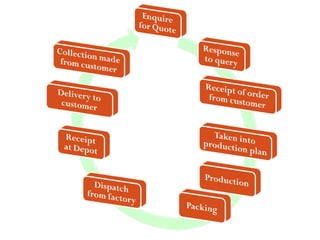
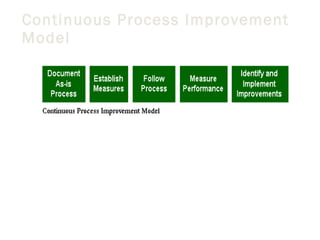
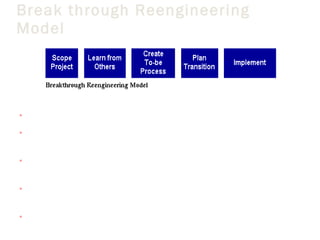
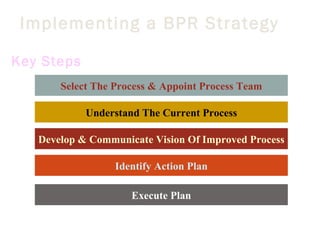
This document outlines a 5-step methodology for implementing business process reengineering (BPR). The steps are: 1) Developing a process vision and objectives, 2) Defining the processes to reengineer, 3) Understanding and measuring existing processes, 4) Identifying IT levers, and 5) Designing and building a prototype. The methodology focuses on understanding current processes, creating a vision for improved processes, identifying how IT can help, and testing changes through prototypes before full implementation.