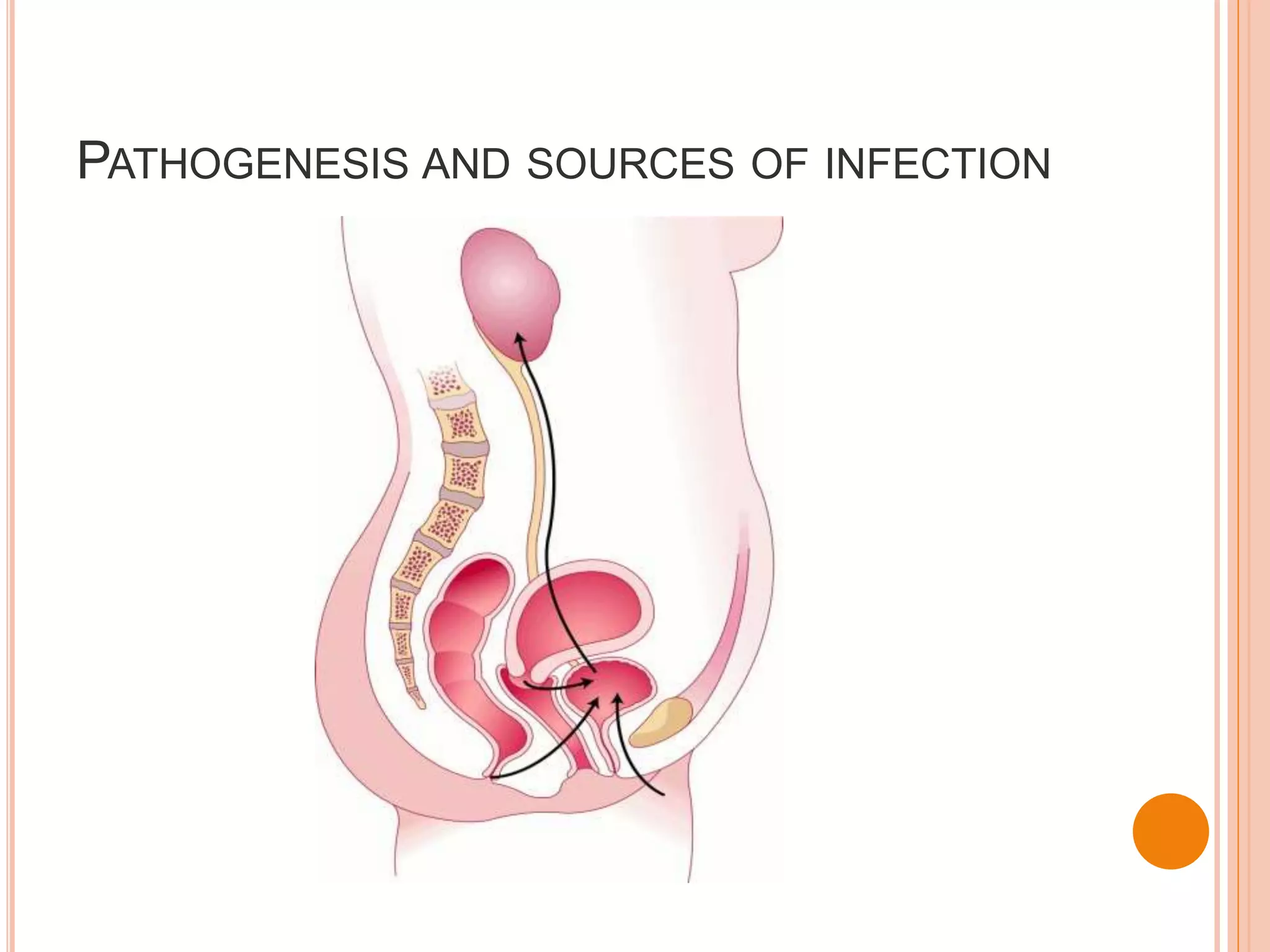
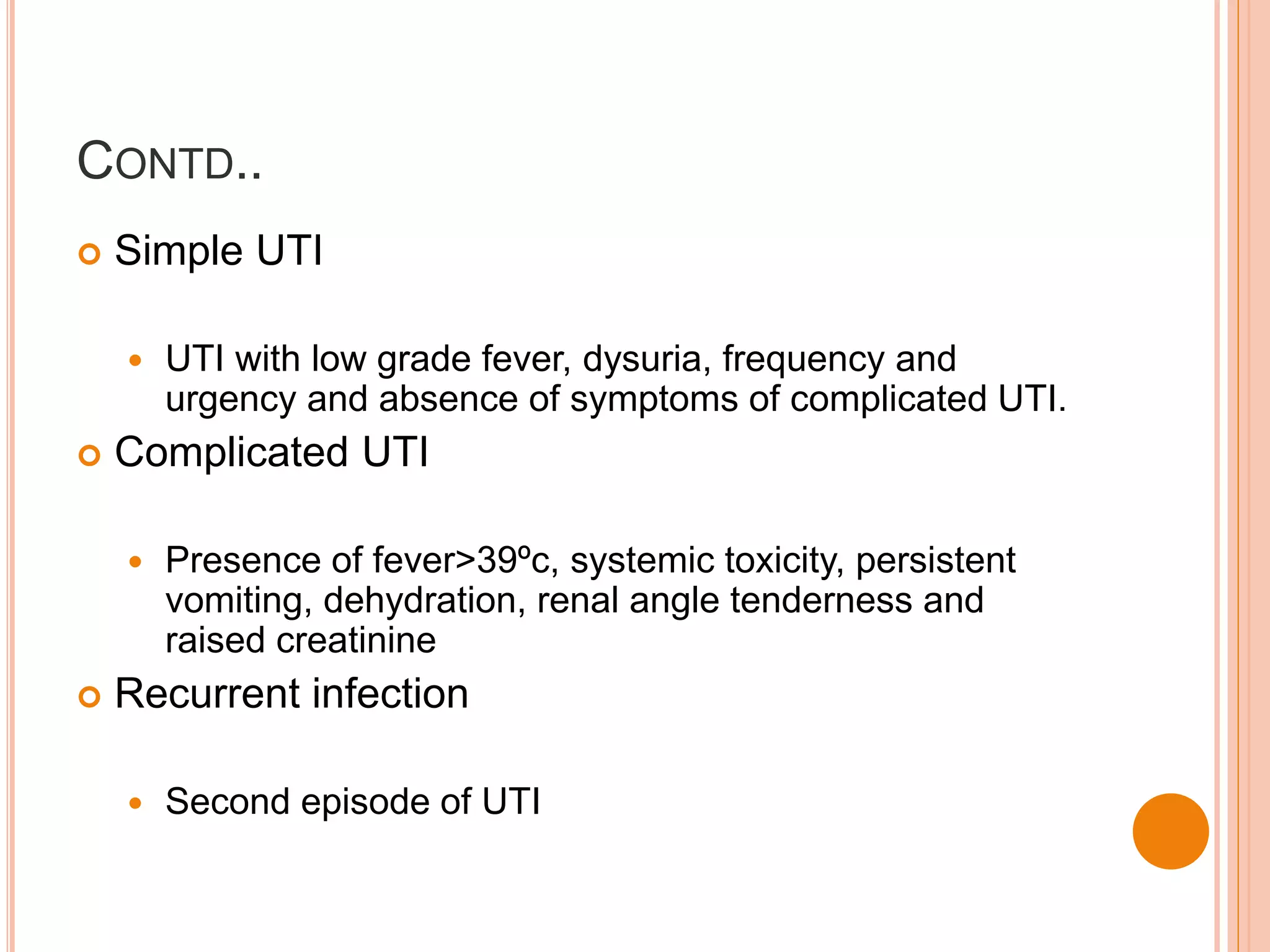
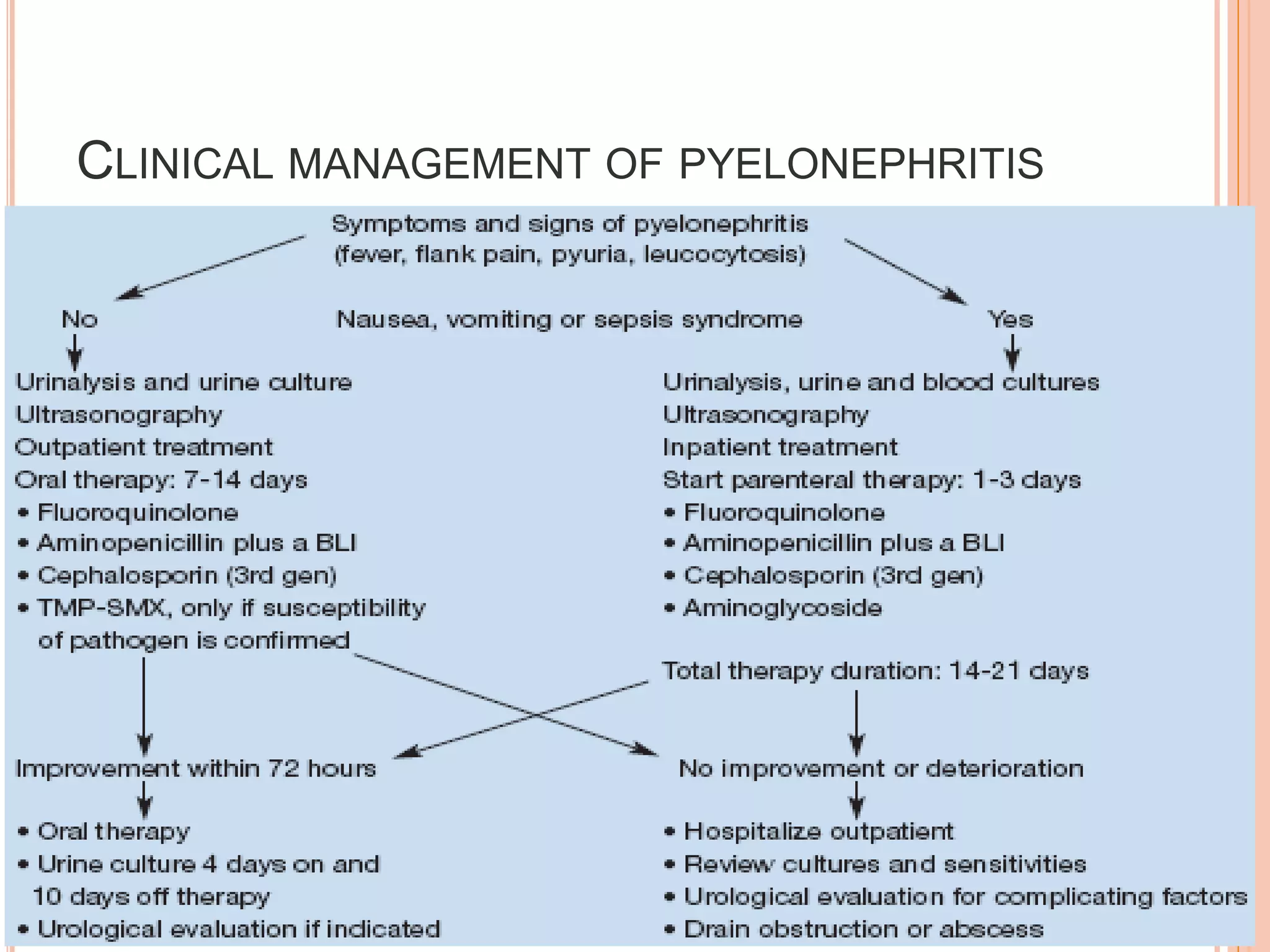
This document discusses the pharmacotherapy of urinary tract infections and provides information on chloramphenicol and tetracyclines. It covers the epidemiology, pathogenesis, definitions, and drug therapy for UTIs. Common causative organisms are E. coli and other gram-negative bacteria. Drug choices depend on the site and severity of infection. For uncomplicated lower UTIs, short 3-day courses of antibiotics like TMP-SMX are often used. More severe infections involving the kidneys may require parenteral antibiotics in hospital. The document also discusses UTI in specific groups like children, pregnant women, and those with structural abnormalities.