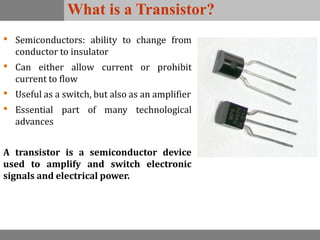
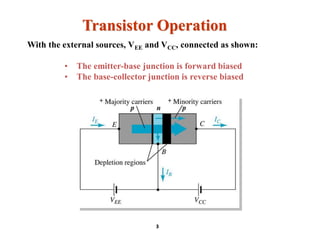
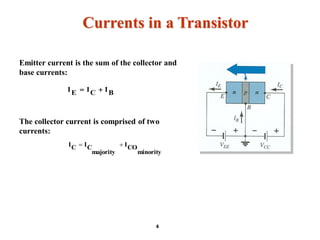
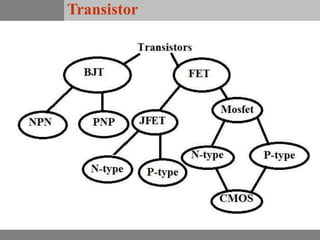
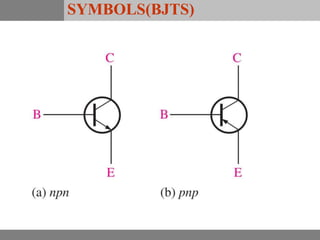
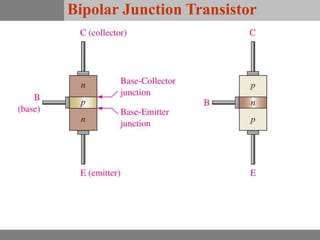
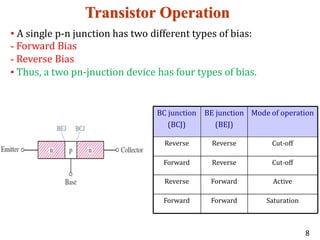
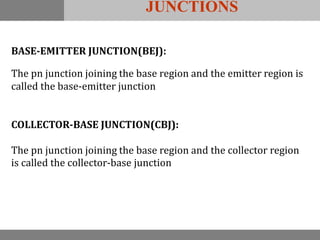
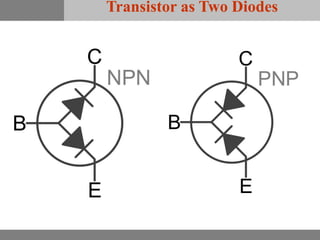
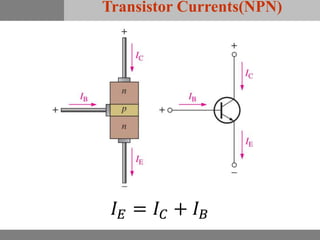
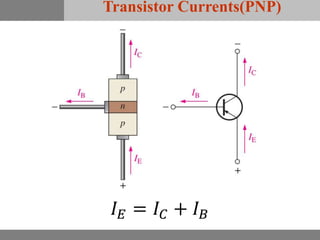
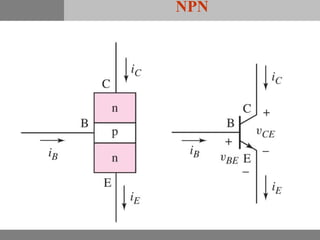
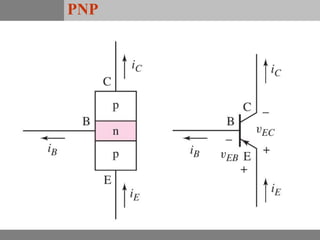
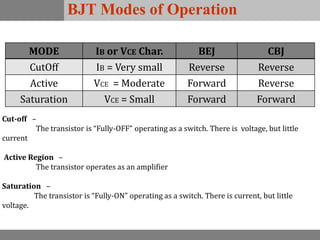
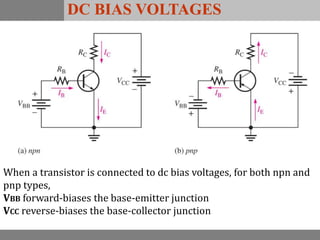
