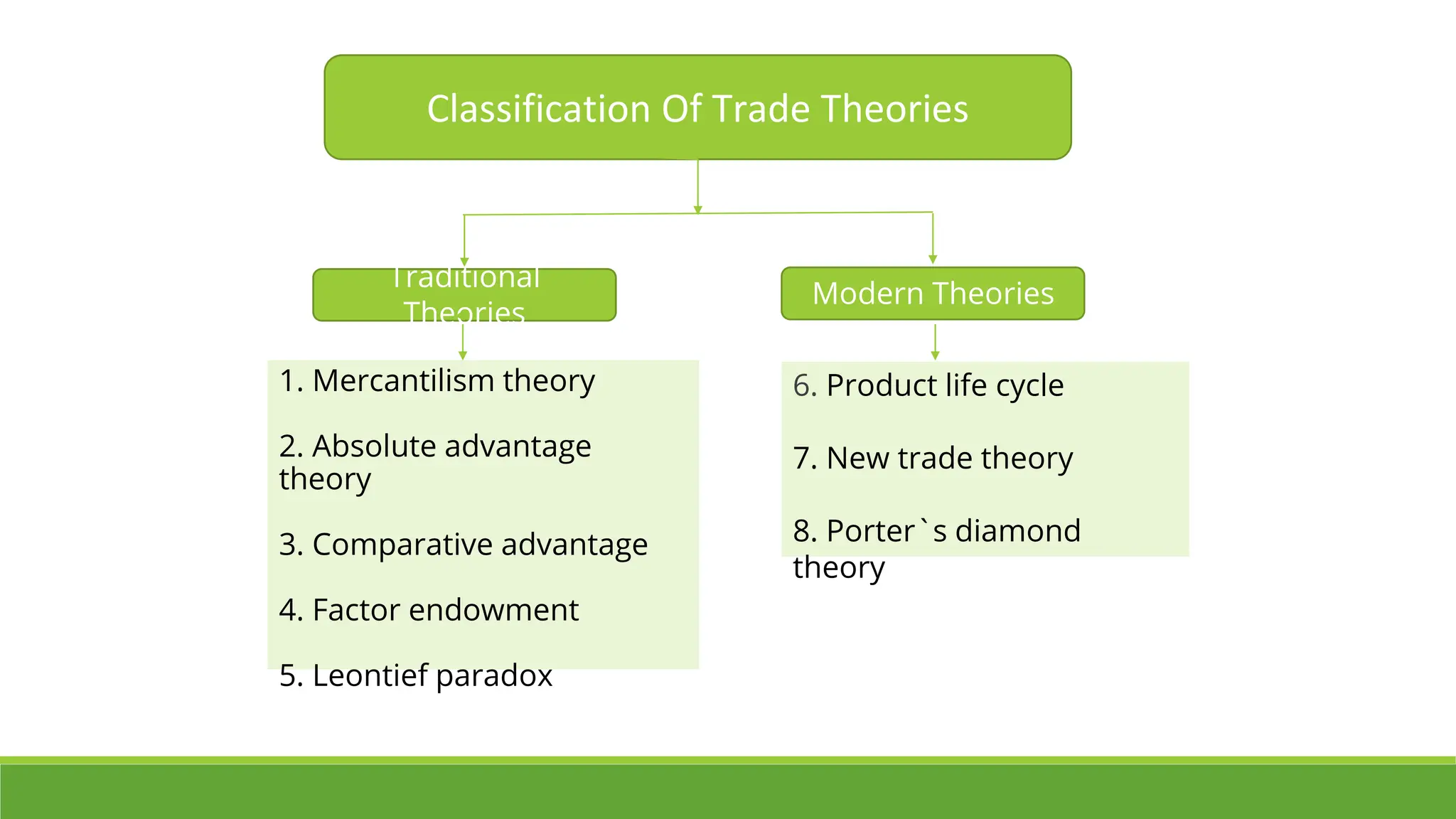
Trade theories provide explanations for how and why international trade occurs. There are traditional and modern trade theories. Traditional theories include mercantilism, absolute advantage, and comparative advantage. Mercantilism focused on accumulating gold by promoting exports and limiting imports. Absolute advantage refers to when a country can produce a good more efficiently. Comparative advantage expanded on this by comparing production efficiencies between two goods. Modern theories include factor endowments, product life cycles, new trade, and Porter's diamond model. Factor endowments ties trade to a country's abundant production factors. Product life cycles track a good through stages from introduction to decline. New trade incorporates economies of scale and product differentiation. Porter's diamond model identifies national factors that can