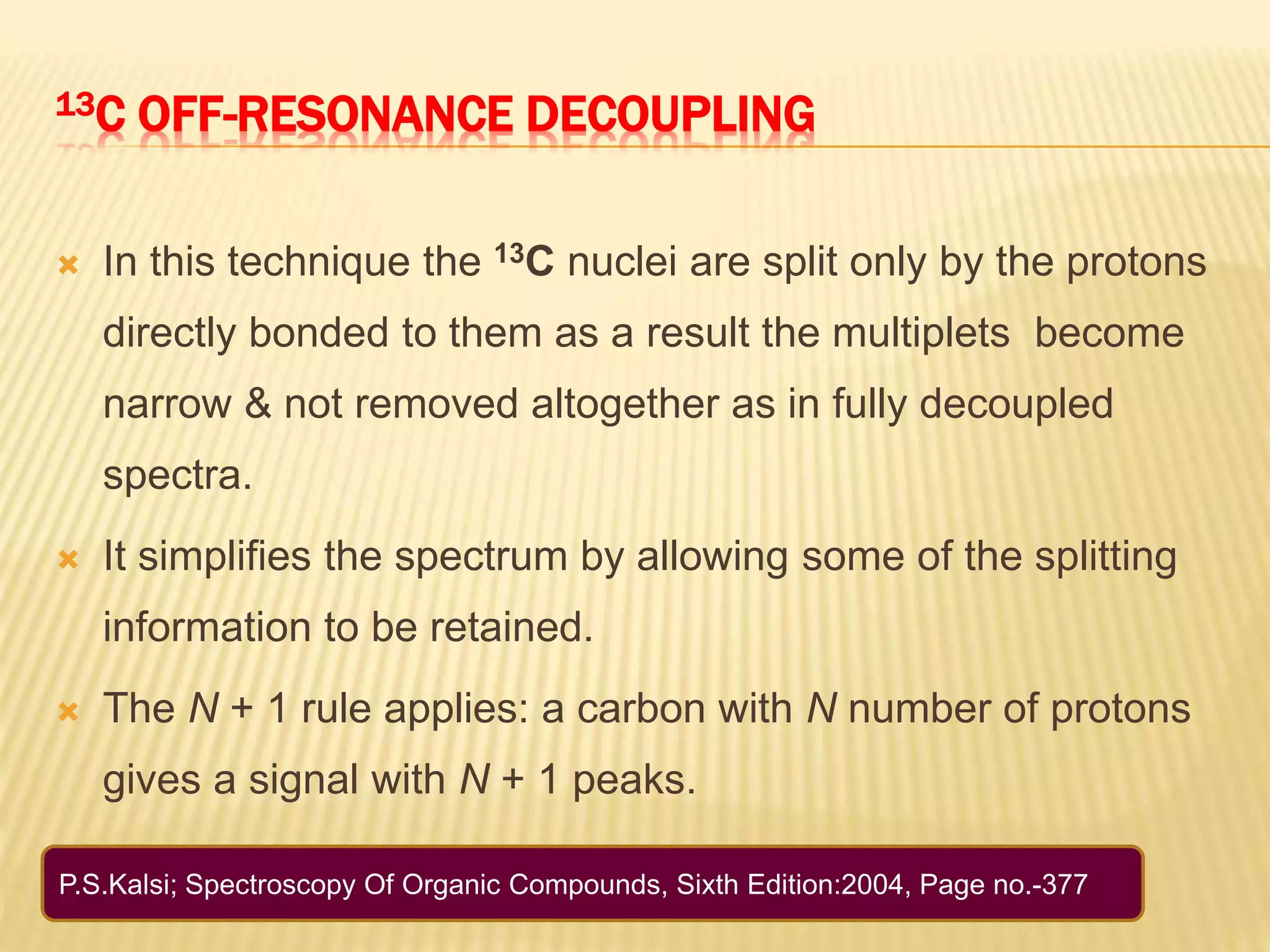
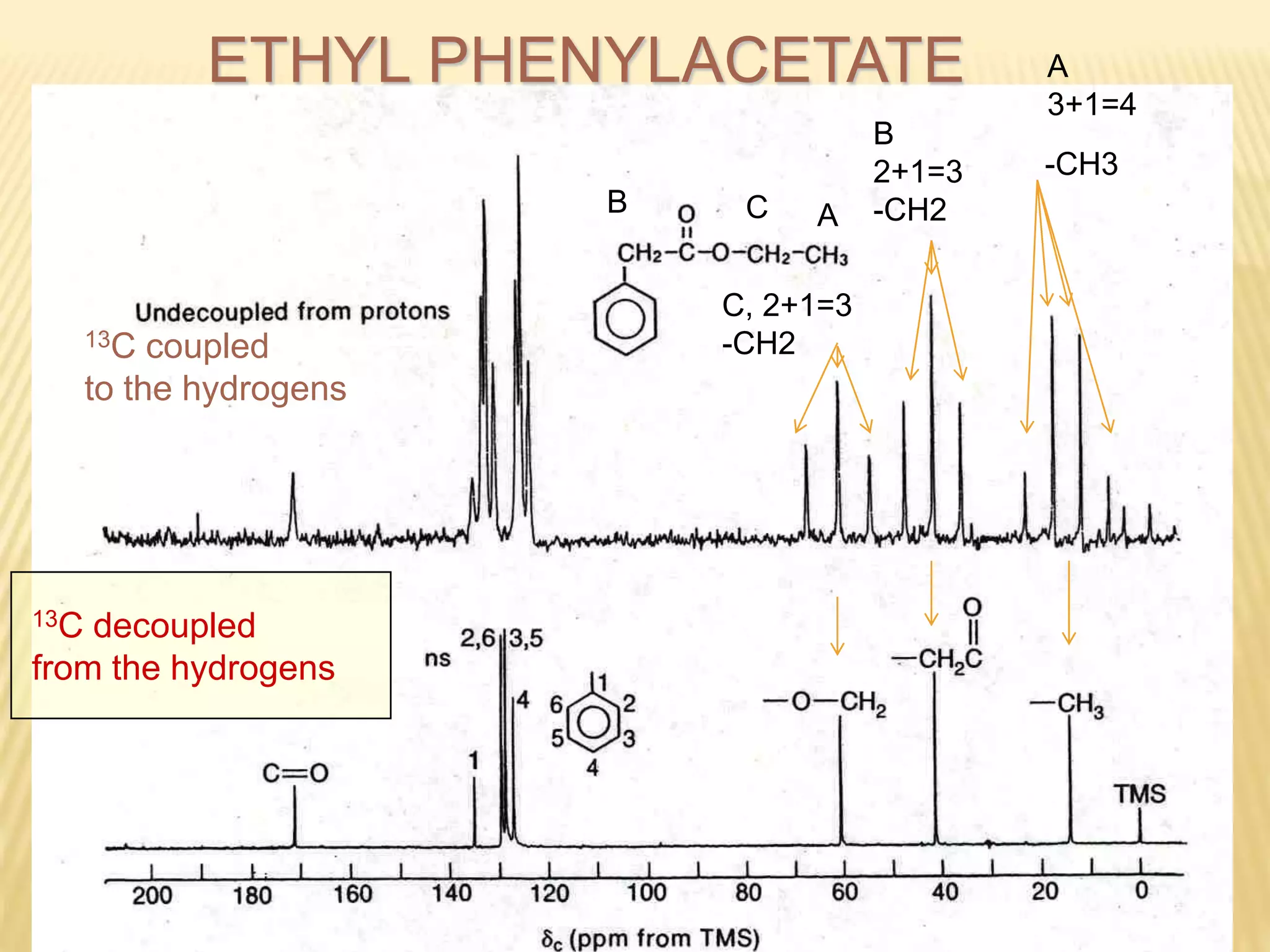
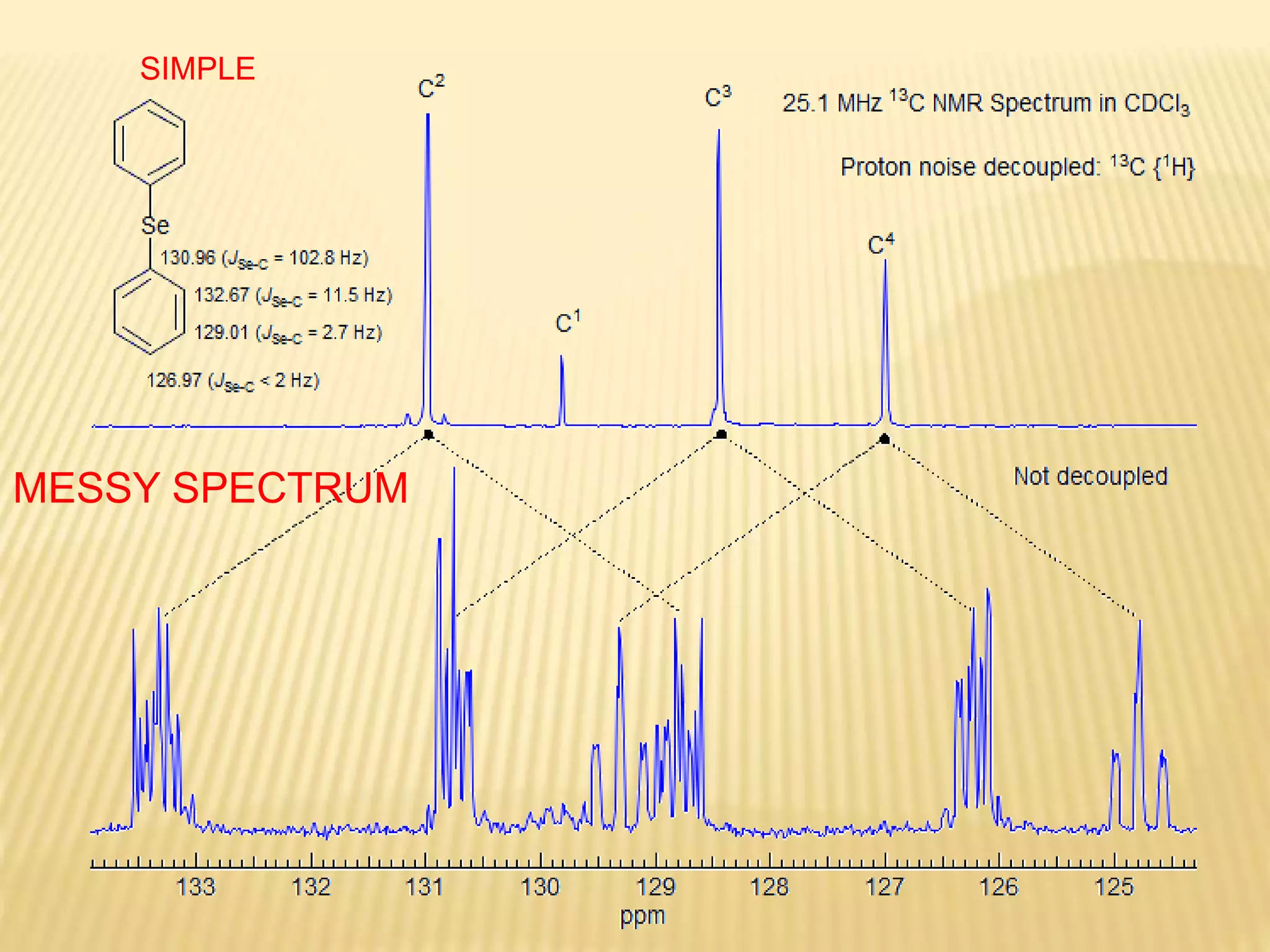
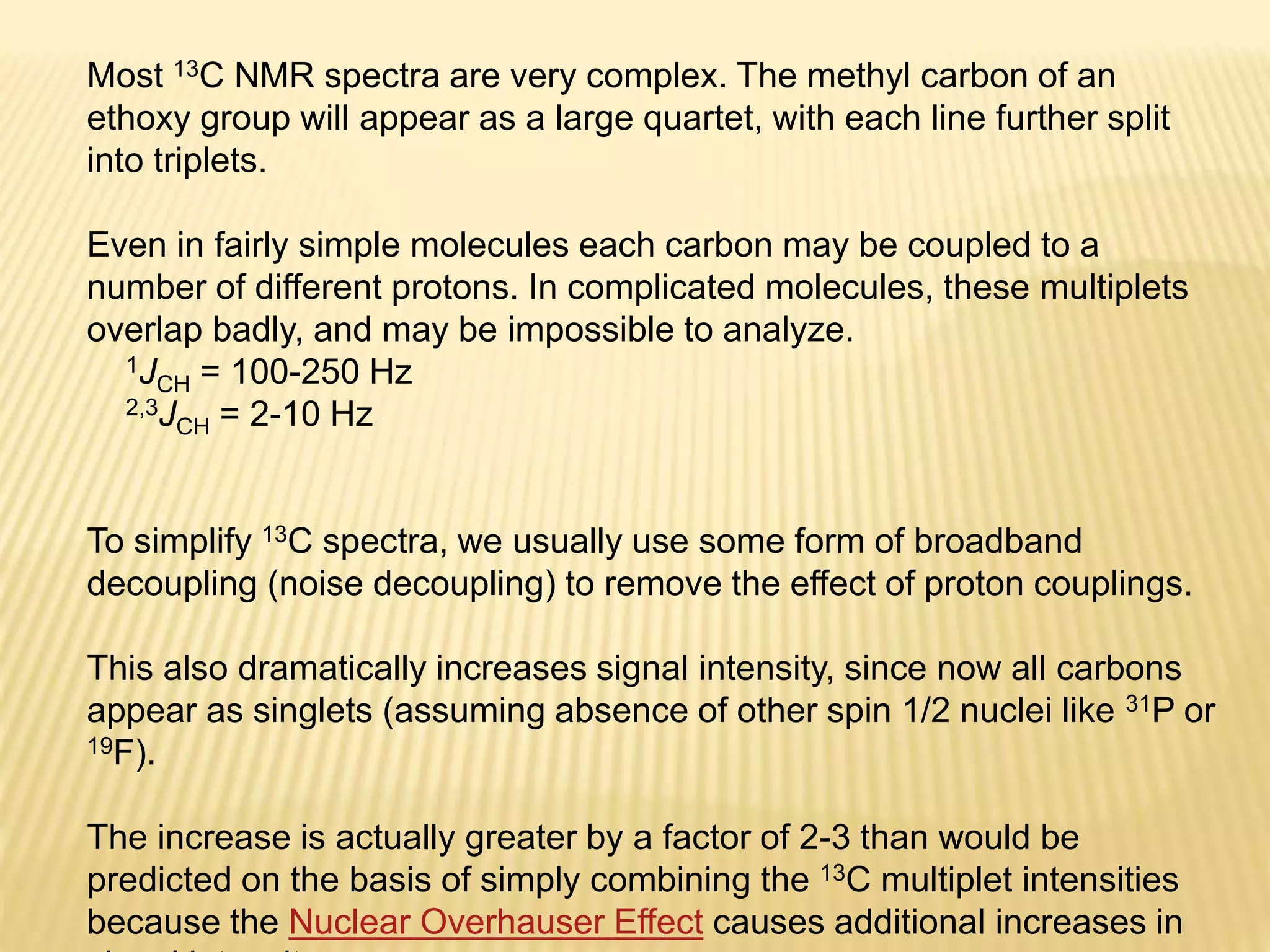
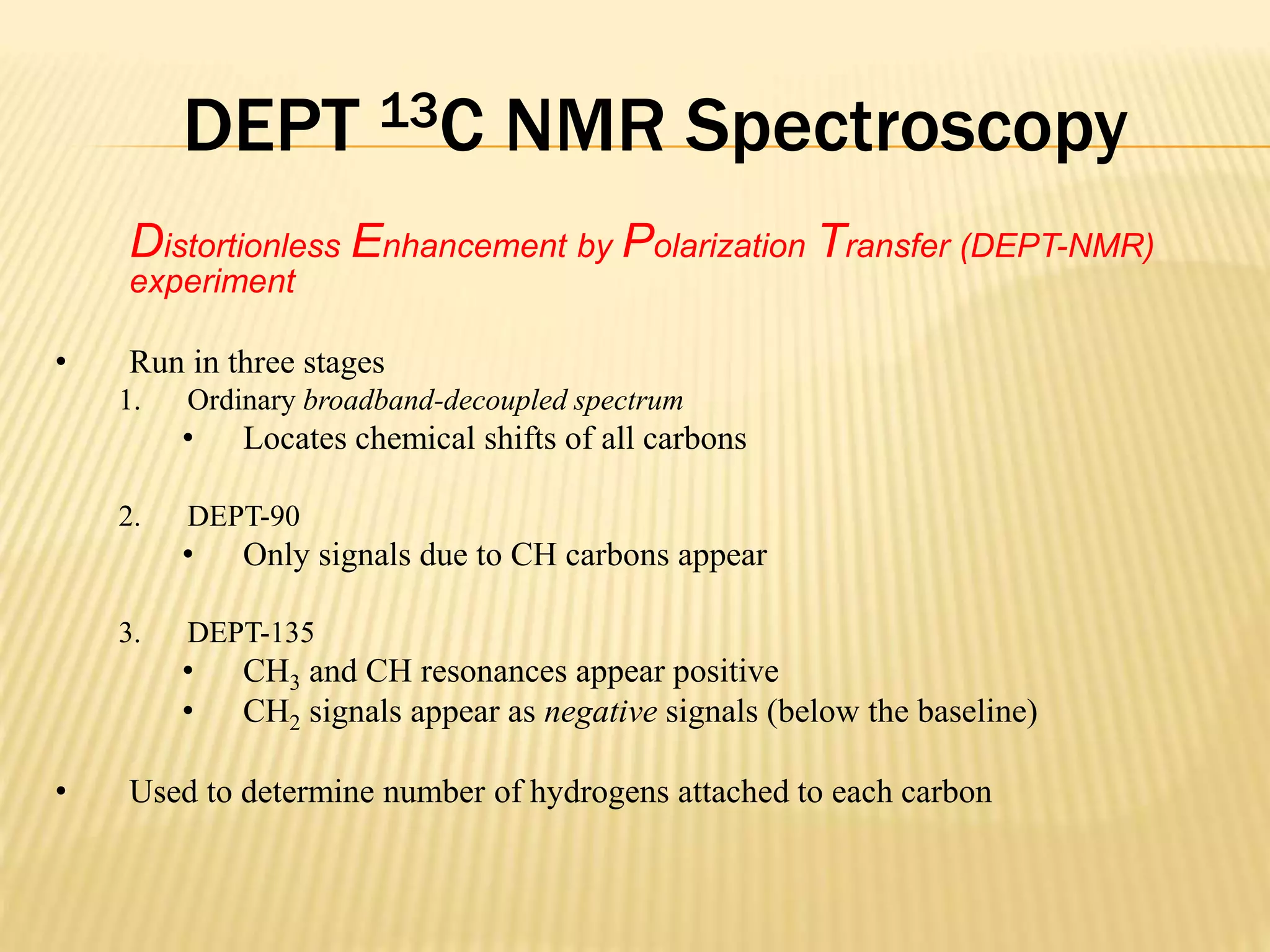
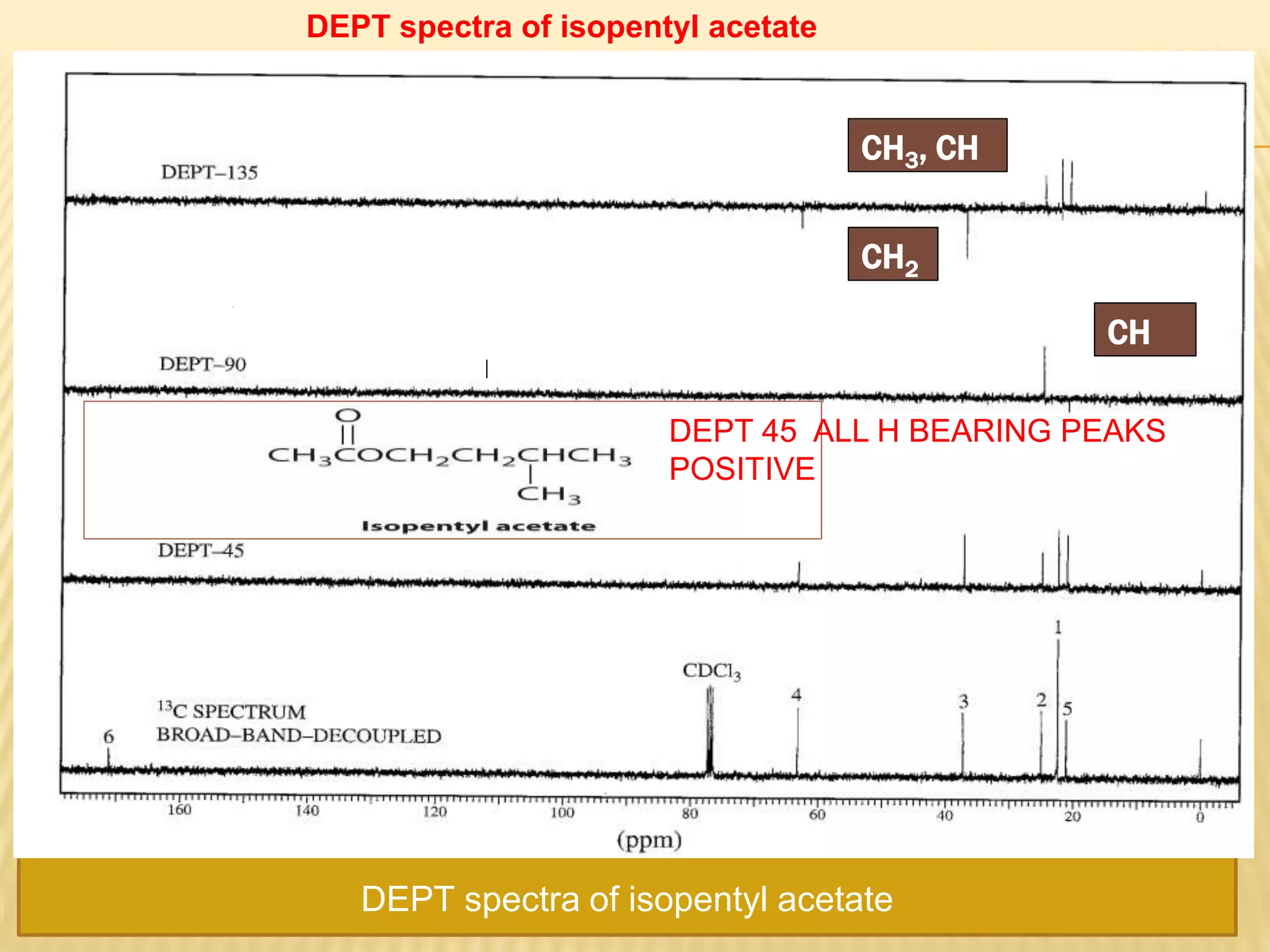
