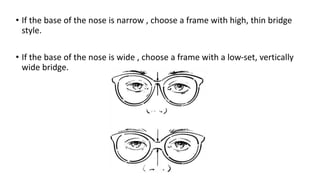
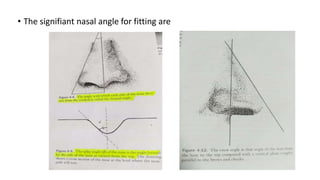
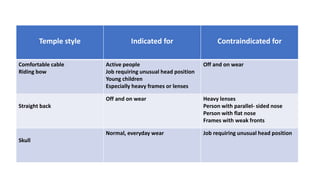
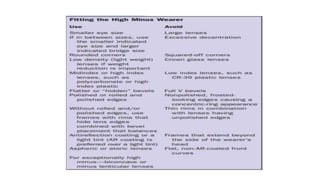
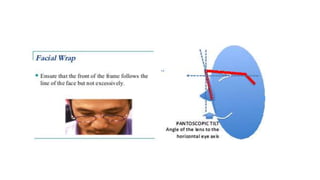
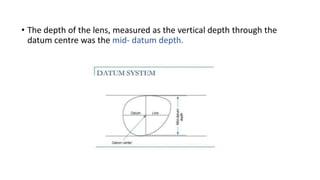
This document discusses frame selection and parameters for dispensing glasses. It describes the boxing system used to measure frame and lens sizes. Key frame measurements include eye size, bridge size, temple length, and frame center distance. Face shapes like oval, round, square and their best fitting frame styles are outlined. Frame properties that affect balance, length and nose appearance are also covered. Special considerations for children, older adults and other patient types are provided. The goals of proper frame selection are to support lenses comfortably while matching facial features.



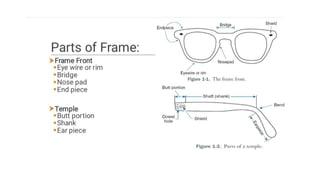



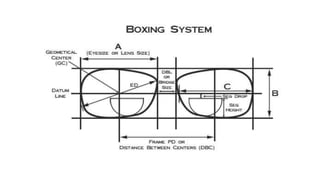


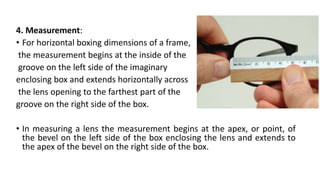

![• ‘A’ Dimension: It is the horizontal boxing width.It is the width of the
enclosing box not the width of the lens at the middle of the shape.
• ‘B’ Dimension : It is the vertical boxing length.
• ‘C’ Dimension : It is the width of the lens along the horizontal midline.
[Note: C-size is the circumference of the edged lens and is used to
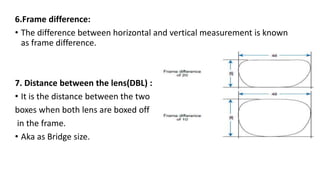
increase accuracy when duplicating an old lens size when edging.]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basicsofdispensing-230217154629-2770603a/85/Basics-of-dispensing-pptx-14-320.jpg)