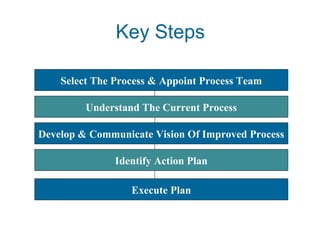
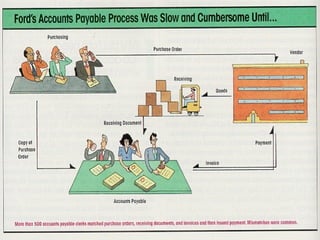
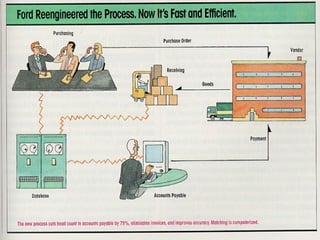
This document provides an overview of business process reengineering (BPR). It discusses BPR as fundamentally rethinking and redesigning processes to dramatically improve performance metrics like cost, quality and speed. Six key principles of BPR are outlined, along with the typical steps of selecting processes and teams, understanding the current process, developing a new vision, identifying an action plan, and executing that plan. Phases of a BPR project and examples of organizations that have implemented BPR are also summarized.