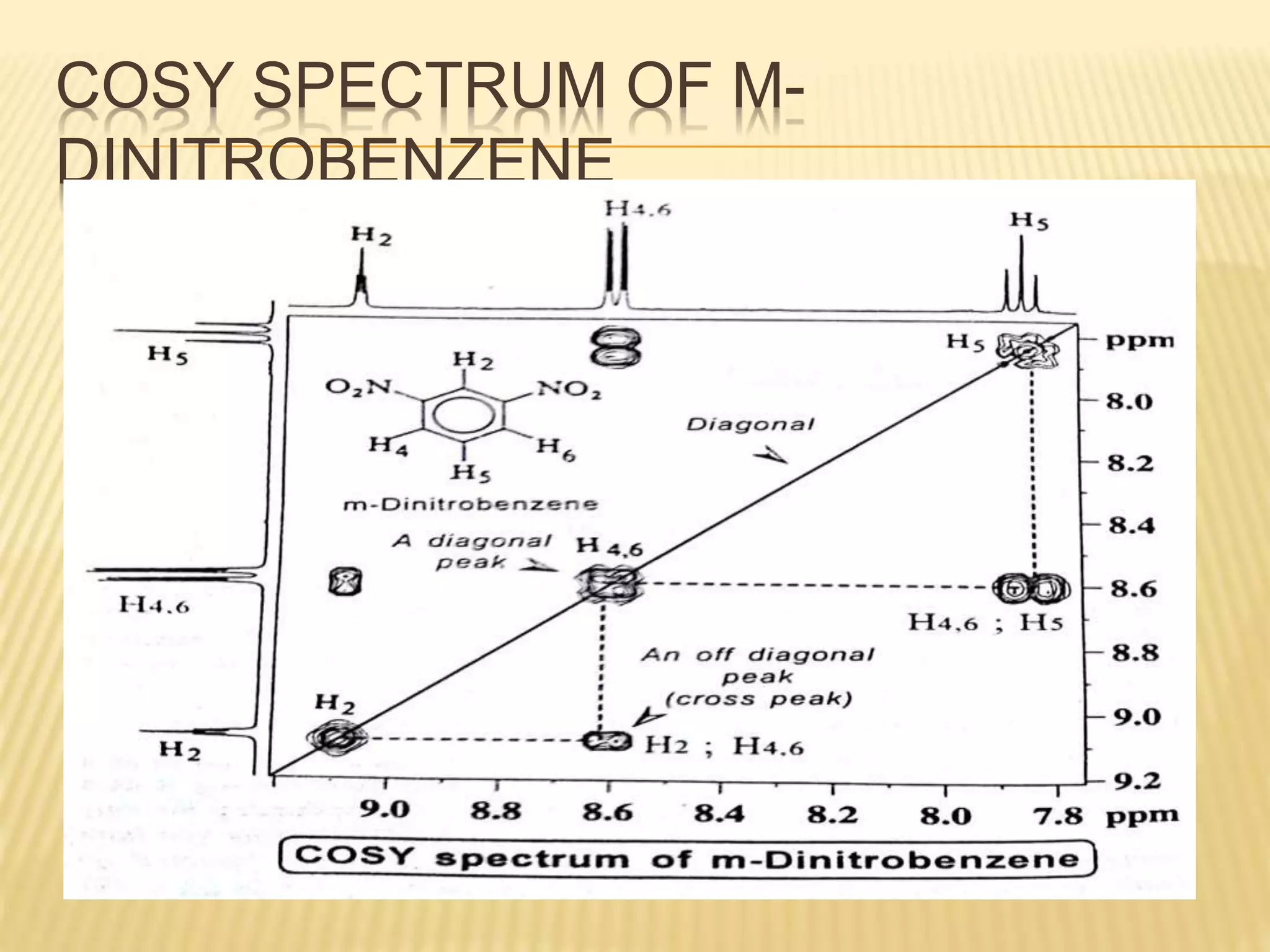
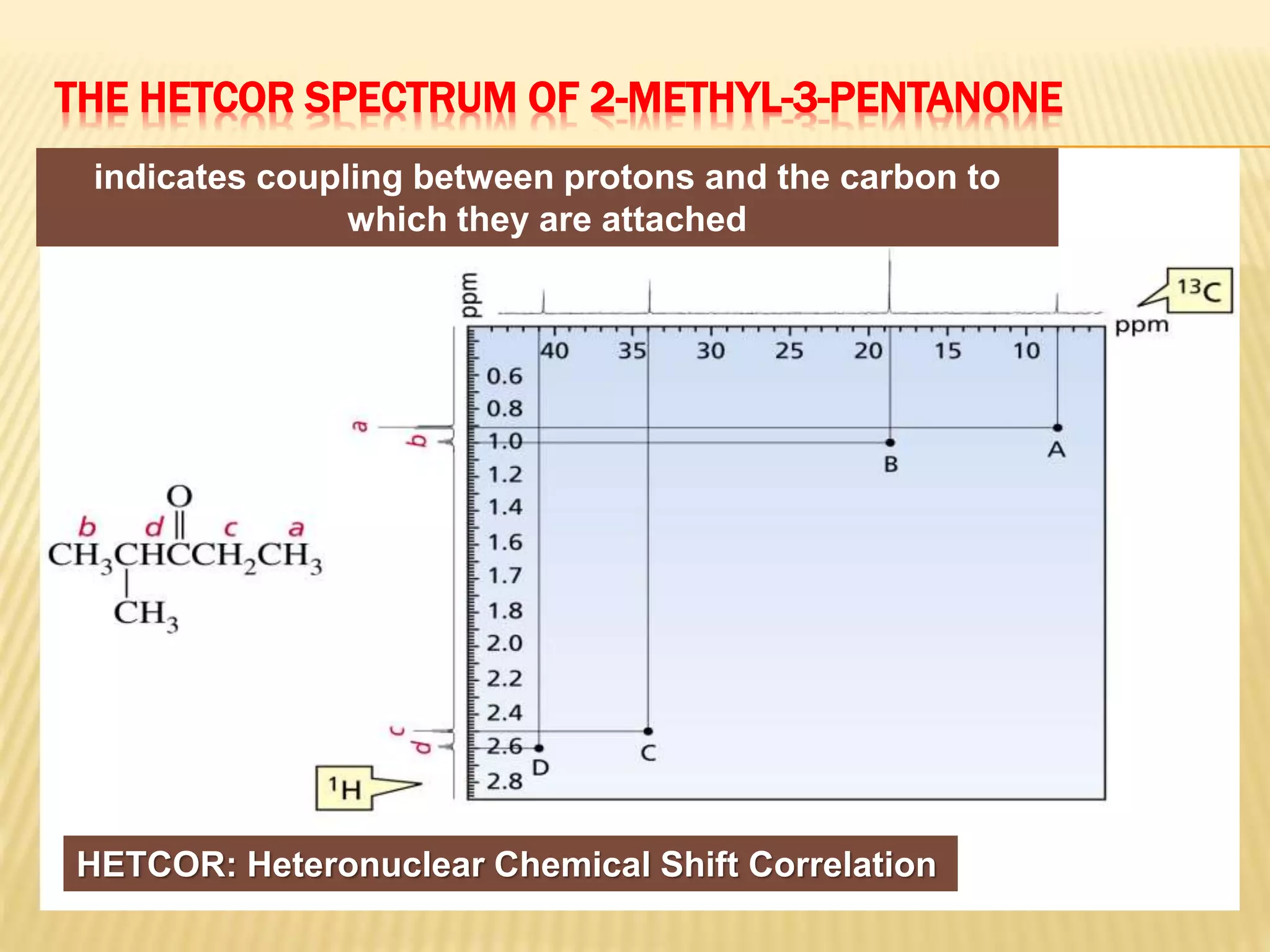
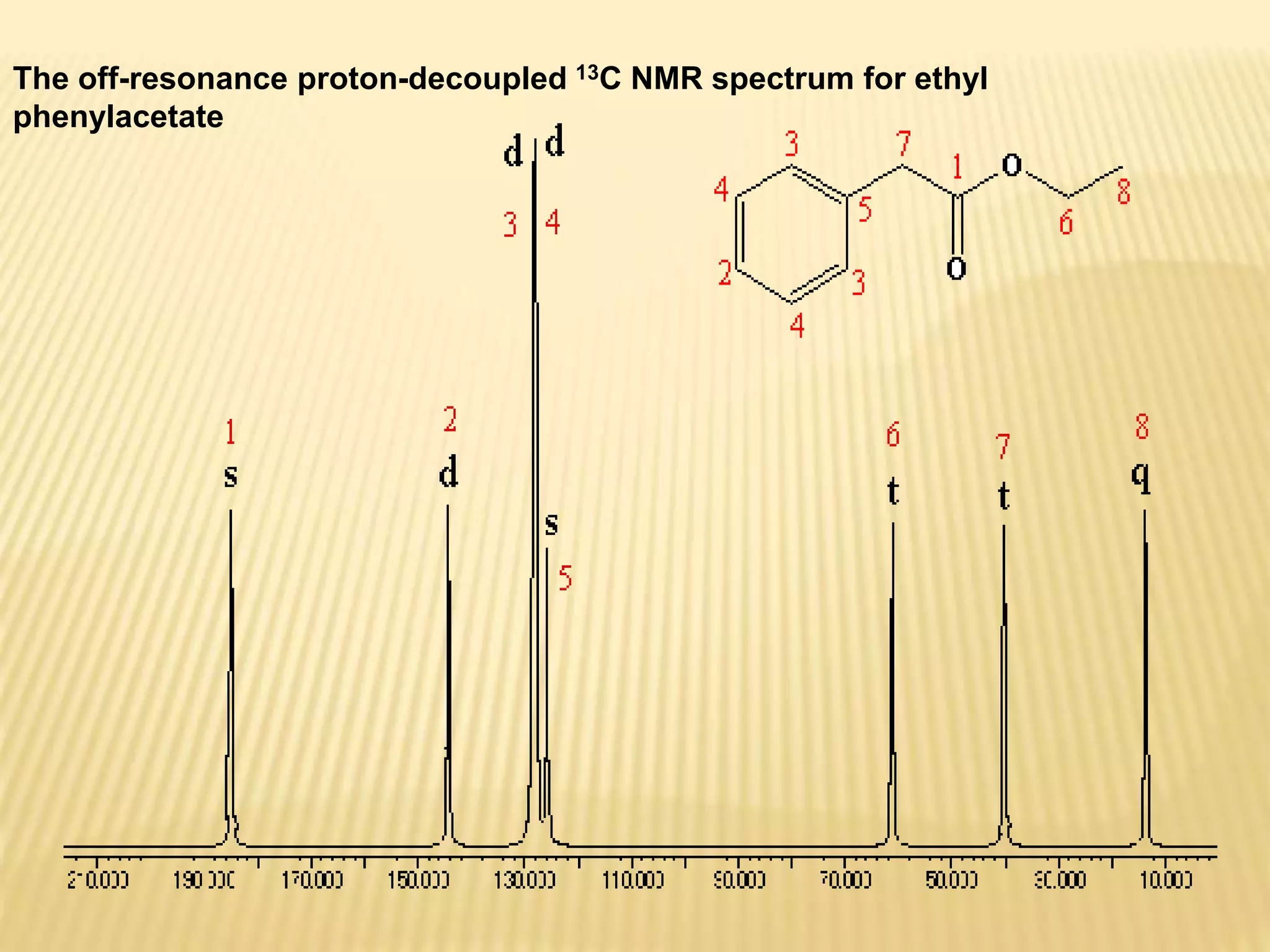
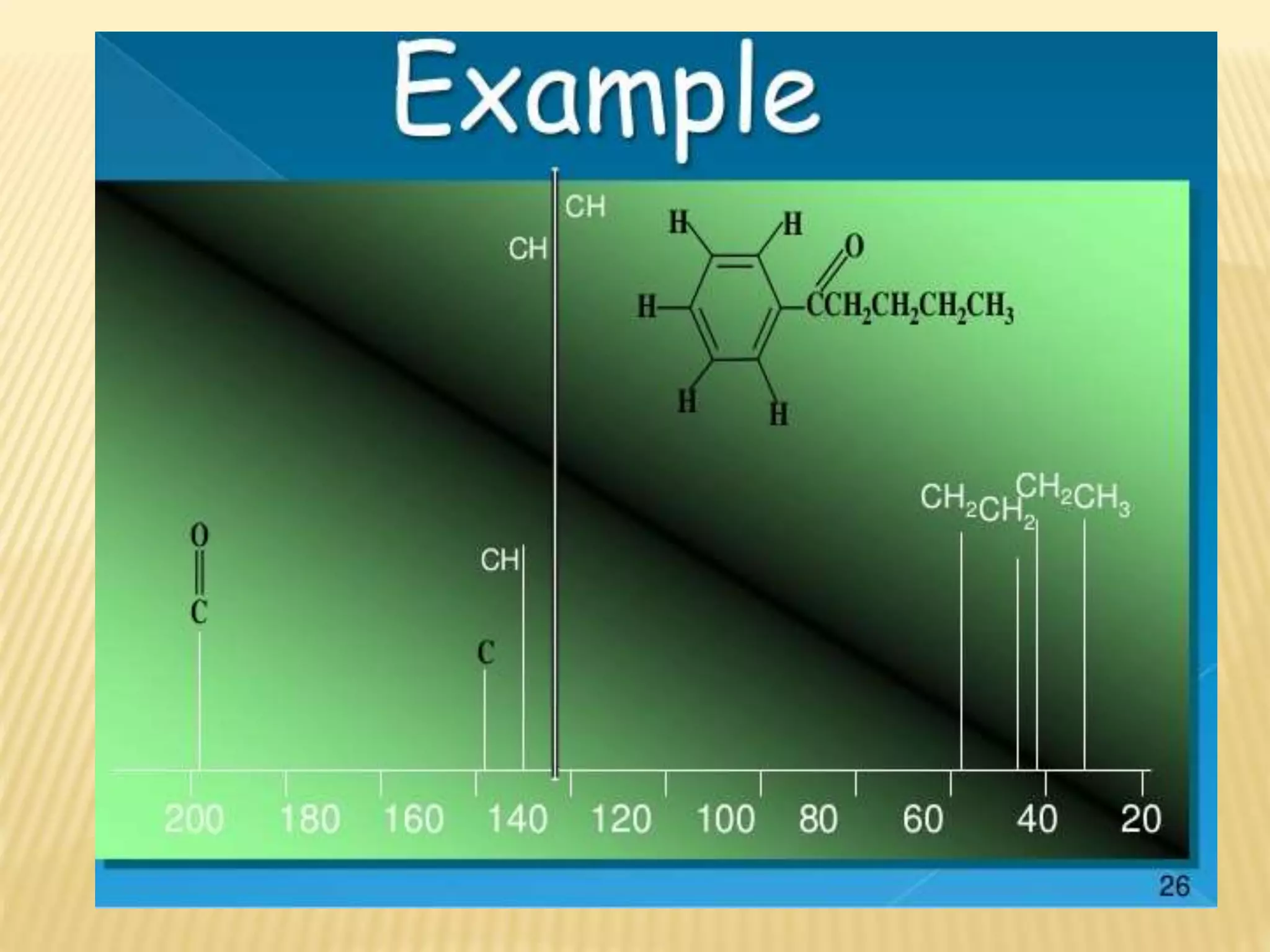
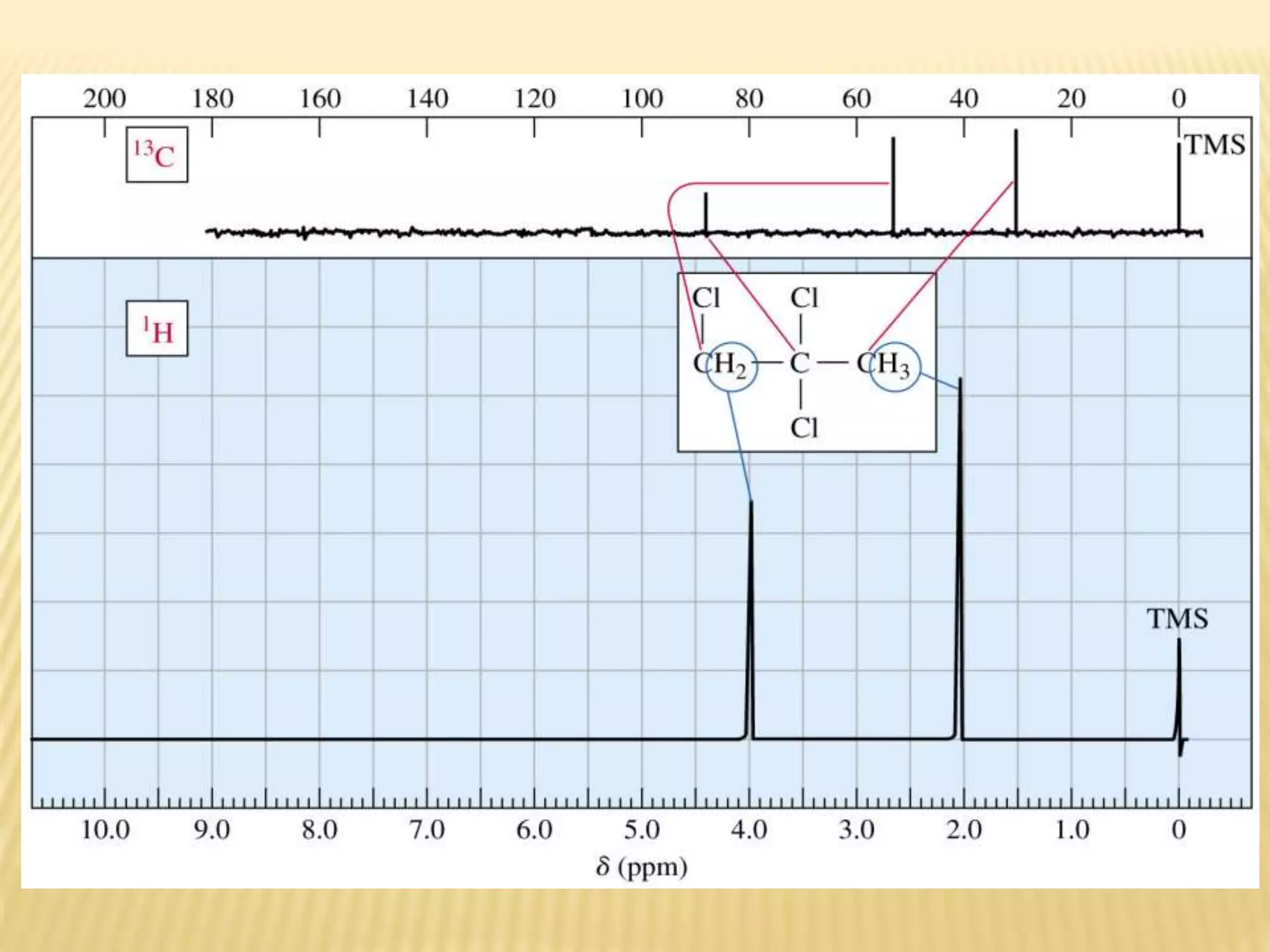
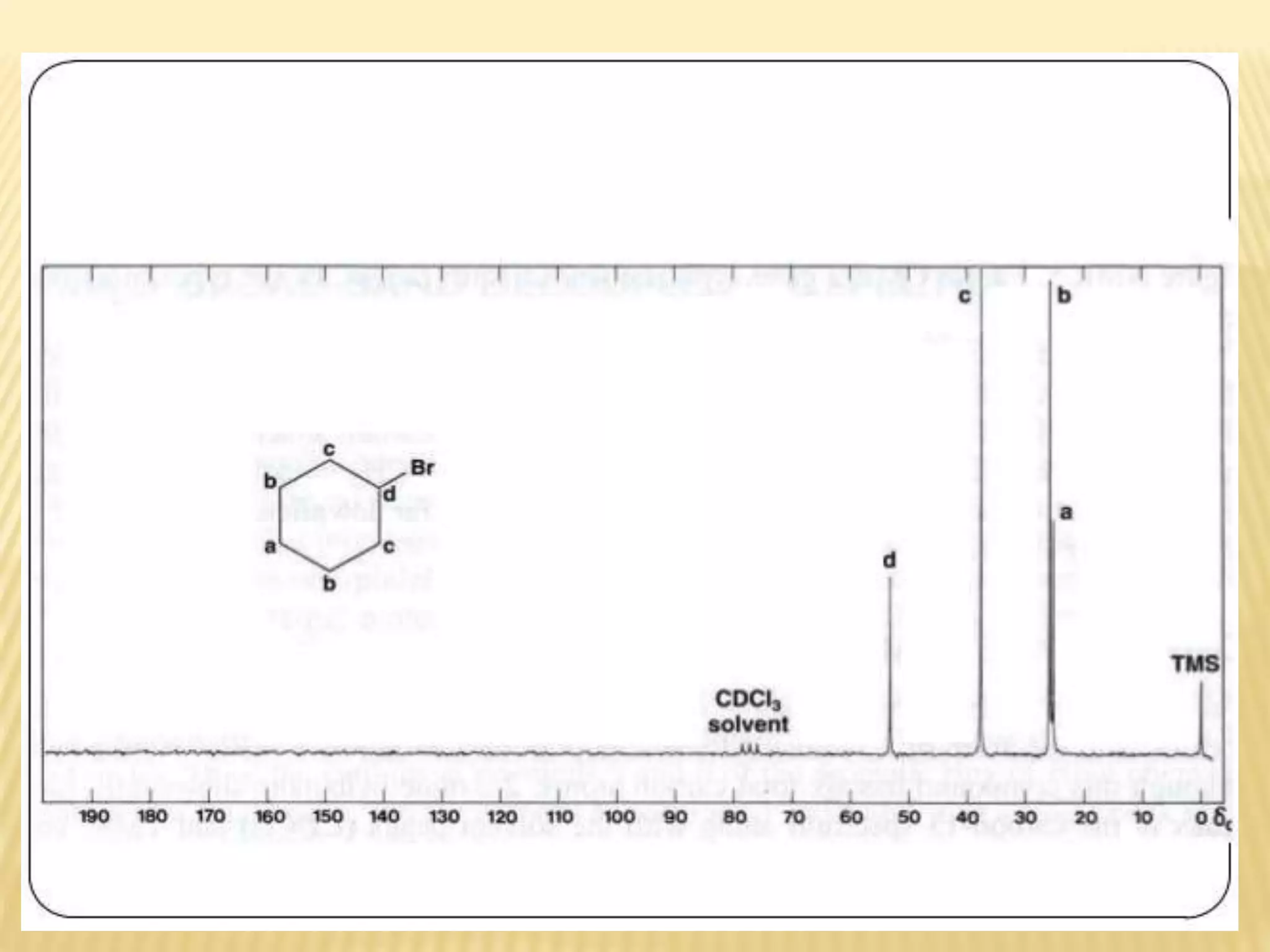
