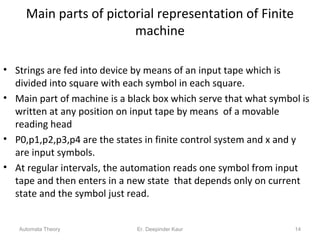
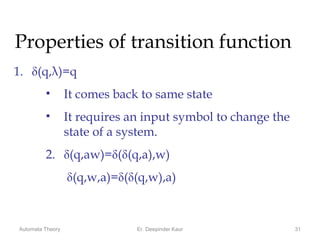
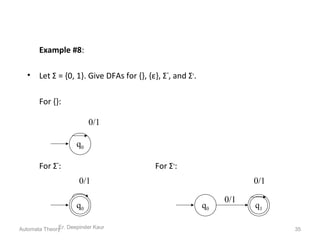
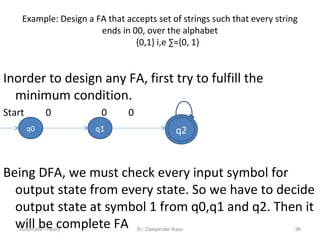
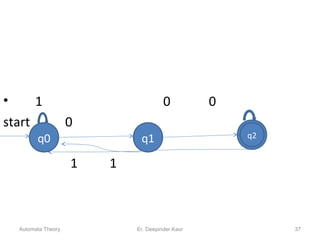
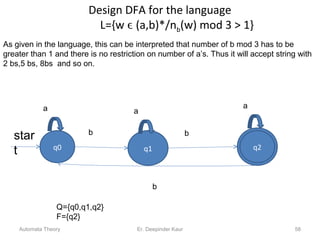
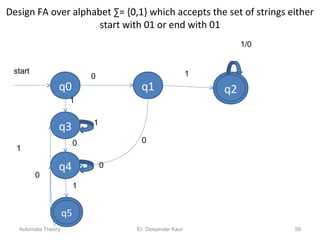
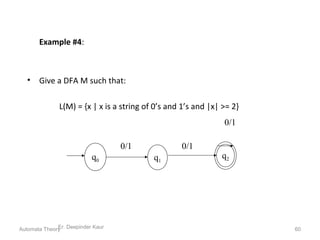
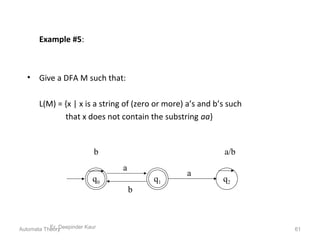
1. Automata theory is the study of abstract machines and the problems they are able to solve. It is closely related to formal language theory as automata are often classified by the formal languages they can recognize.
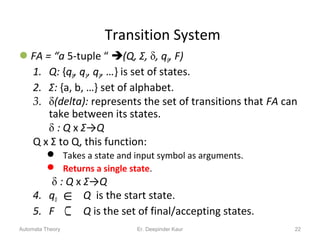
2. A finite automaton is an abstract machine that consists of a finite number of states. It reads an input string and based on its current state and the next input symbol, transitions to the next state according to its transition function. If it ends in an accepting state, the input is accepted.
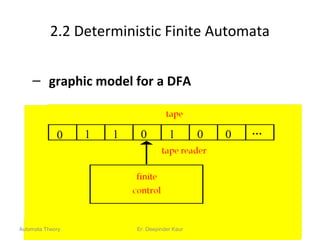
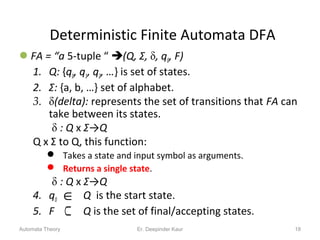
