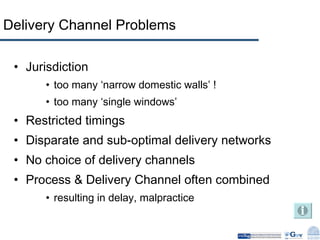
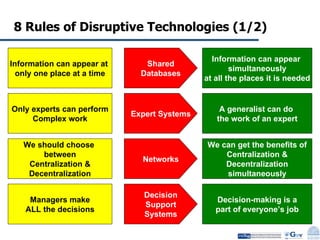
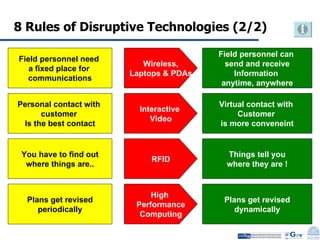
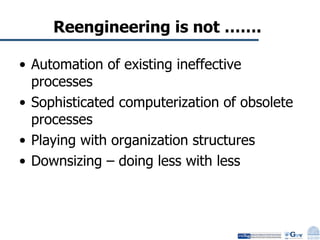
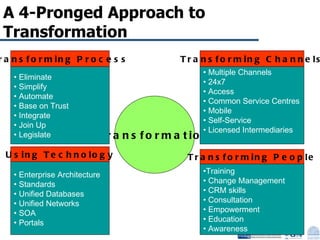
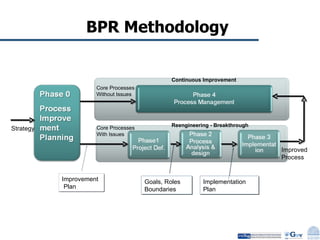
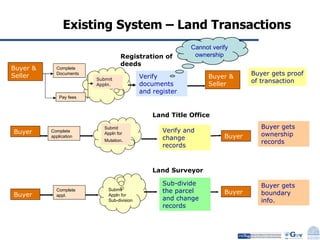
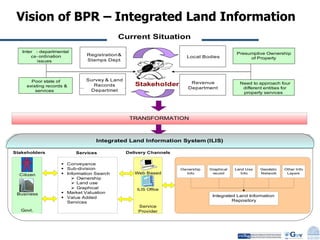
Business Process Re-engineering (BPR) is the fundamental rethinking and radical redesign of business processes to achieve significant improvements in performance metrics such as cost, quality, service, and speed. The document outlines the need for BPR in modern governance, highlighting its principles, methodologies, challenges, and critical success factors, while providing examples of BPR in action, like land records management in India. A structured approach, top management commitment, and effective change management are essential for BPR's success.


























![Thank You [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bpr-110807054223-phpapp02/85/Business-Process-Reengineering-36-320.jpg)