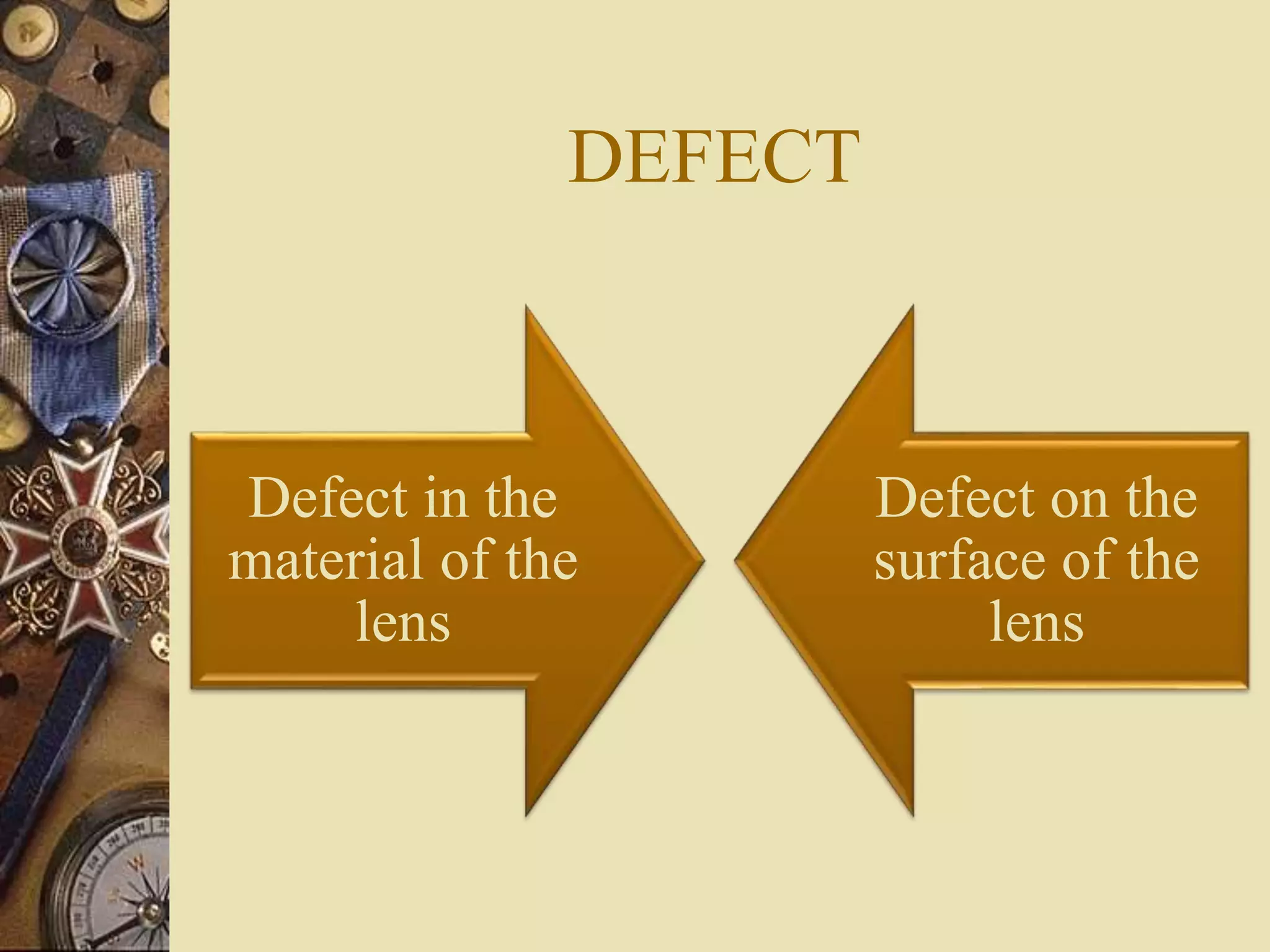
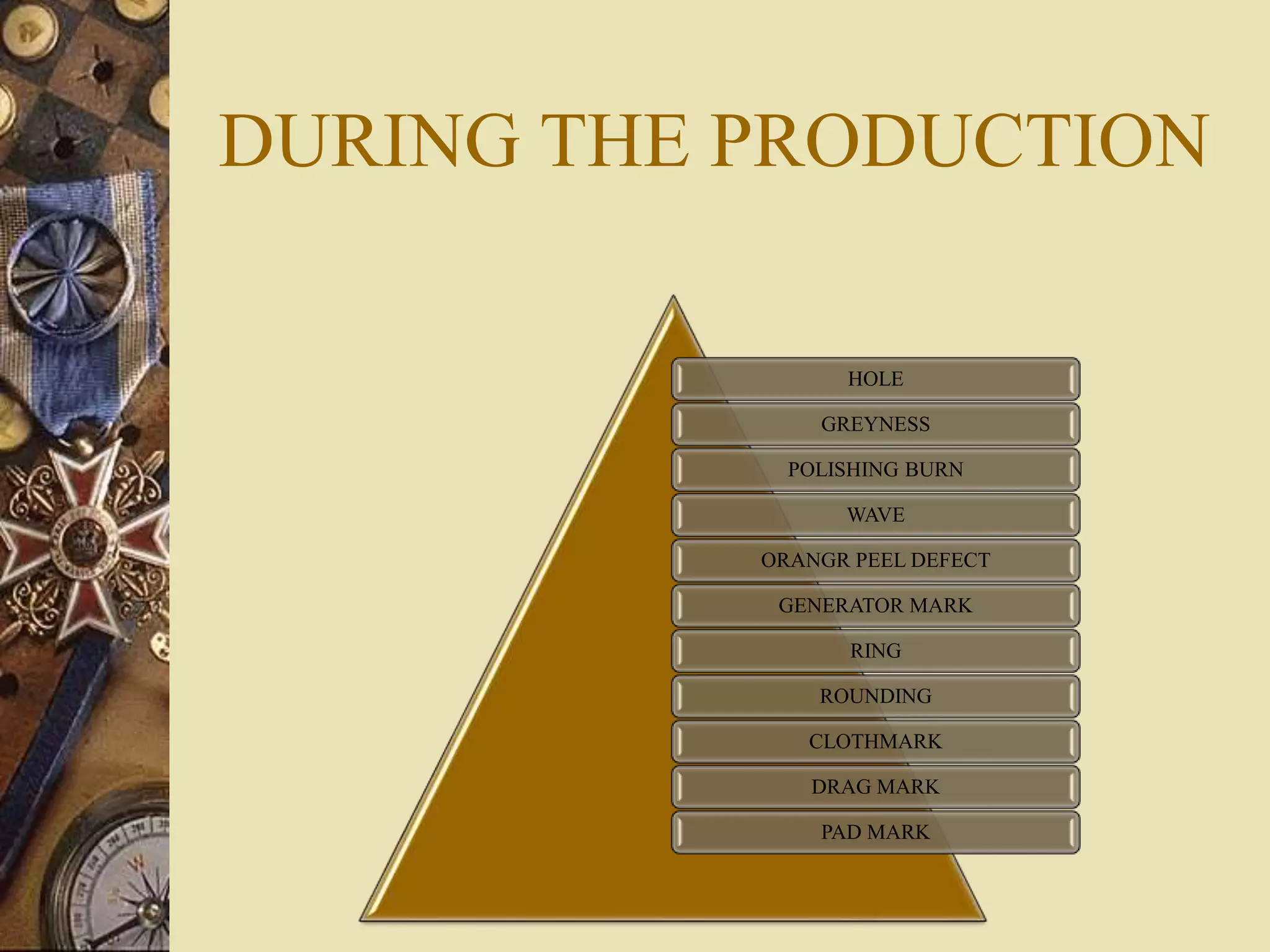
This document summarizes various types of defects that can occur in ophthalmic lenses. It categorizes defects as occurring either in the material of the lens, on the surface of the lens, or from maltreatment of the finished surface. Defects in the material include bubbles, feathers, veins, coloration and strain. Surface defects from production include holes, greyness, polishing burns, waves, rings and generator marks. Maltreatment can cause scratches, chips, bruises and other abuse marks. The document provides detailed descriptions and examples of each type of defect.











































