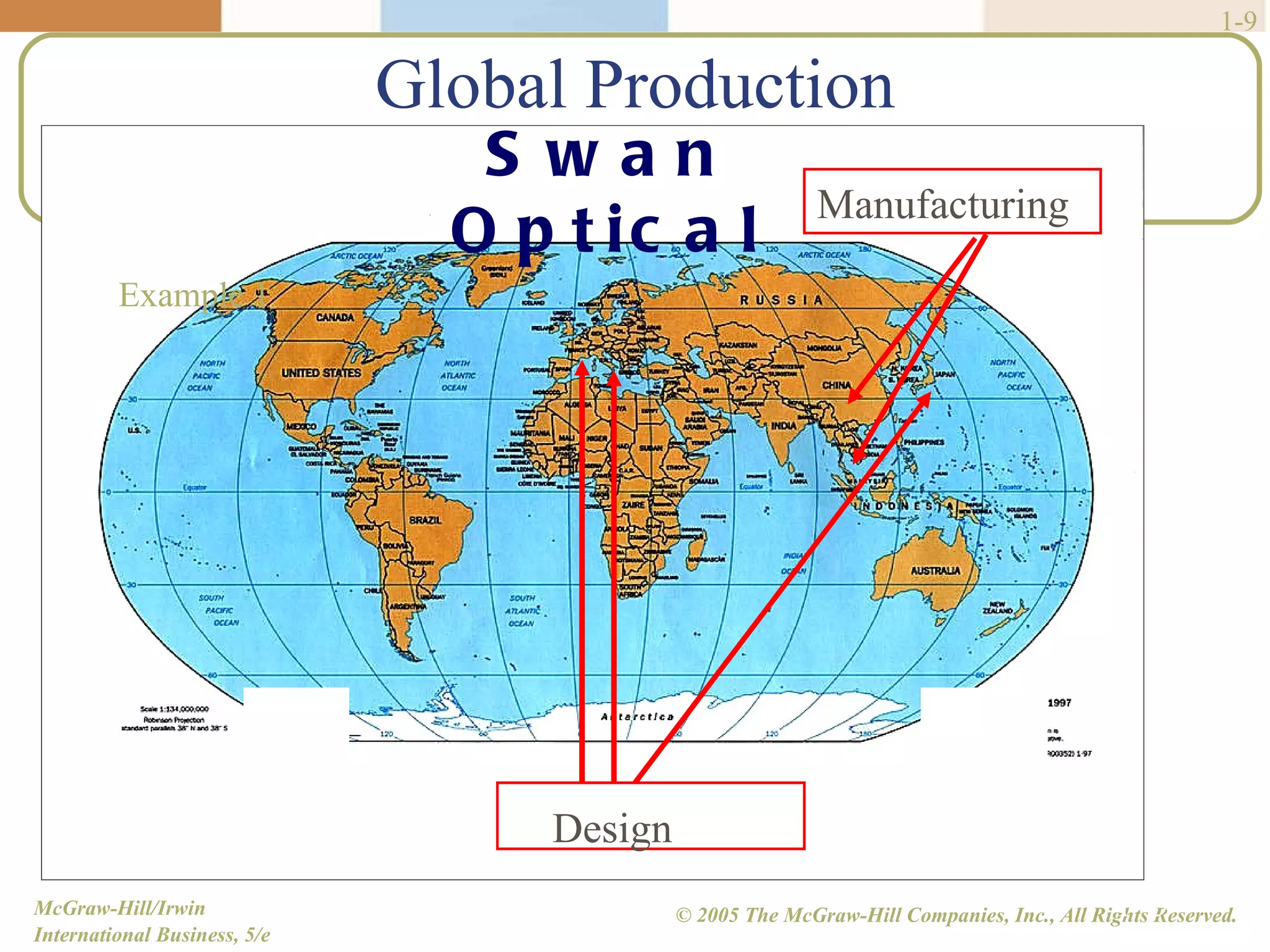
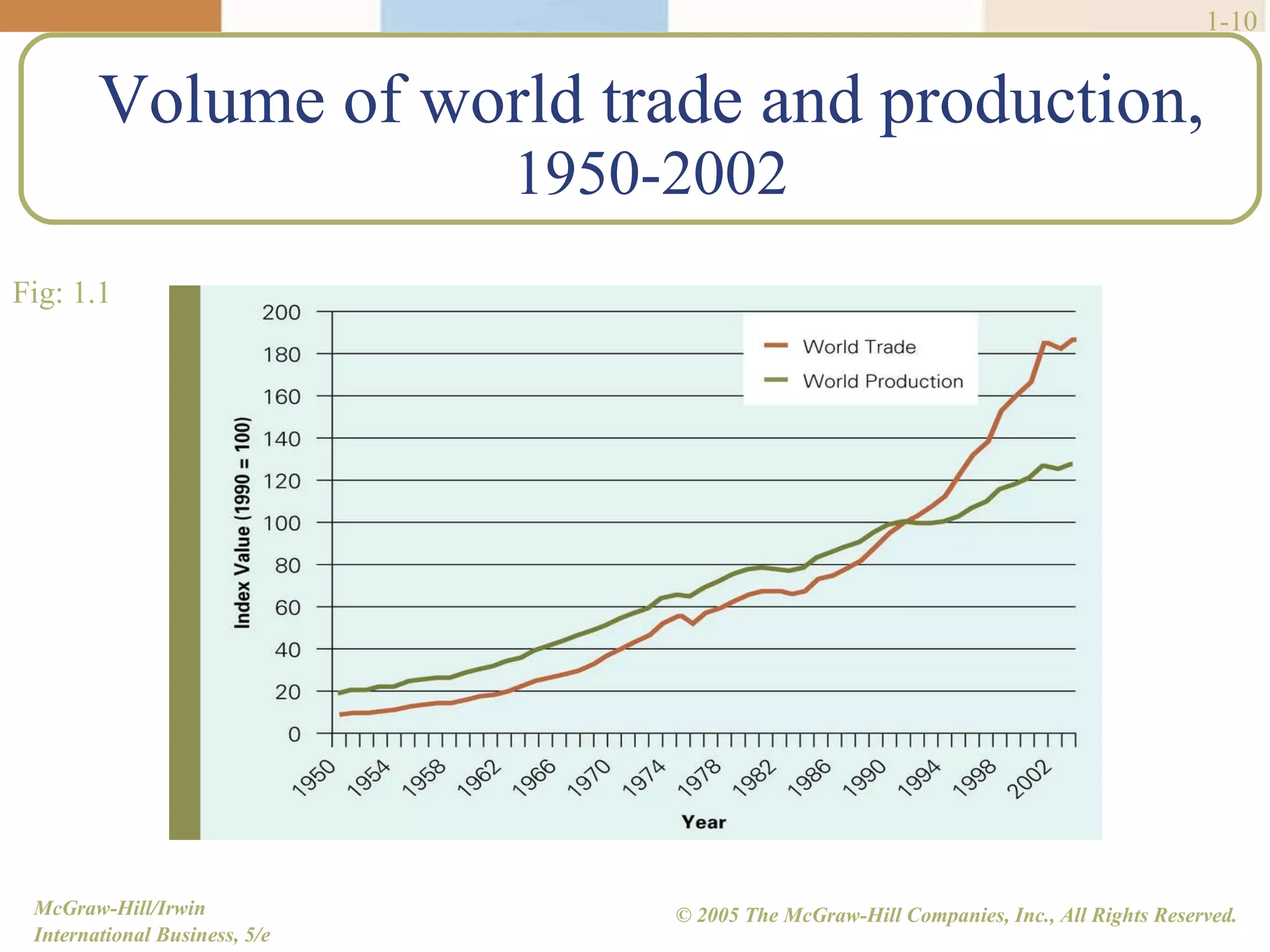
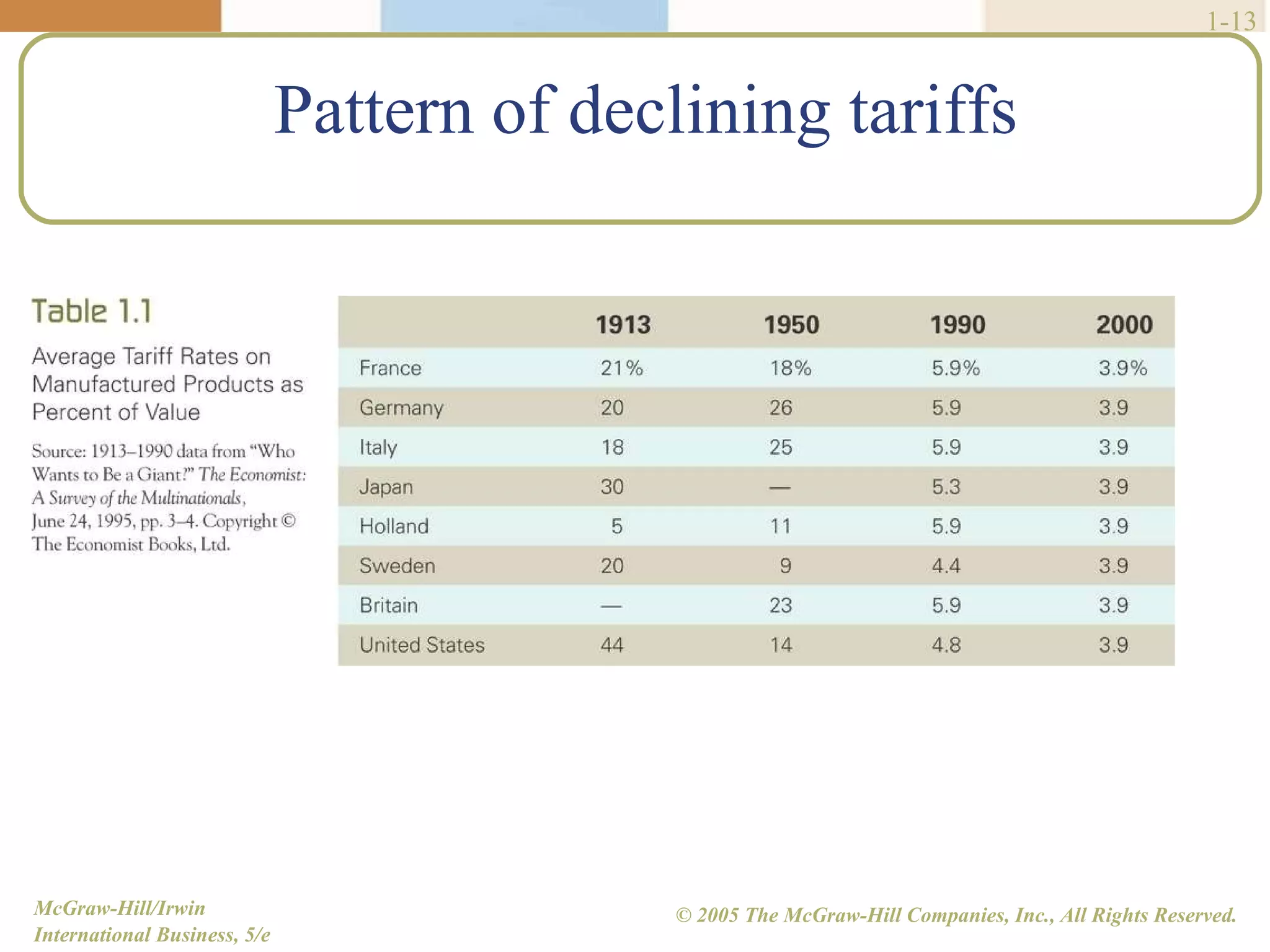
