Embed presentation
Downloaded 10 times




















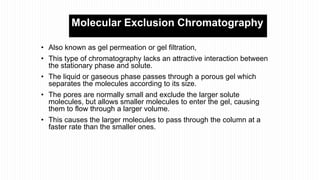
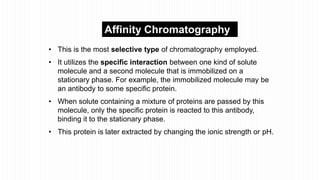










This document provides an overview of different chromatographic techniques classified based on their mechanism of separation, physical state, shape of the chromatographic bed, and physical or chemical methods. It describes key techniques including adsorption chromatography, partition chromatography, gas-liquid chromatography, ion-exchange chromatography, size exclusion chromatography, thin layer chromatography, paper chromatography, normal phase chromatography, reverse phase chromatography, and high performance liquid chromatography. The document serves to introduce common chromatographic concepts and provide examples of different techniques.