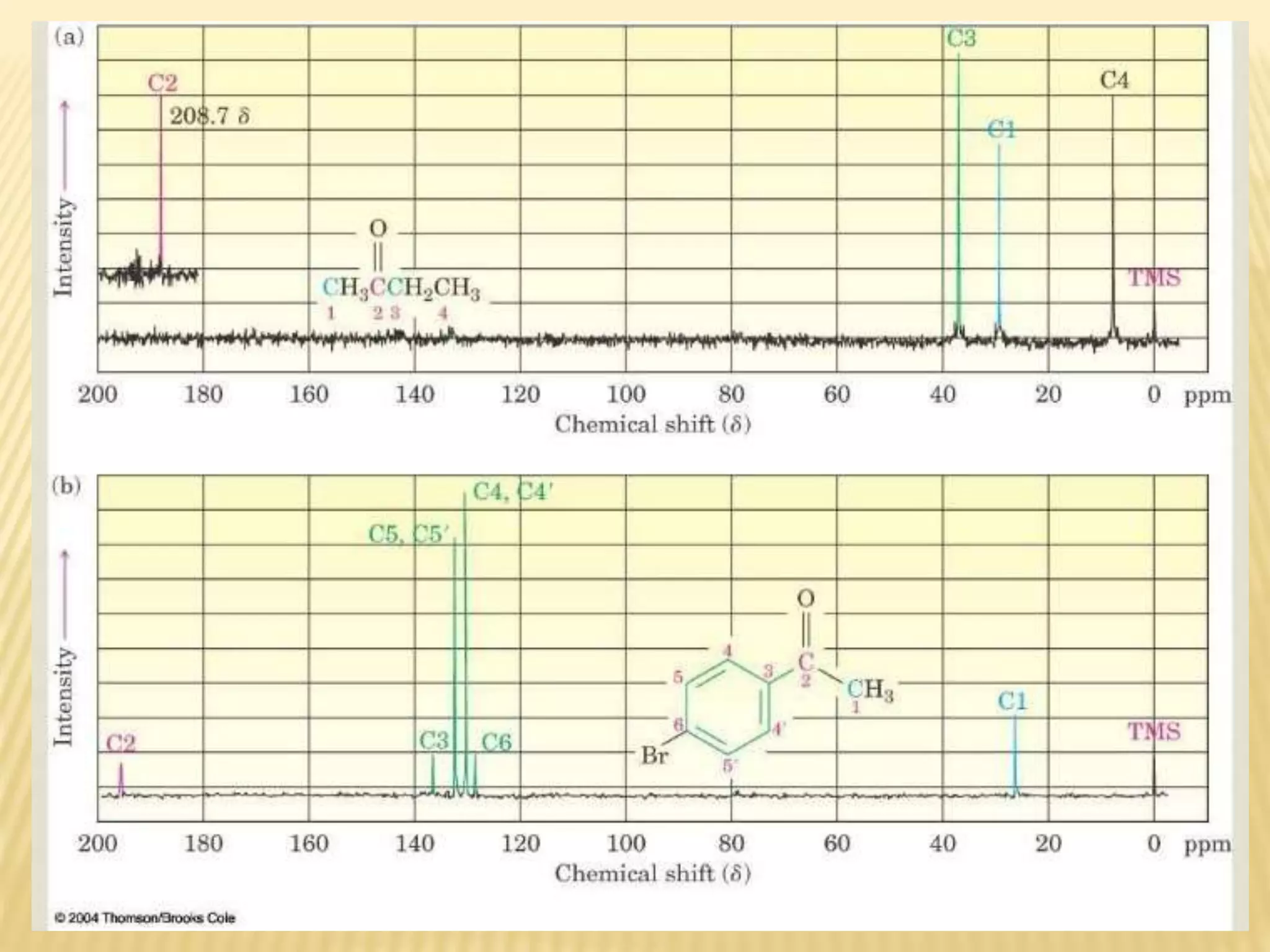
13C-NMR spectroscopy provides information about carbon atoms in organic compounds. It works by applying a strong magnetic field to excite carbon-13 nuclei, which make up about 