Embed presentation
Download as PDF, PPTX

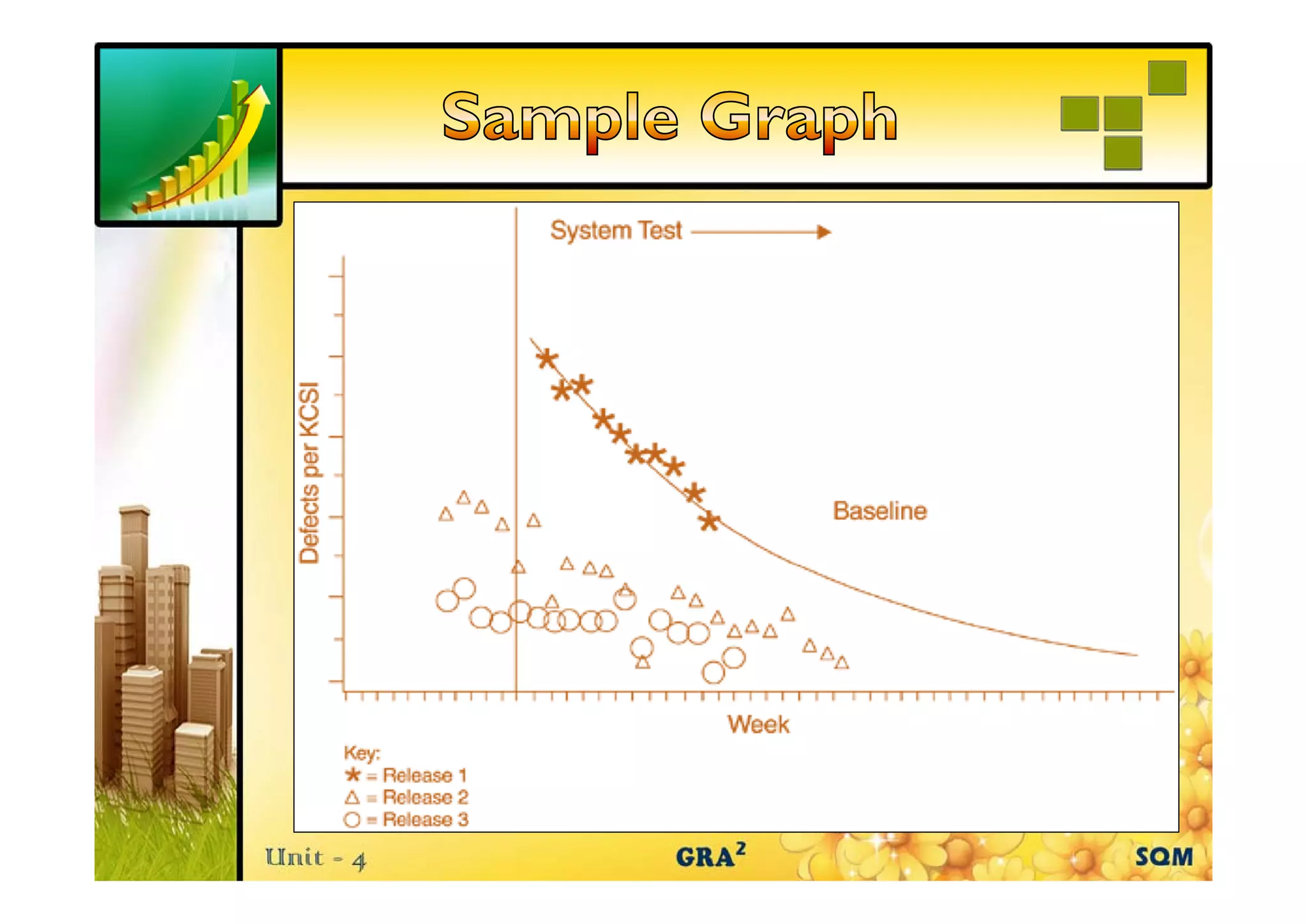
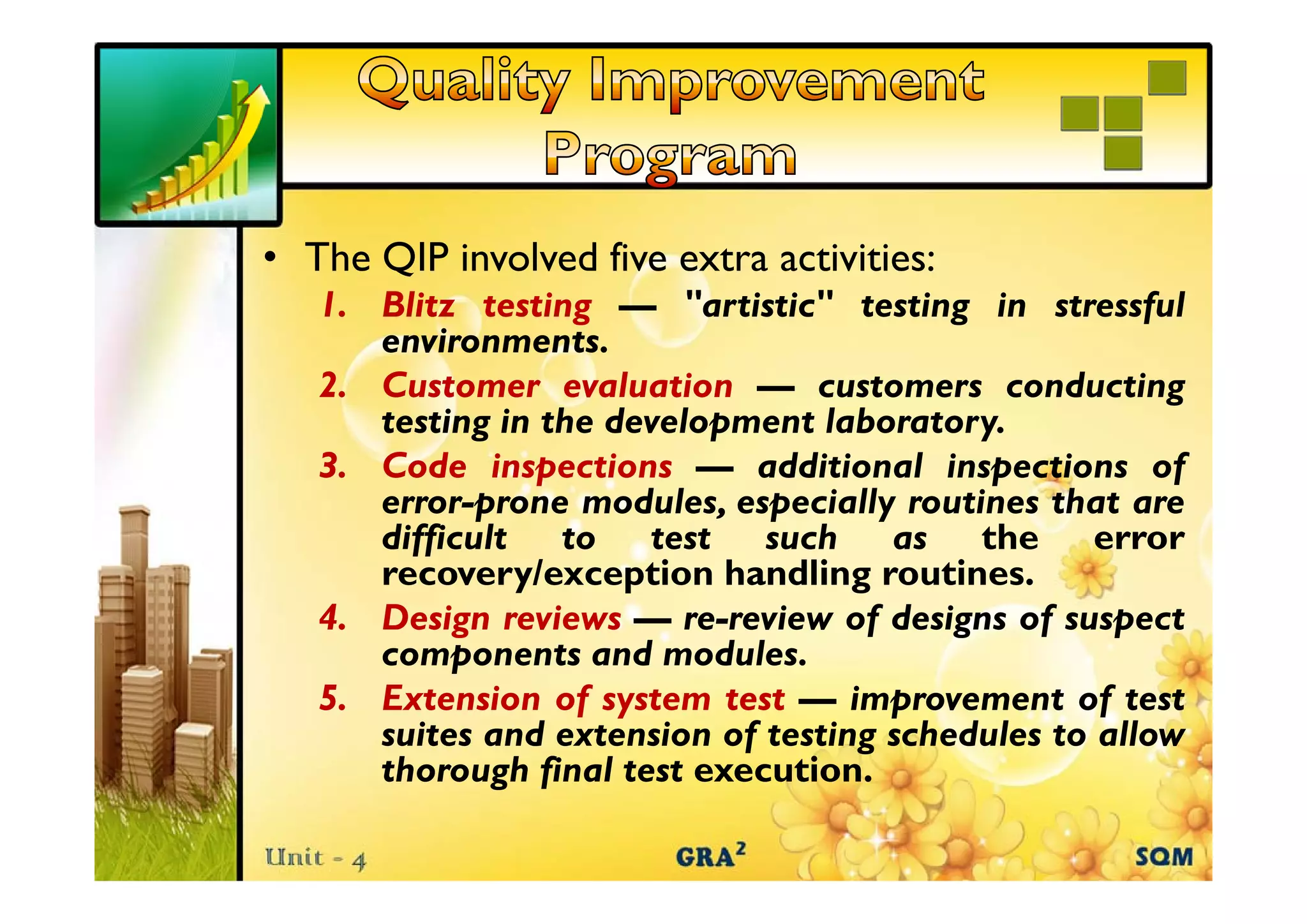


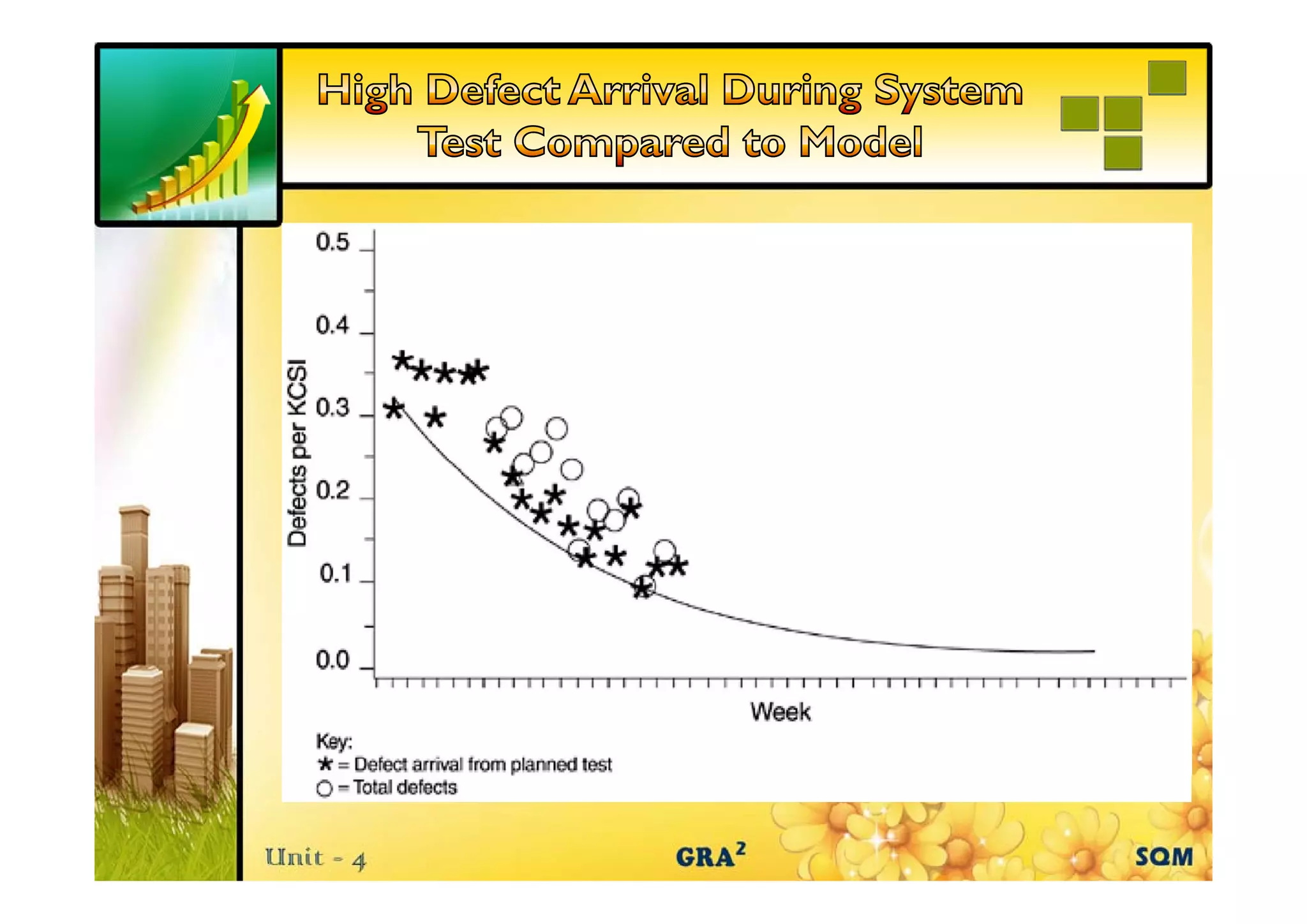

The document discusses the role of reliability growth models in software quality management, highlighting their utility in assessing and improving product quality during development. It outlines five key activities involved in a Quality Improvement Process (QIP), including blitz testing and customer evaluations, which delayed the product shipment by one month but ultimately led to the identification and removal of over 250 field defects. Consequently, the overall field quality of the product showed significant improvement over the years.









