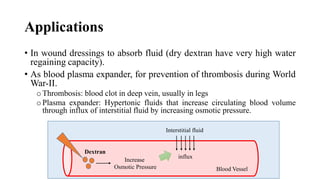
The document discusses microbial polysaccharides, specifically xanthan, dextran, and pullulan, which are produced by bacteria and fungi during their growth phases. Xanthan, produced by Xanthomonas campestris, is widely used in the food industry as a thickener and stabilizer, while dextran is produced by Leuconostoc mesenteroides and has applications in wound dressings and as a blood plasma expander. Pullulan is a versatile polysaccharide produced by Aureobasidium pullulans, used in dietary applications, drug delivery, and as a binder in various food products.