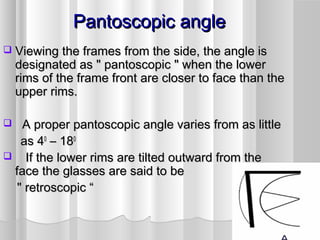
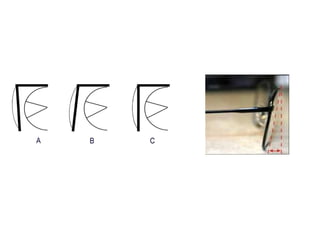
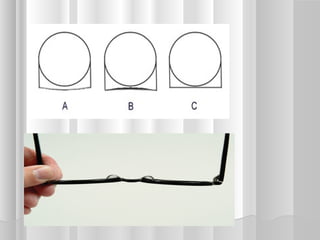
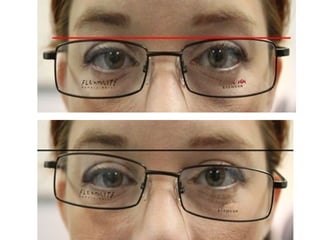
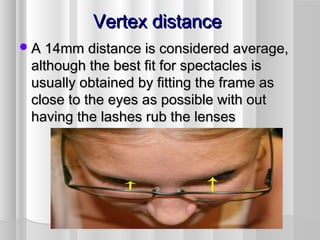
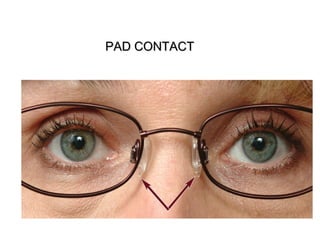
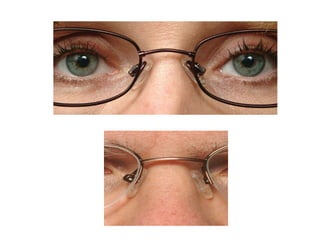
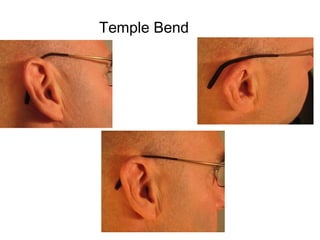
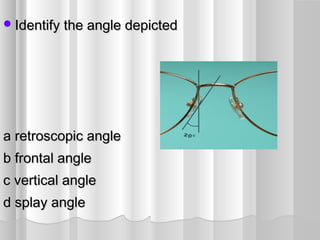
This document discusses frame adjustment and quality checking. It describes 7 off-face adjustments including x-ing, temple spread, pantoscopic angle, temple fold angle, pad angles, face form, and 4-point touch. It also discusses 7 on-face adjustments including horizontal alignment, vertex distance, frame height, segment height, temple bend, pad contact, and skin/lash clearance. Key details are provided about properly adjusting specific angles and alignments during the fitting process.