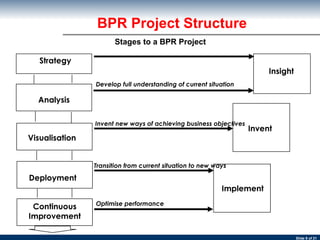
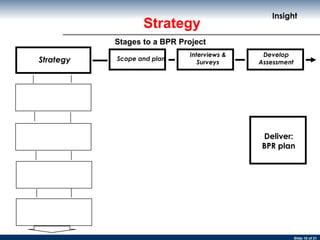
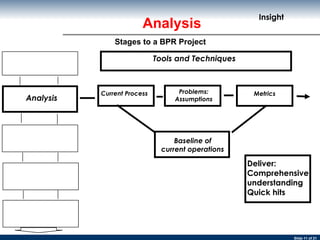
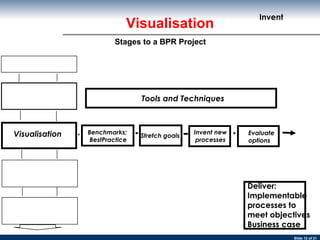
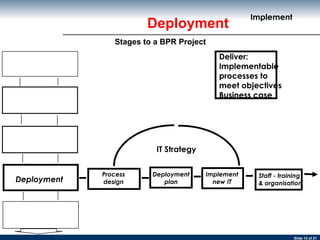
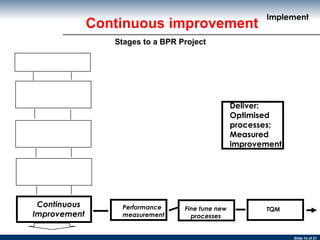
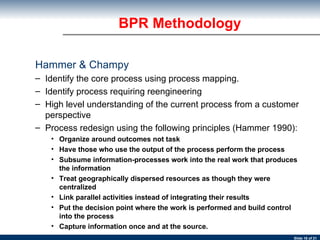
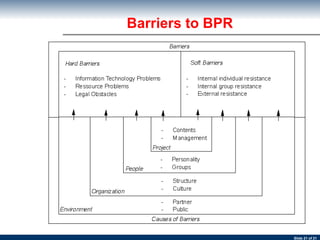
The document discusses business process re-engineering and provides information on various aspects of process re-design and improvement such as the two approaches to business process re-engineering, defining processes, guidelines for selecting processes, visualization, process redesign issues, BPR project structure and methodology, and barriers to BPR.