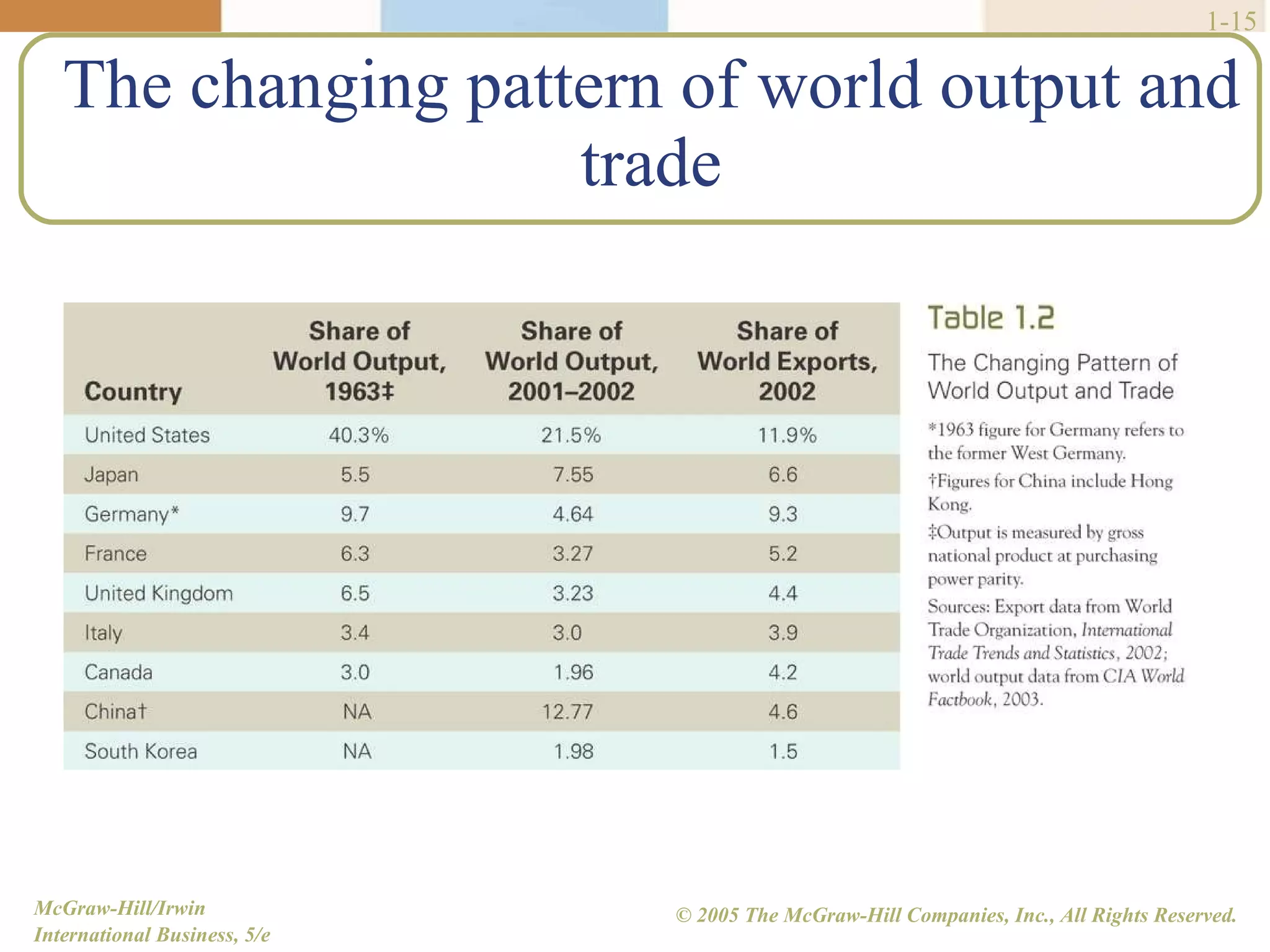
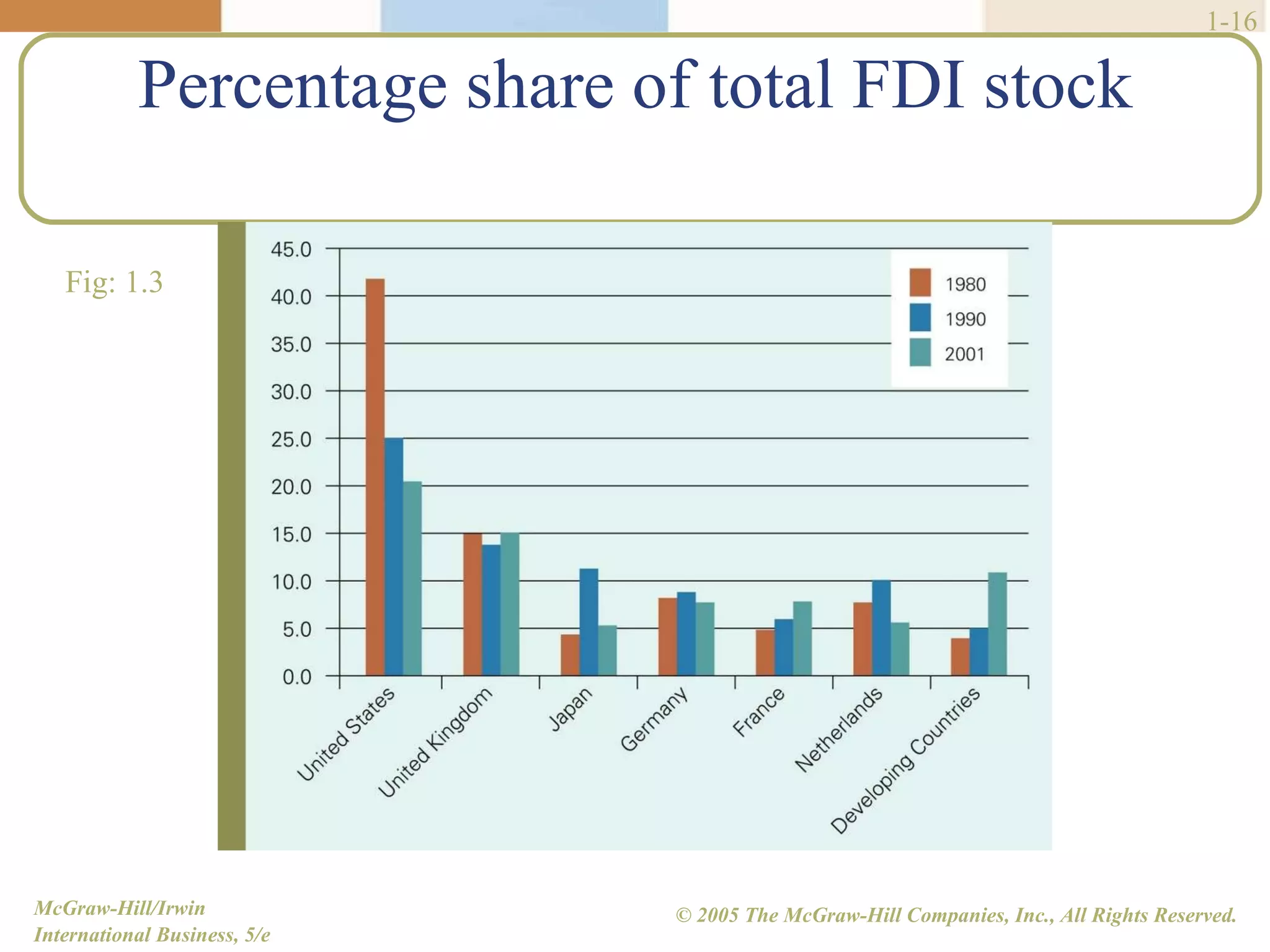
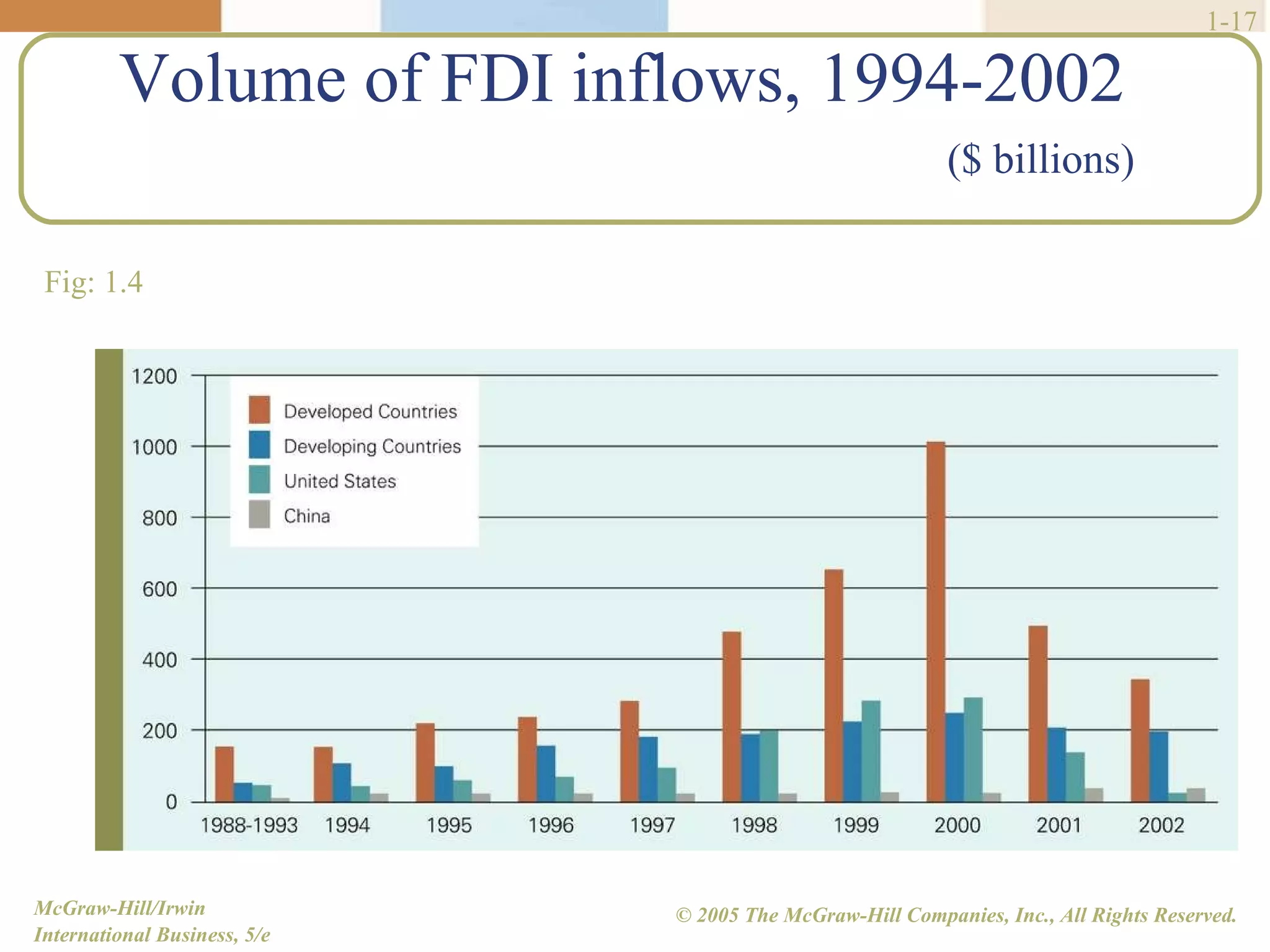