![NO TRANSMISSION
[T]
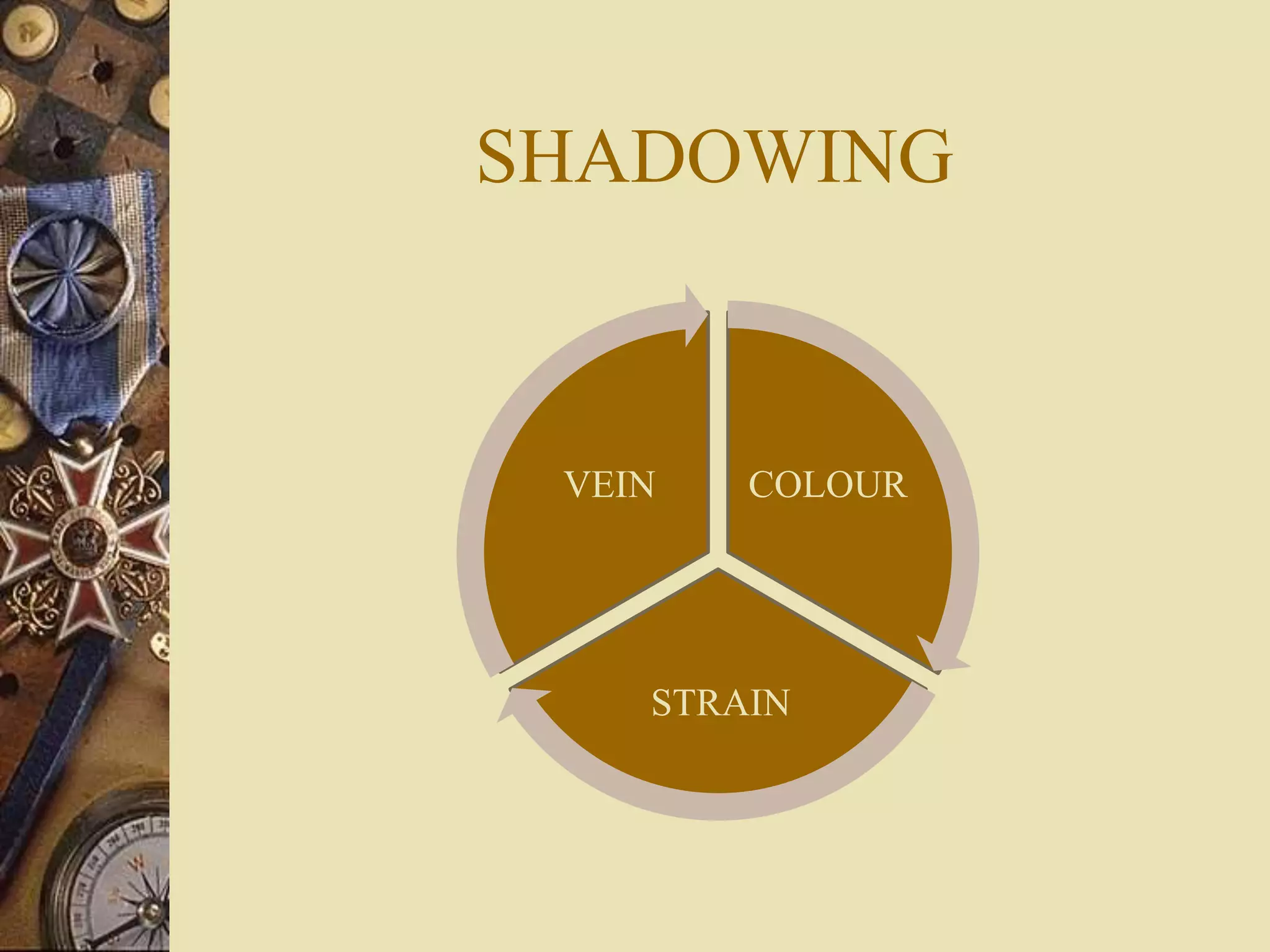
SHADOWING
[S]
REFLECTION
[R]
