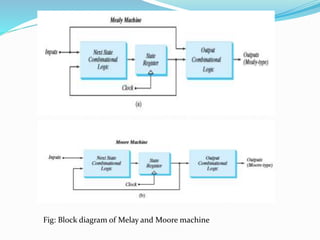
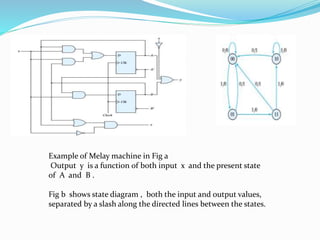
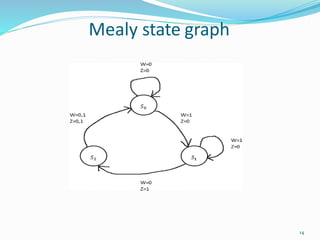
- The document discusses the differences between Mealy and Moore models of sequential circuits.
- In a Mealy model, the output is a function of both the present state and input. In a Moore model, the output is a function of just the present state.
- Some key differences are that Mealy machines react faster to inputs but are more difficult to design, while Moore machines react more slowly but require less hardware and are easier to design.