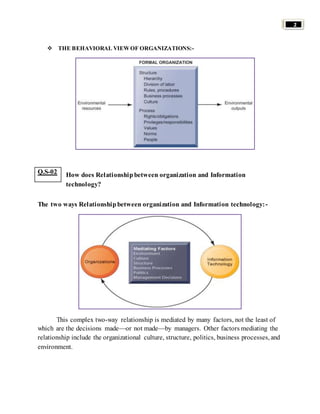
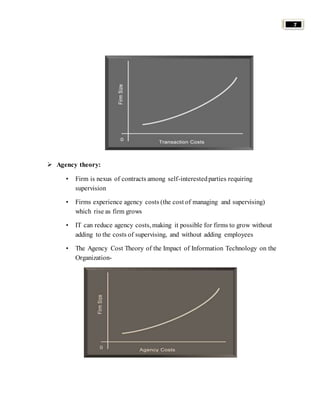
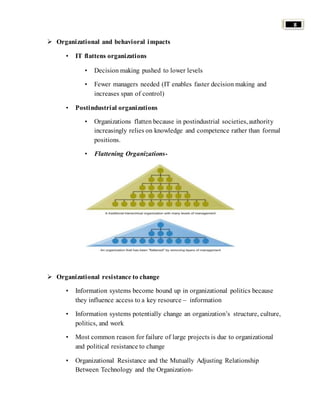
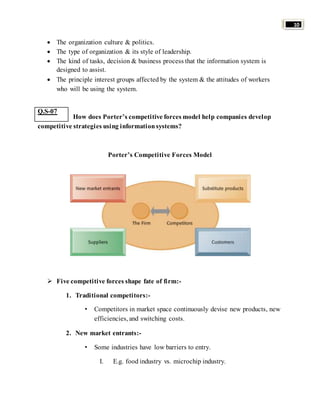
Organizations use information systems to gain competitive advantages in several ways:
1) Information systems can help lower costs through efficiencies like inventory management (e.g. Walmart) or reduce transaction costs (e.g. Dell's customization).
2) Systems can enable product differentiation, like Google's continuous innovations or Apple's customized iPhone.
3) Niche strategies using systems include Hilton Hotels' customer profiling to better serve specific markets.
4) Strengthening relationships is another approach, like Chrysler's supplier integration system.