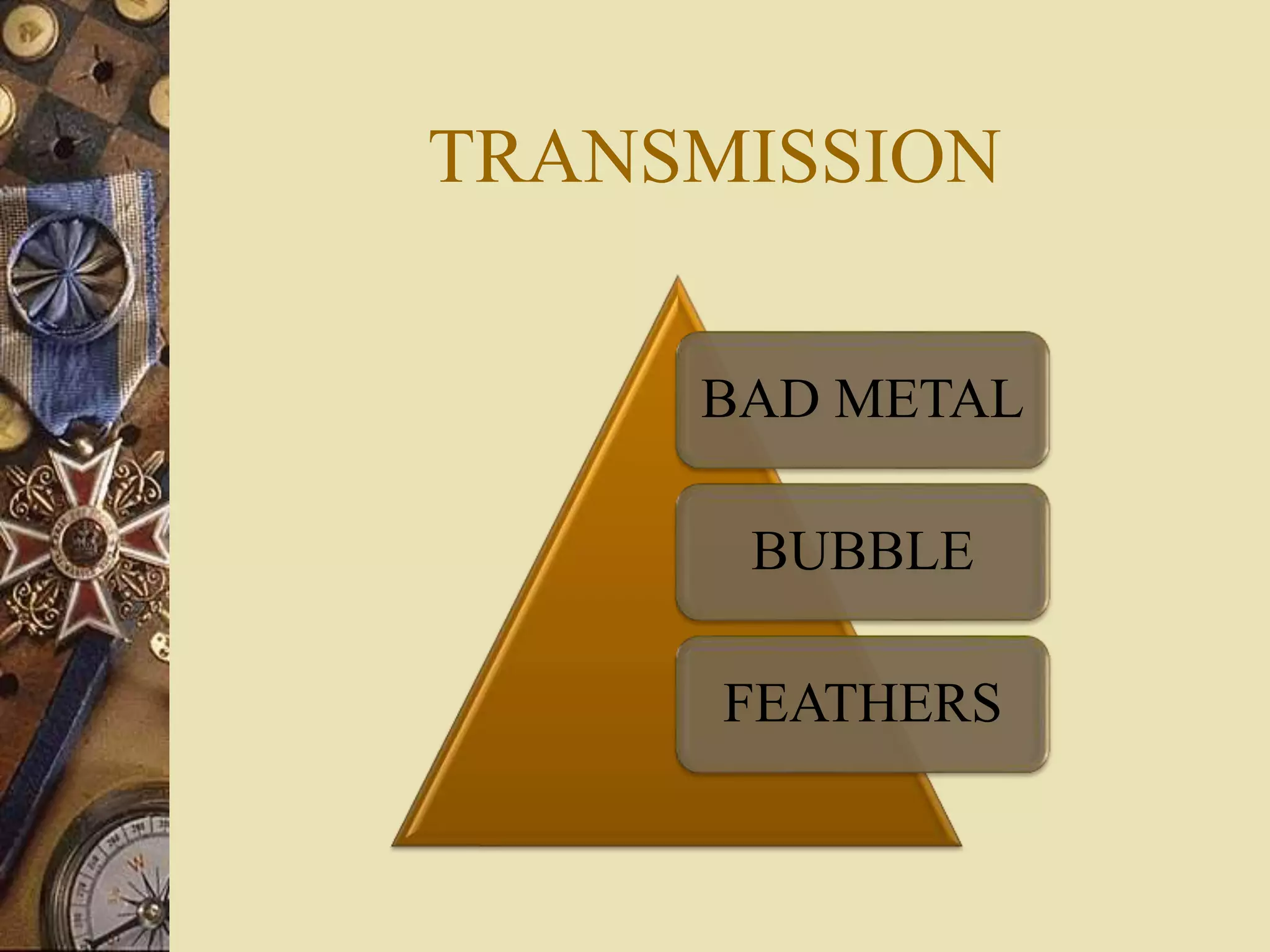
1. BAD METAL VEINS TARNISH
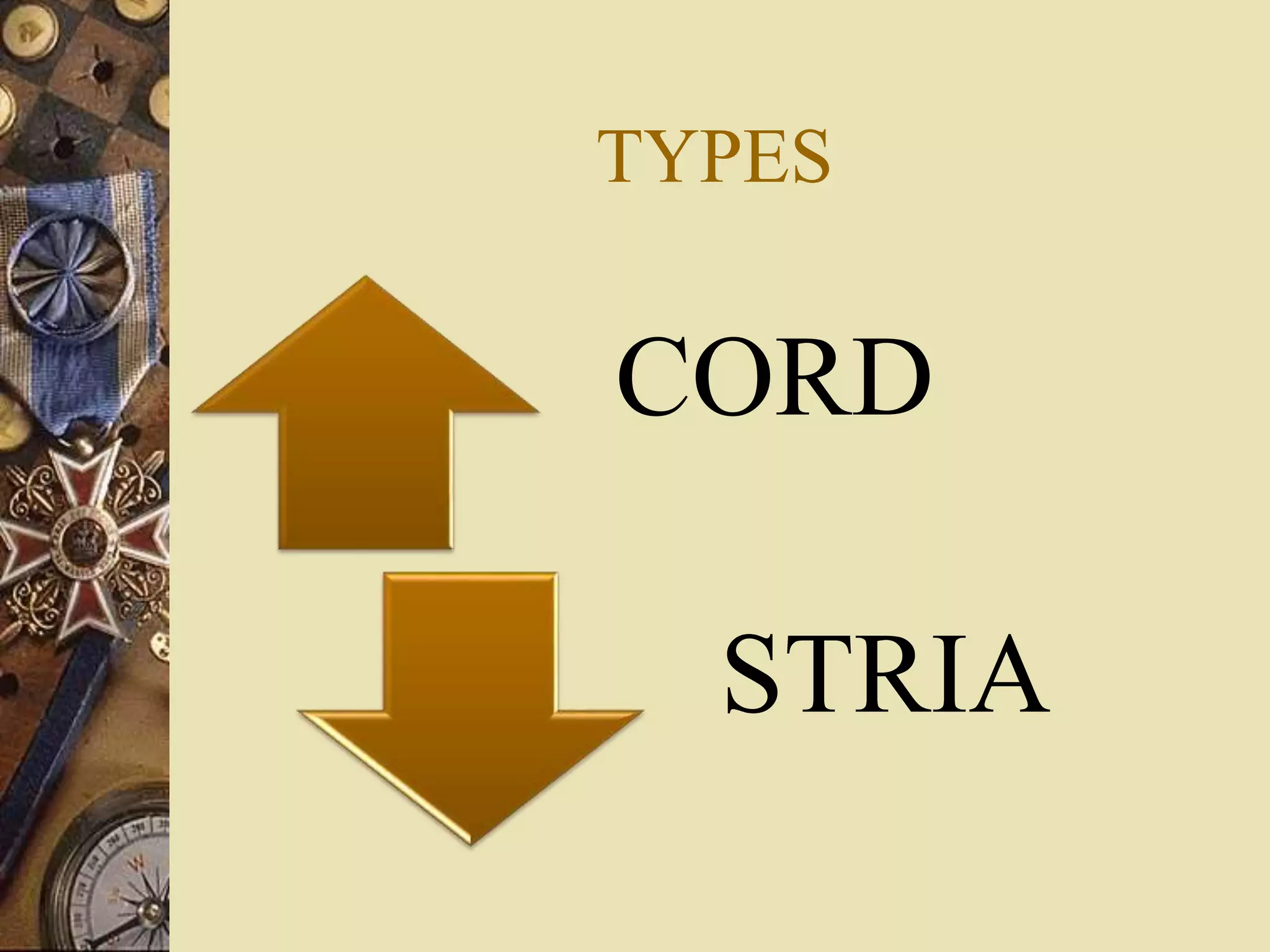
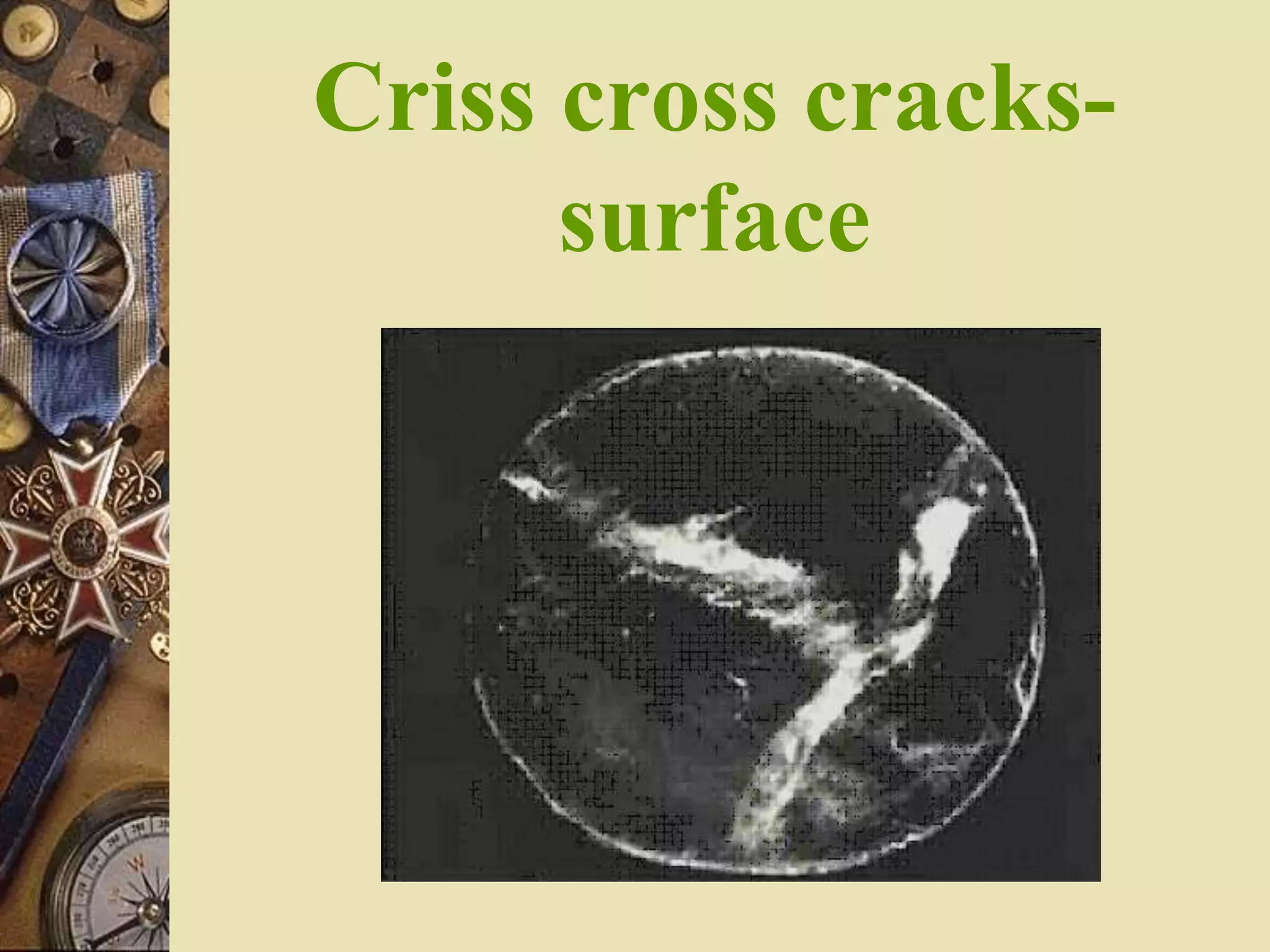
2. BUBBLES CORD CRAZING
3. FEATHERS STRIA HOLE
4. POLISHING
BURN
CLOTH
MARKS
GREYNESS
5. WAVES WAVES SCRATCH
6. RINGS RINGS DIG
7. DRAG
MARKS
SLEEK
8. ORANGE
PEAL
BRUISE
CHECK
9. ROUNDING CHIPS
10. ABUSE
MARKS](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fault-140509045917-phpapp01/75/Fault-54-2048.jpg)
