Finite-State Machine
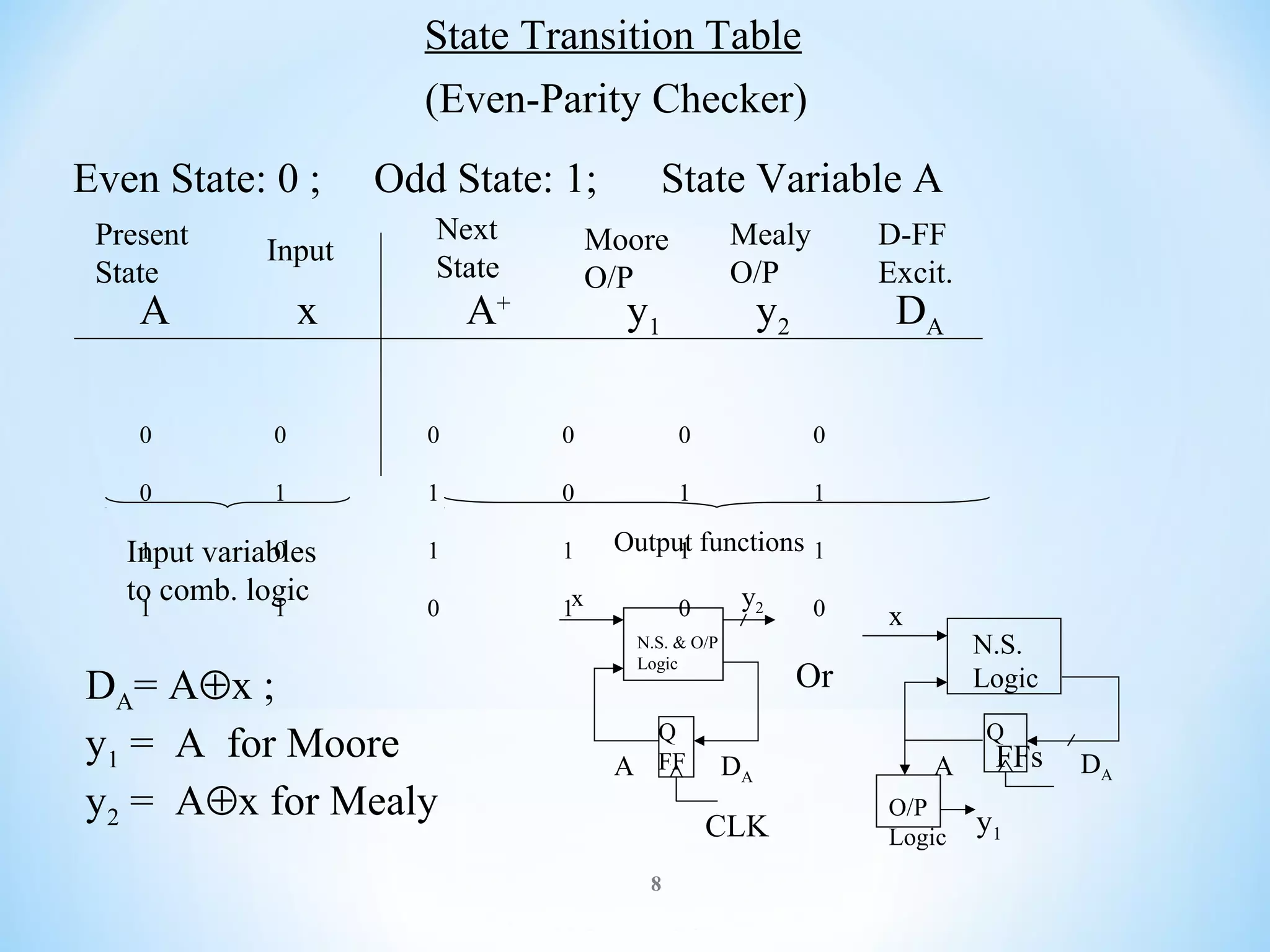
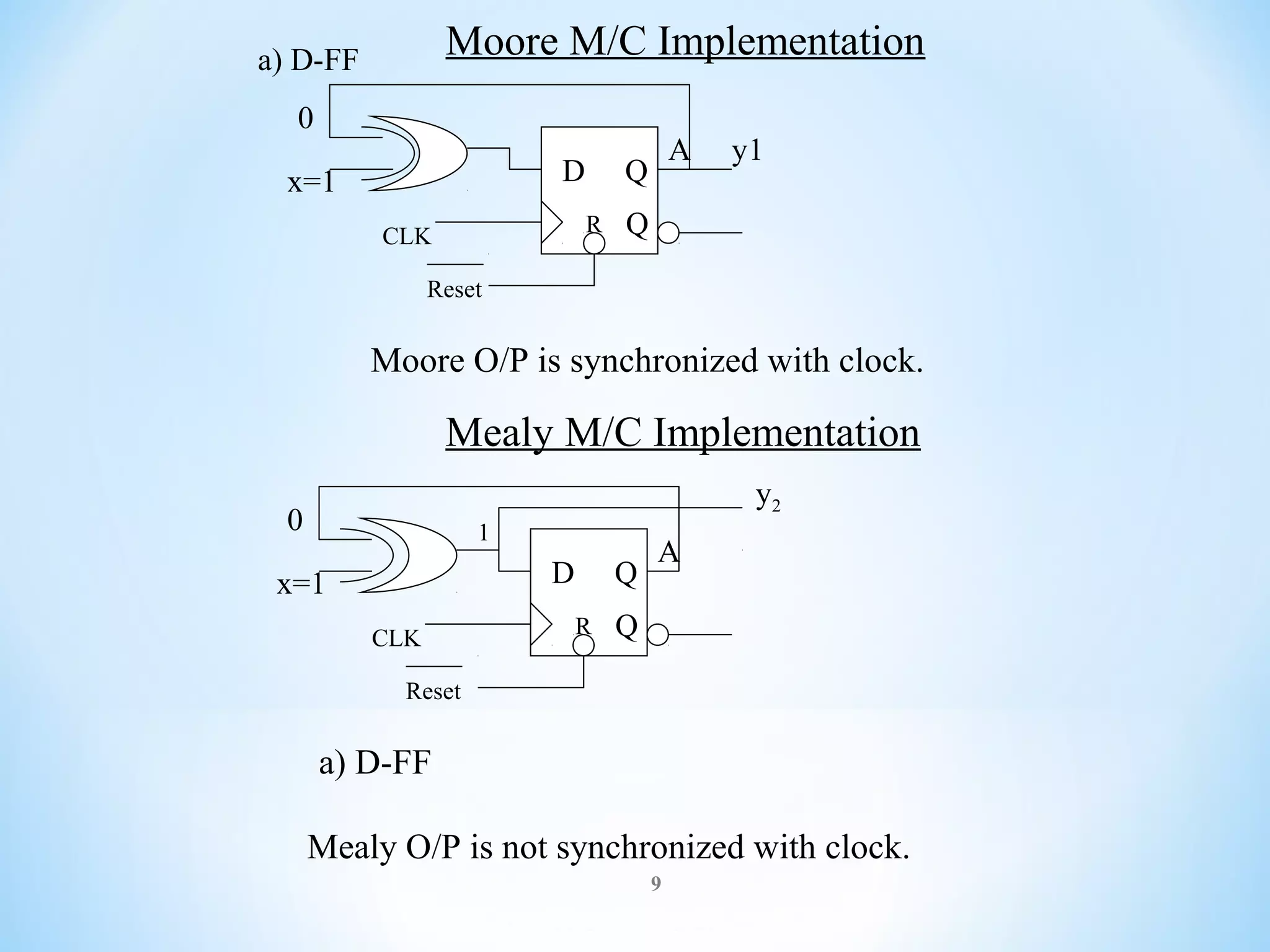
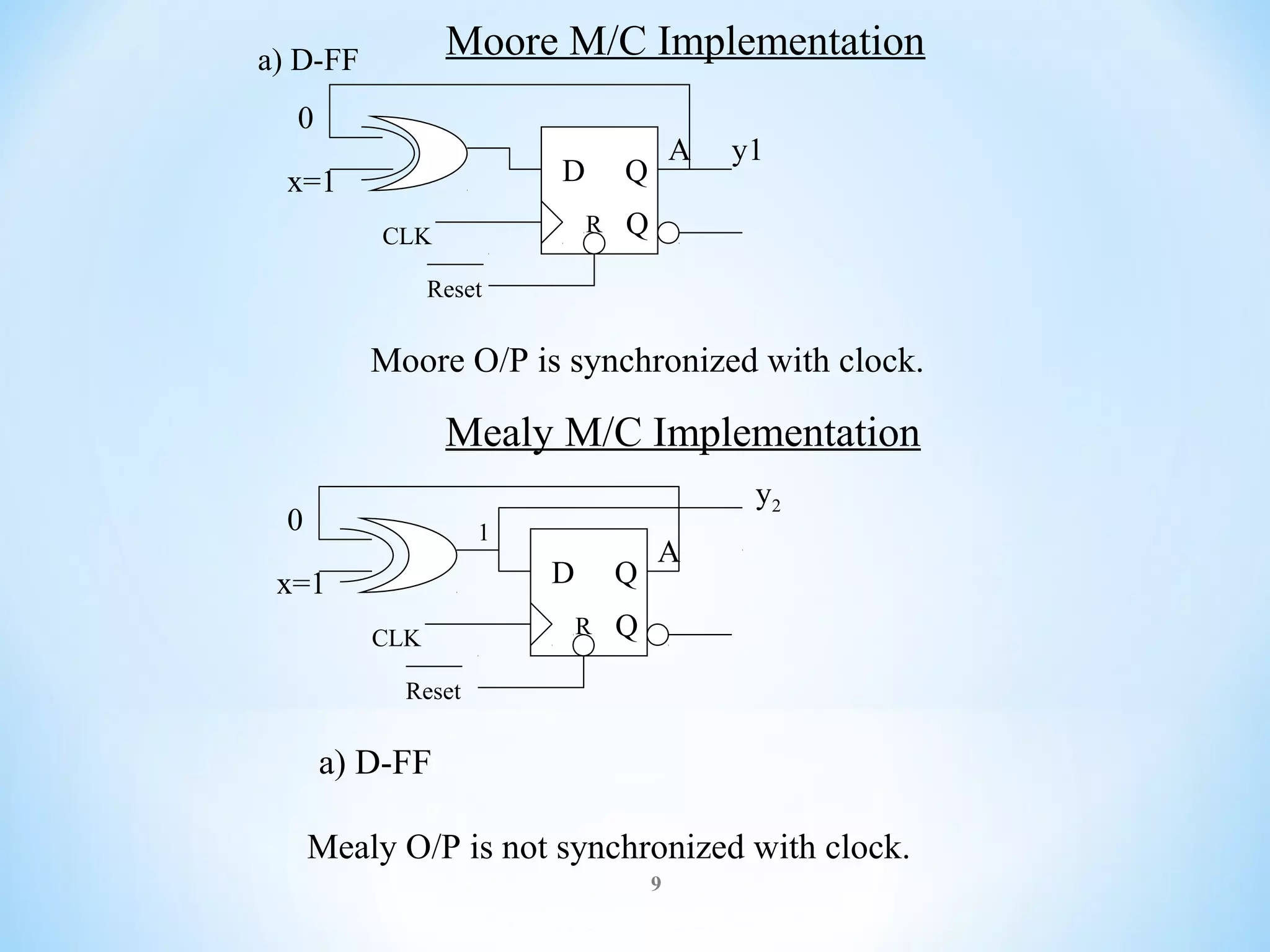
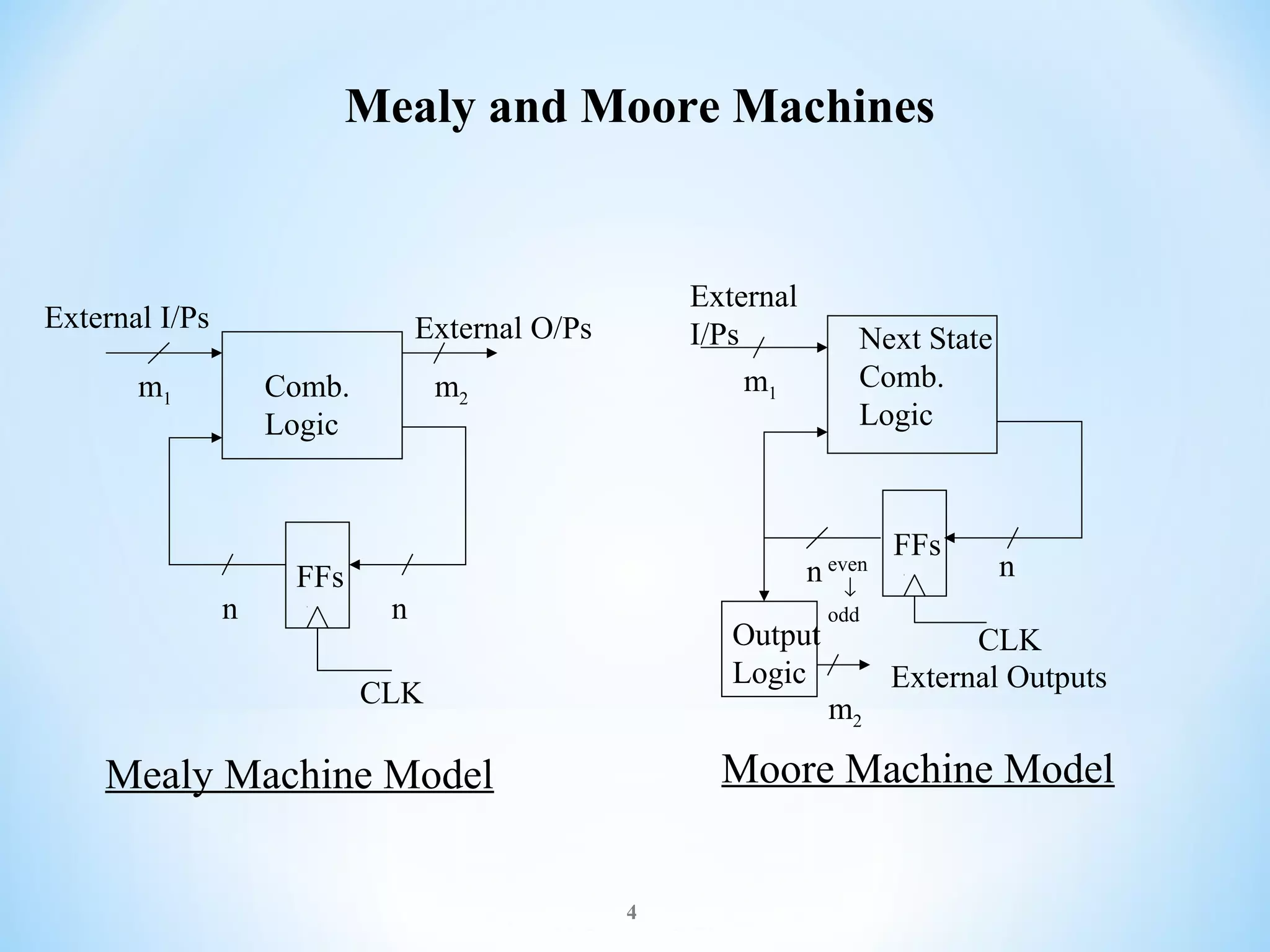
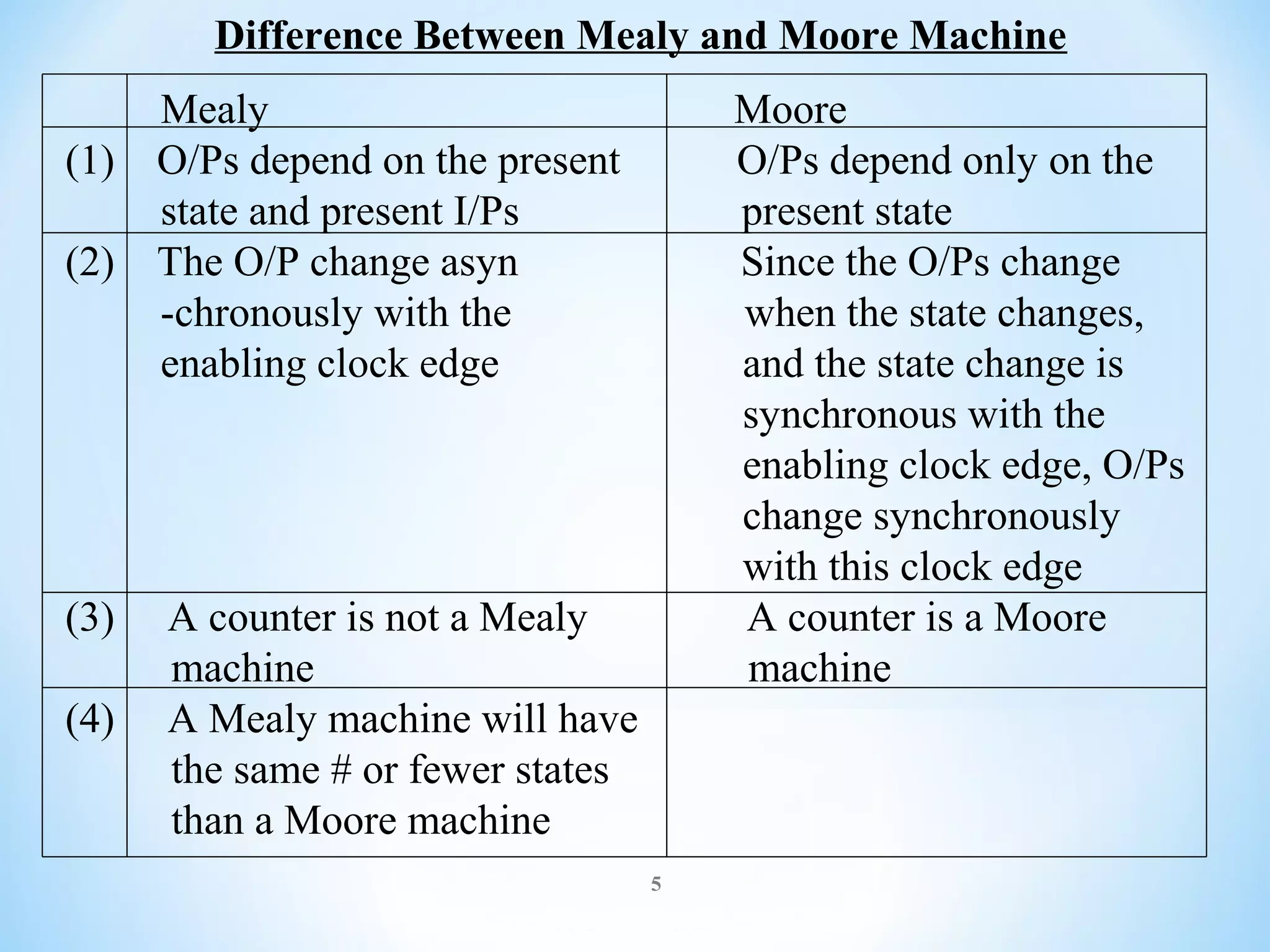
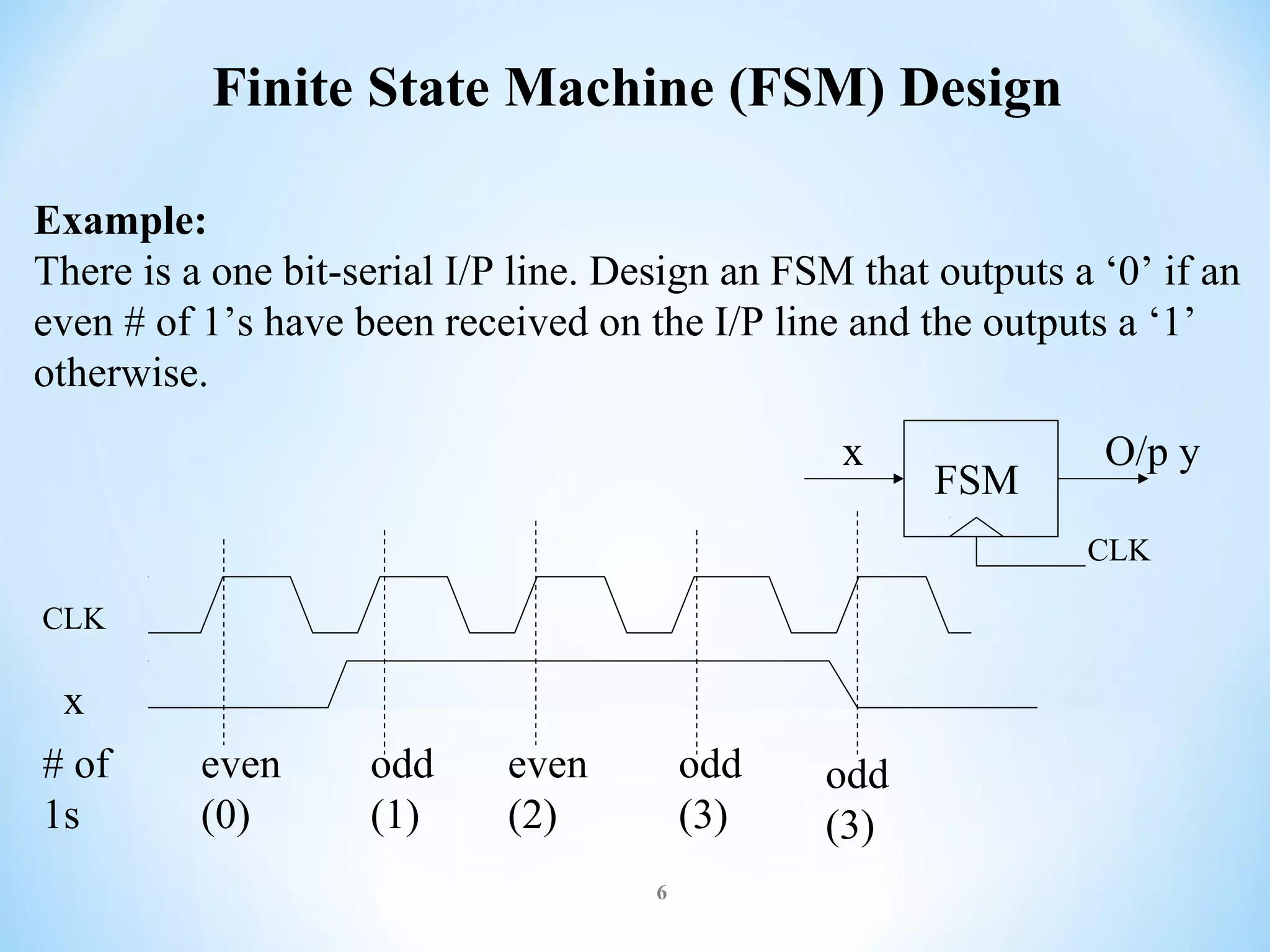
The document discusses finite-state machines (FSM), which model sequential logic circuits. It describes two types of FSMs: Mealy and Moore machines. Mealy machines output depends on the present state and input, changing asynchronously with the clock. Moore machines' output depends only on the present state, changing synchronously with state changes and clock. The document provides an example of designing an FSM to output 0 if an even number of 1's have been received on the input, and 1 for odd. It shows solutions as both a Mealy and Moore machine using state transition tables and logic diagrams.


![Solution 1: (Mealy)
Solution 2: (Moore)
0
0/0
Reset
Even
Transition
Arc
Input
1/1
1/0
Odd
Reset
Output
Even
Output
[0]
O/P is dependent
on current state and
input in Mealy
1
1
Odd
[1]
0
0/1
Mealy Machine: Output is associated
with the state transition, and appears
before the state transition is completed
(by the next clock pulse).
Input
Output is
dependent only
on current state
Moore Machine: Output is associated
with the state and hence appears
after the state transition take place.
7](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mooremealymachines-131229092709-phpapp01/75/Moore-and-Mealy-machines-7-2048.jpg)