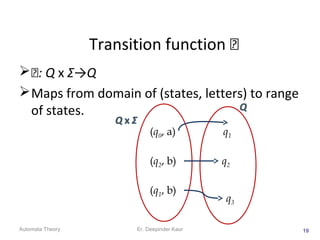
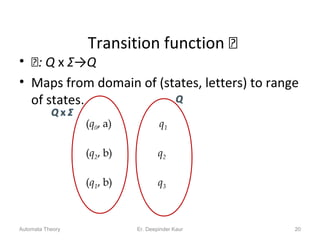
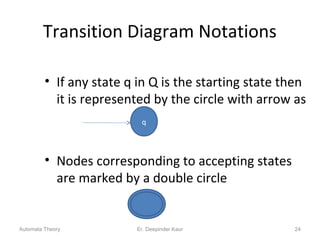
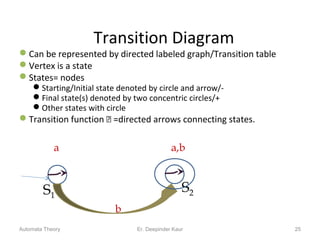
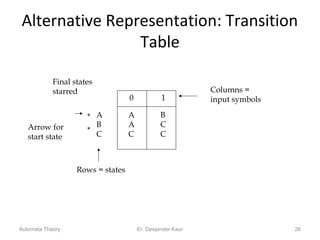
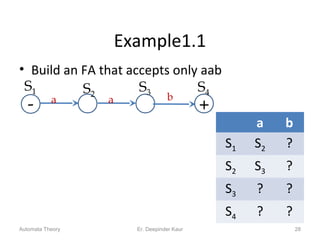
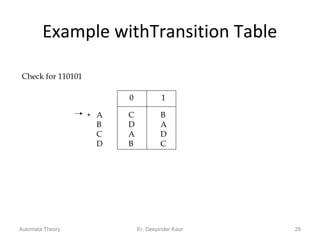
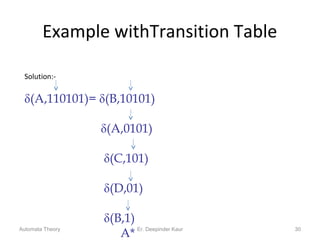
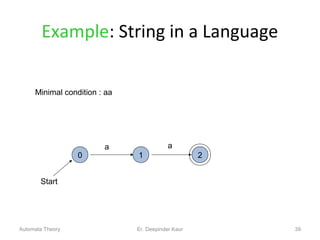
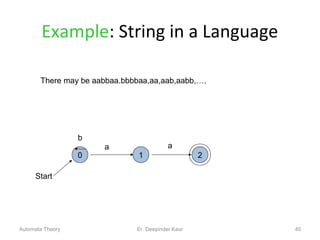
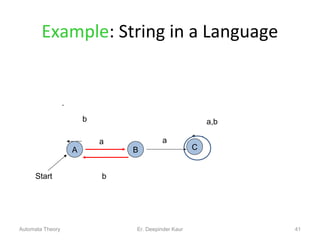
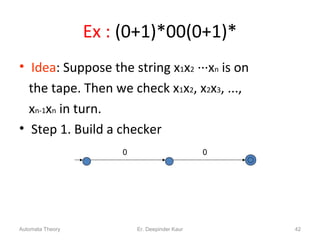
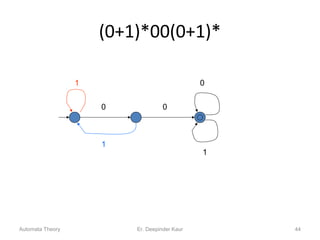
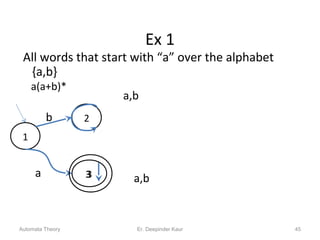
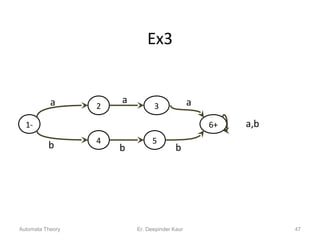
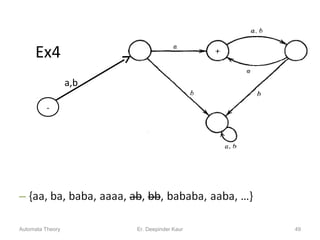
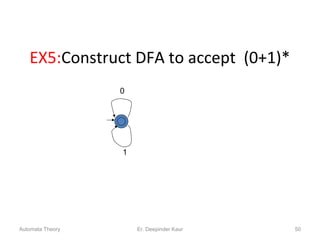
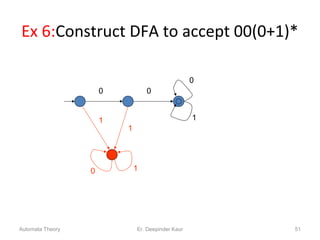
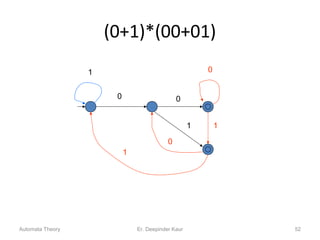
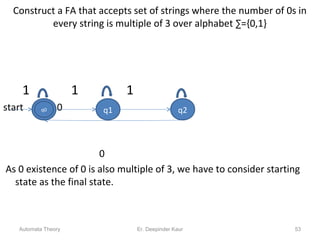
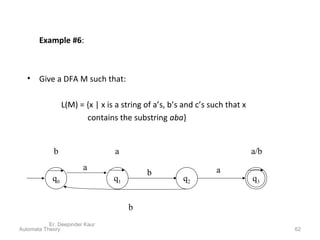
3. Deterministic finite automata (DFAs) are a type of finite automaton where the transition function maps each state-symbol pair to a unique next state. DFAs can be represented