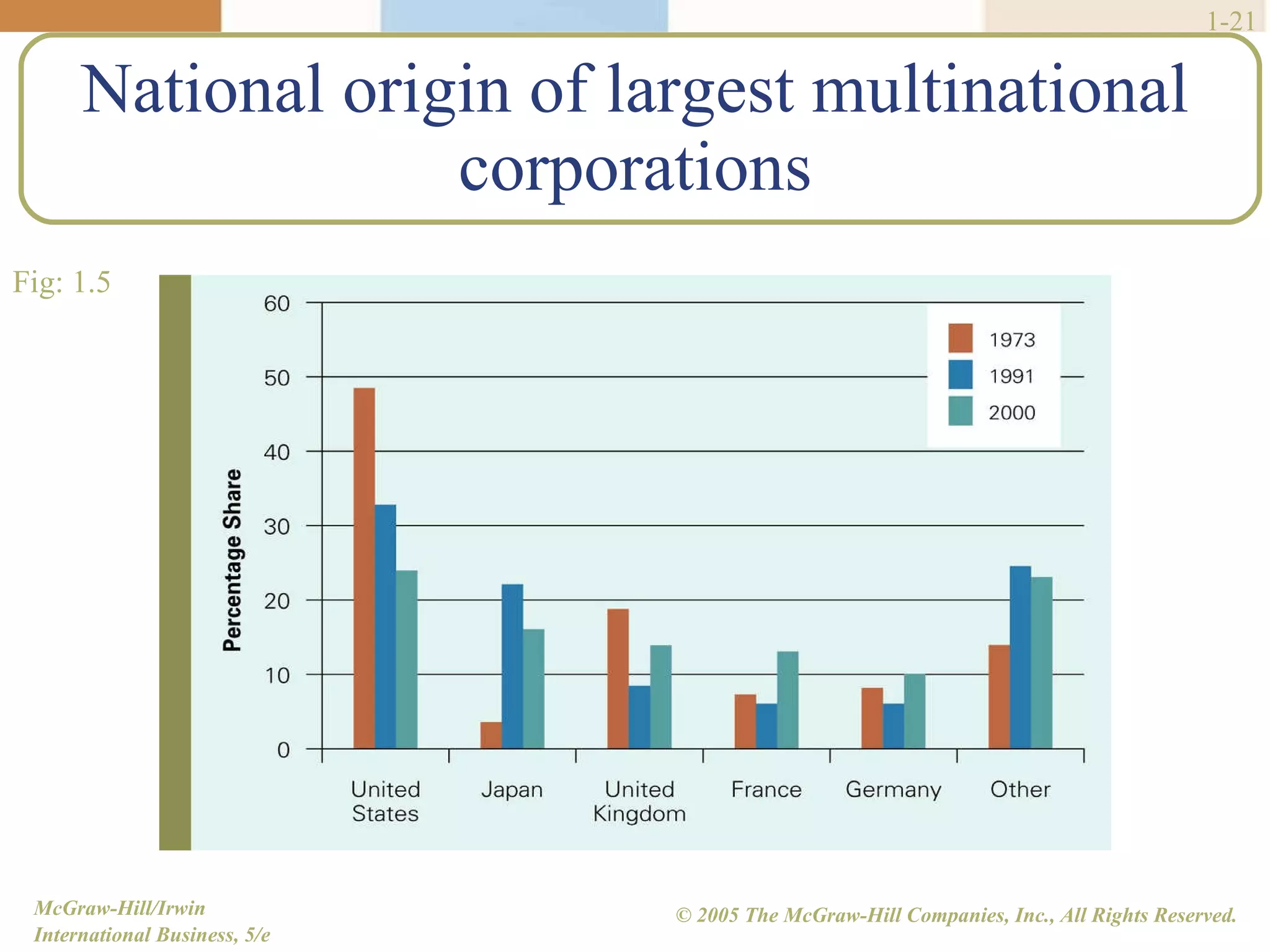
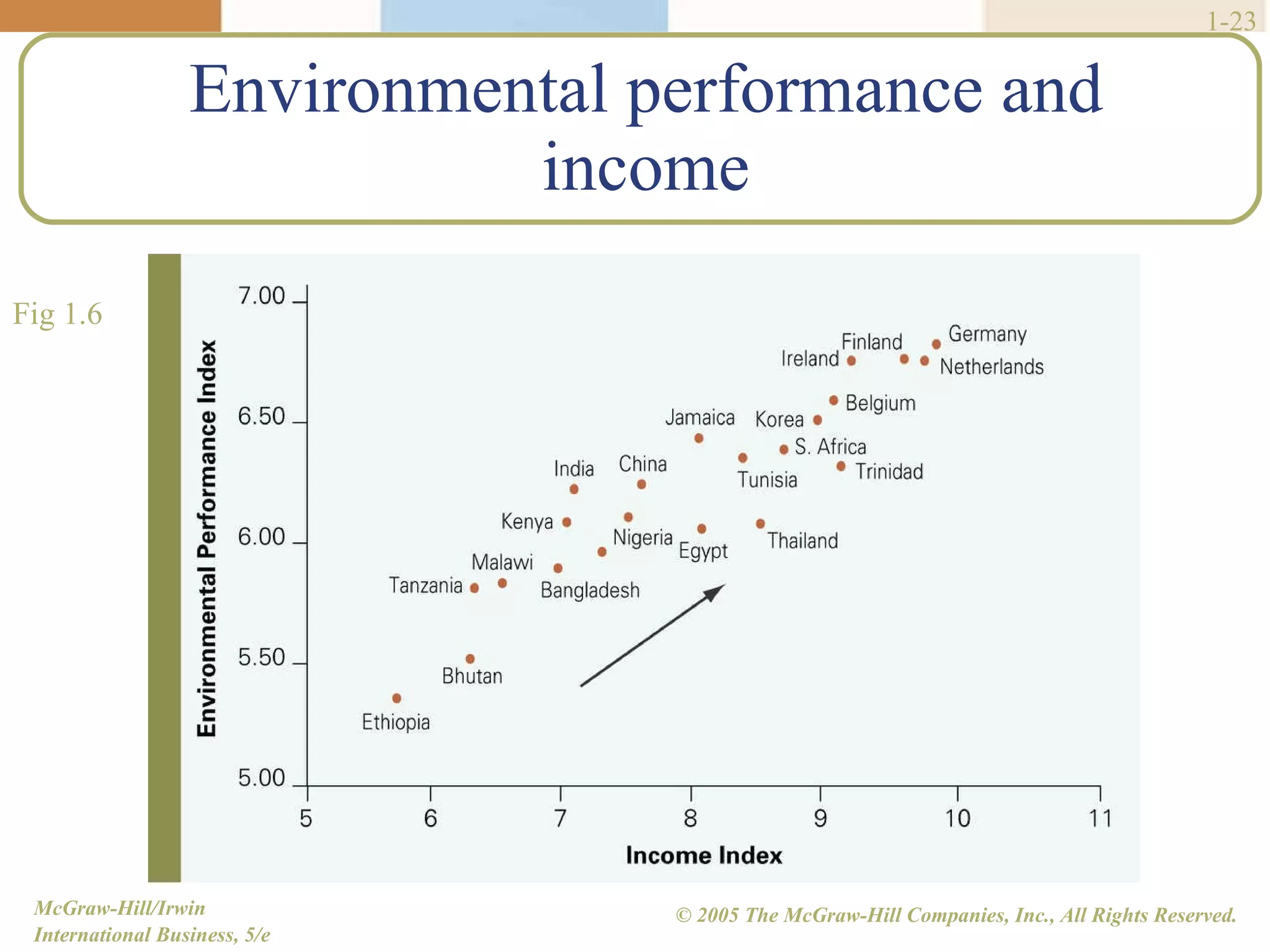
Walmart began its global expansion in 1991 with its entry into Mexico in response to market saturation in the US. It has since opened over 4500 stores internationally and adopted a localization strategy after initial trials. Walmart faces competition from other global retailers but has a first mover advantage in some markets. Globalization refers to the increasing integration and interdependence of world economies through both the globalization of markets and production. While markets and production have become more global, differences still exist between countries that require customized strategies.