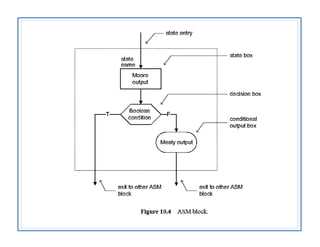
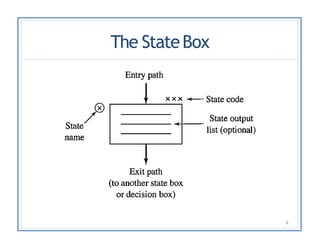
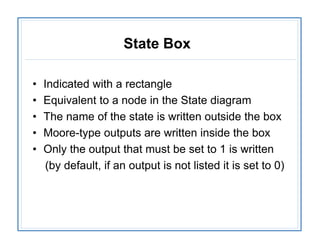
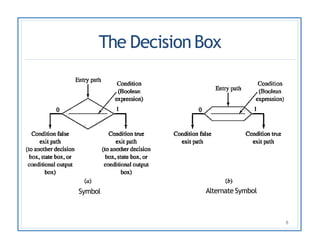
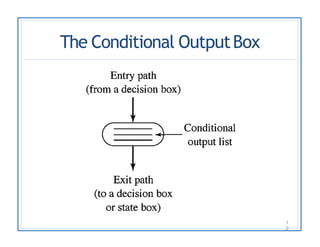
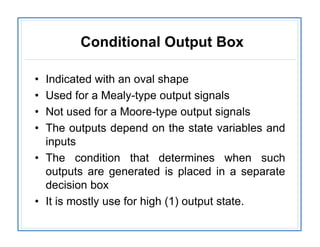
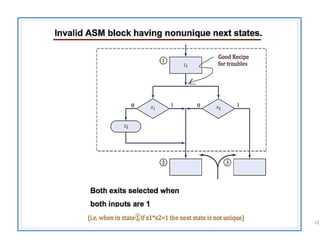
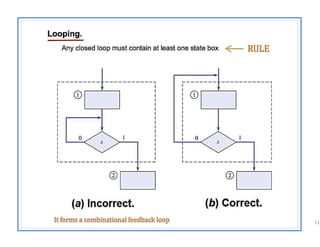
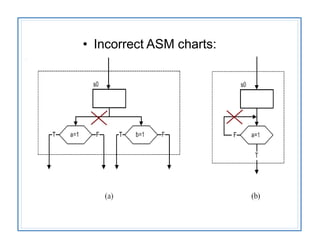
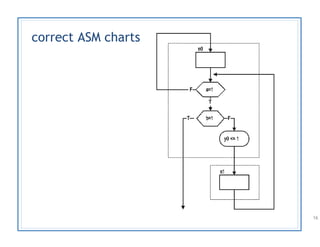
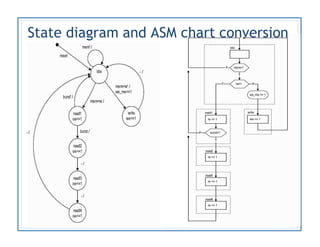
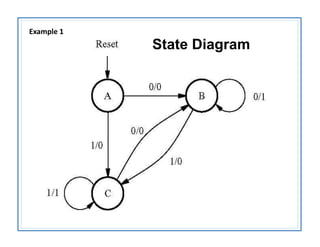
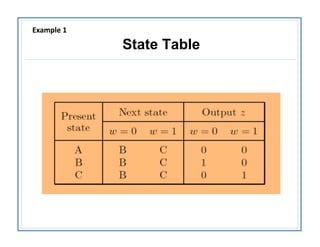
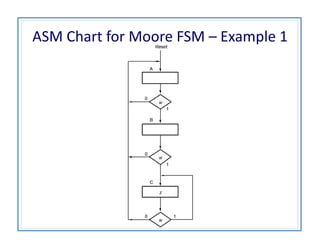
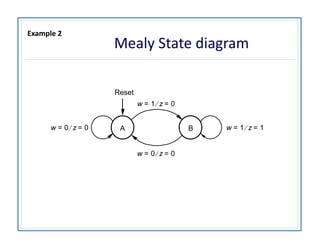
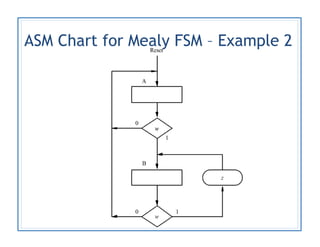
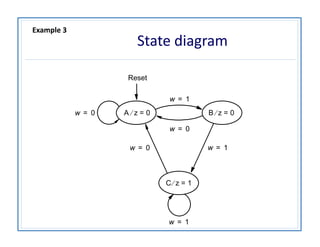
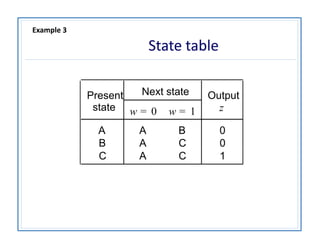
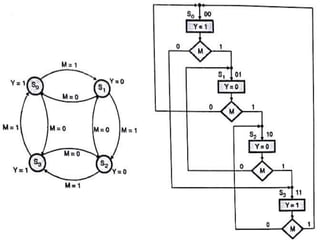
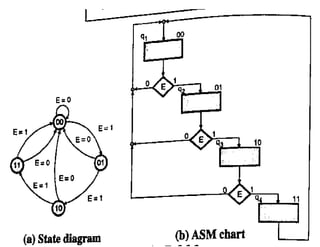
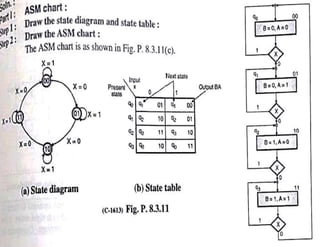
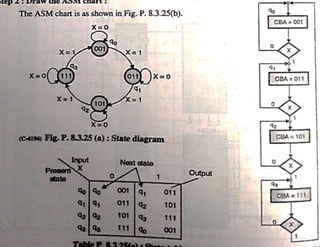
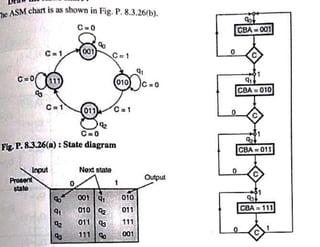
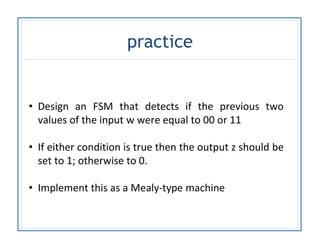
The document discusses finite state machines (FSMs) and algorithmic state machines (ASMs). FSMs have a fixed set of states and can only be in one state at a time. ASMs provide a flowchart-like diagram representation of FSMs and are suitable for more complex FSMs with many inputs and outputs. ASMs have three main building blocks - state boxes, decision boxes, and conditional output boxes. State boxes represent states, decision boxes represent condition expressions, and conditional output boxes represent Mealy-type outputs that depend on state and inputs. The document provides examples of converting state diagrams to ASM charts and vice versa.