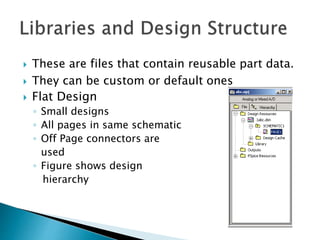
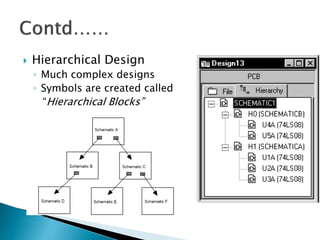
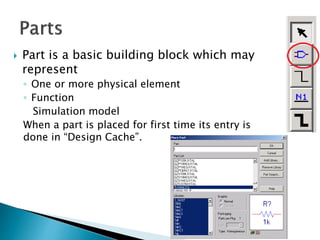
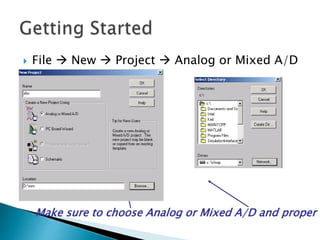
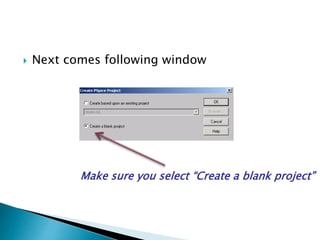
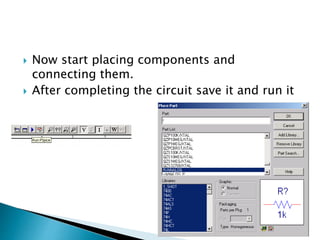
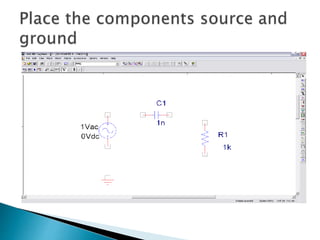
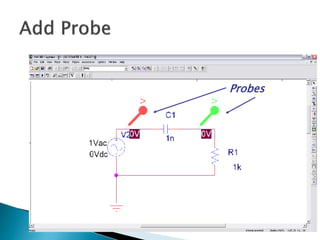
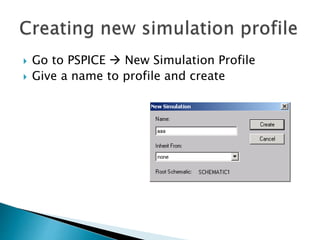
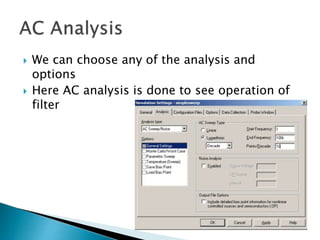
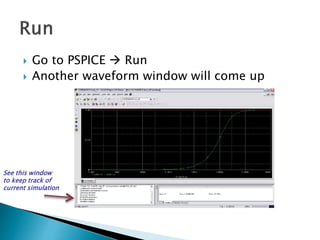
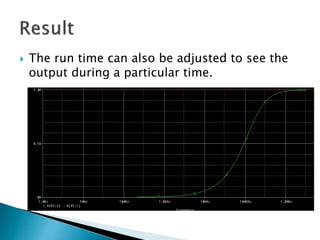
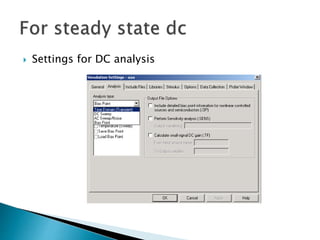
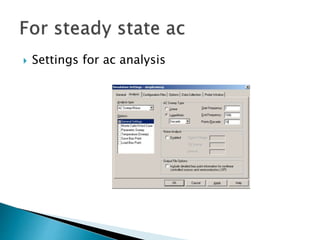
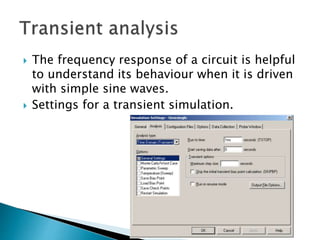
This document discusses SPICE (Simulation Program with Integrated Circuit Emphasis) and PSpice, a version of SPICE used for circuit simulation on PCs. It describes the basic steps for simulating a circuit using PSpice: 1) drawing the circuit in Capture, 2) simulating it using PSpice models, and 3) analyzing output using Probe. PSpice can perform various types of circuit analyses and contains models for common circuit elements.