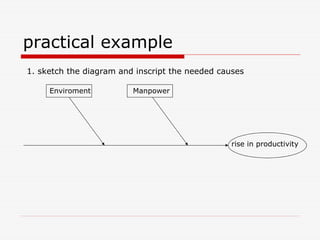
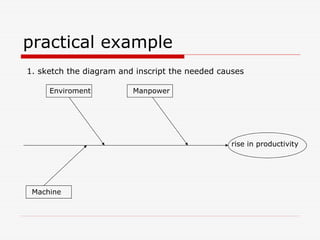
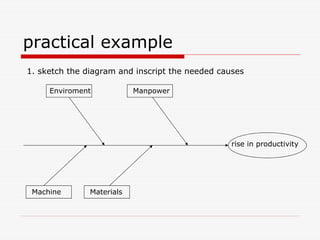
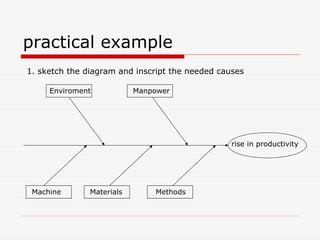
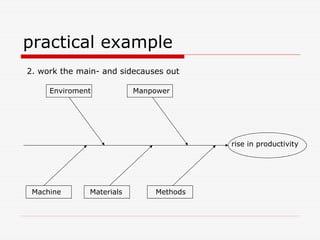
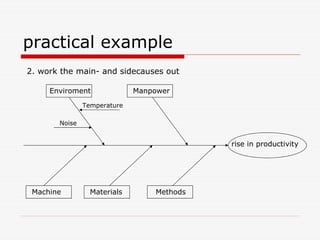
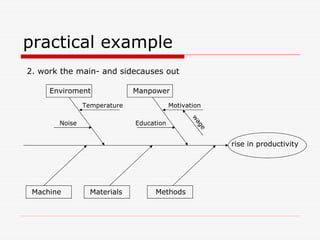
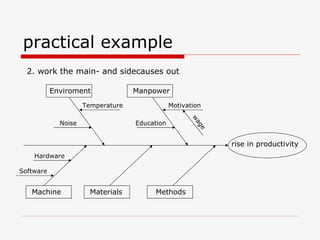
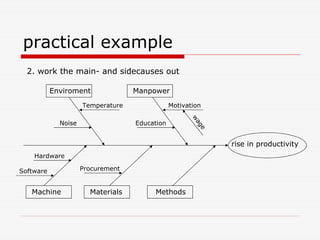
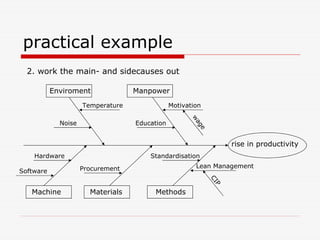
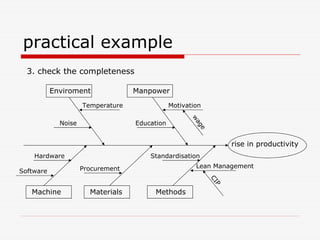
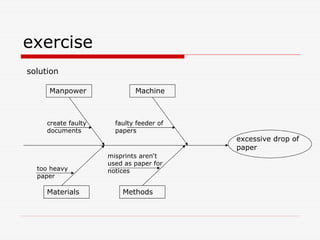
The document describes Kaoru Ishikawa and the Ishikawa diagram, also known as a fishbone diagram or cause-and-effect diagram. It was developed by Ishikawa to help teams visualize and analyze the potential causes of a particular problem or effect. The diagram structures causes into main categories, typically including methods, machines, materials, measurements, management, manpower, and environment. It then maps potential causes in each category that could contribute to the problem or effect. The document provides examples of using the diagram to analyze the causes of increased productivity in a company and excessive paper drop in a printing process.