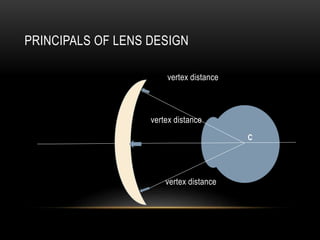
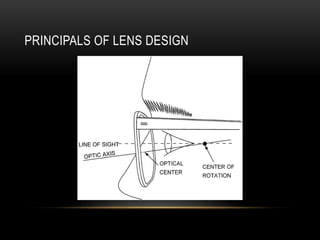
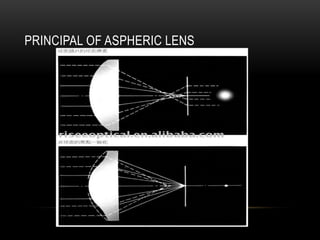
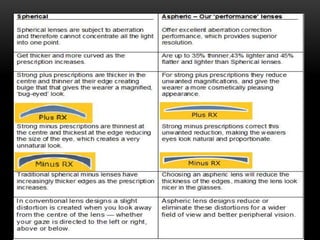
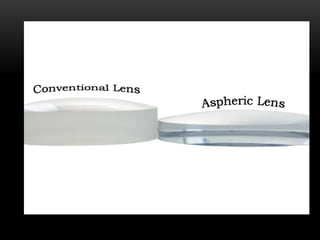
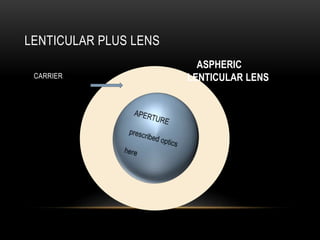
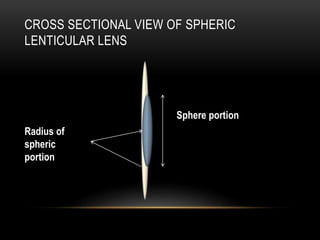
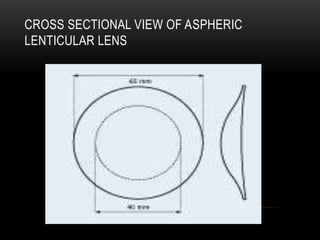
This document discusses lens design parameters and special lens designs used for high plus and high minus prescriptions. It describes key considerations in lens design like surface curvature, optical indices, element spacing, and aspheric lenses. Special lens designs discussed include lenticular lenses, multidrop lenses, and myodiscs for high prescriptions. Aspheric lenses are described as having non-uniform curvature across the surface to reduce thickness and improve cosmesis for high plus and minus prescriptions.