1% of naturally occurring carbon. The document discusses several key aspects of 13C-NMR including: principles of NMR spectroscopy; chemical shifts and peak assignments; coupling patterns; techniques to overcome low carbon abundance like signal averaging and Fourier transform; and decoupling methods to simplify spectra. Examples are provided to illustrate predicting chemical shifts and interpreting 13C-NMR spectra.

































![102
S
N
N
S
NH
CH3
O
NH2
CH3
3c
Molecular Formula: C14H16N4OS2
C=O
CH3
CH
13C NMR spectrum of 2-(Alanyl)-Amino-5-(4-methylphenyl)-5H-thiazolo[4,3-b]-1,3,4-
thiadiazole (3c)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/13cnmrspectroscopywithexamplesdranthony-160303041359/75/13-C-NMR-Spectroscopy-with-examples-by-Dr-Anthony-Crasto-102-2048.jpg)
![103
S
N
N
S
N
O
Cl
H3C
4d
Molecular Formula = C20H16ClN3OS2
C=O
CH3
CH-Cl
CH
13C NMR spectrum of 3-chloro-1-[5-(4-methylphenyl)[1,3]thiazolo[4,3-b][1,3,4]thiadiazol-2-yl]-4-
phenylazetidin-2-one (4d)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/13cnmrspectroscopywithexamplesdranthony-160303041359/75/13-C-NMR-Spectroscopy-with-examples-by-Dr-Anthony-Crasto-103-2048.jpg)