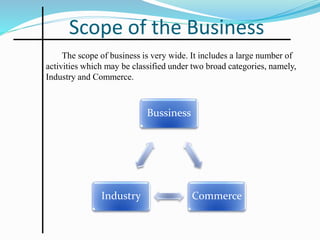
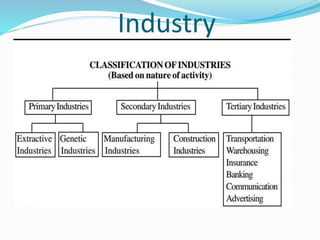
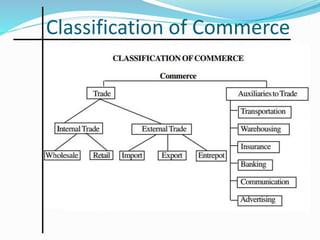
The document outlines the objectives of business and scope of business activities. It discusses the main objectives of a business as earning profits for survival while also achieving economic, social, human, national, and global objectives. It also categorizes the scope of business into industry and commerce. Commerce involves facilitating the exchange and availability of goods and services and includes trade as well as auxiliary activities like banking, transportation, warehousing, insurance, and advertising that support trade. Trade is further divided into internal/domestic trade within a country's borders, international/foreign trade between countries through imports and exports, and entrepot trade which involves buying goods from one foreign country to sell in another.