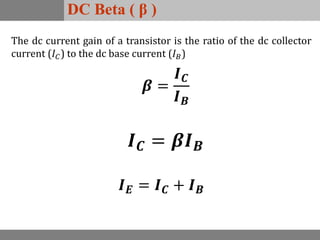
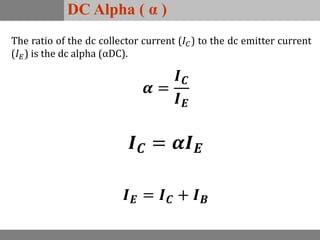
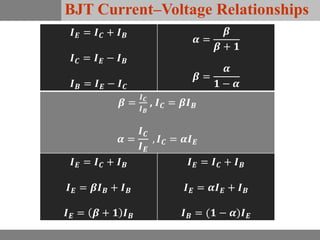
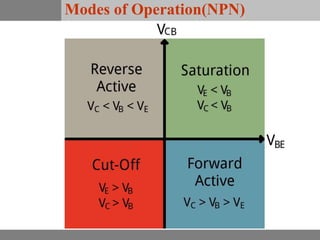
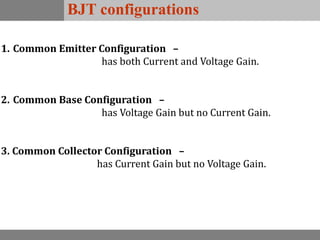
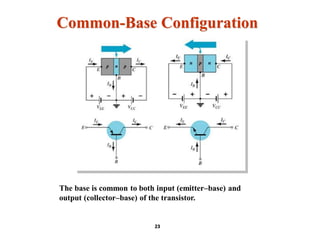
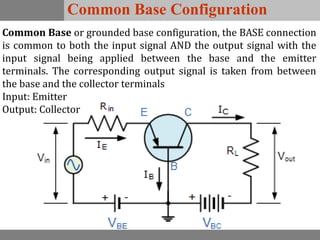
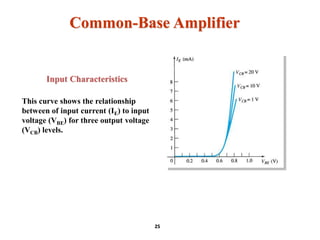
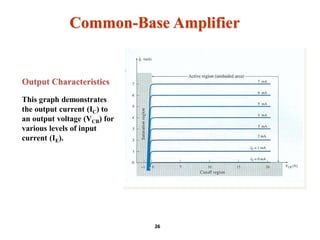
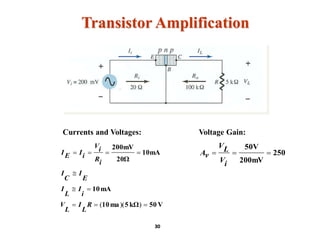
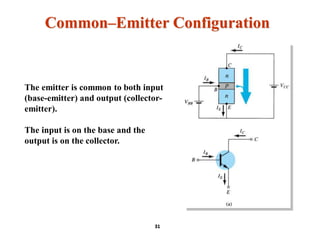
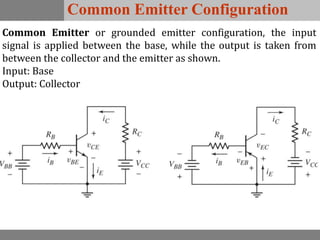
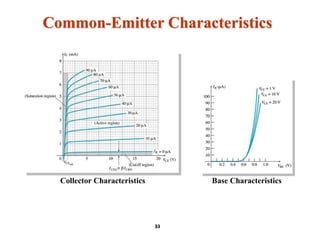
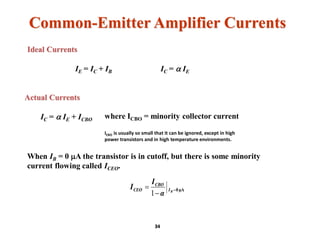
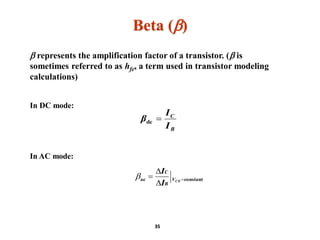
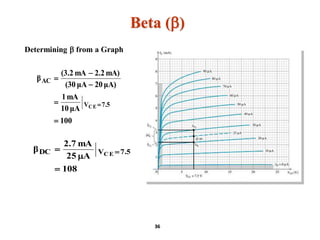
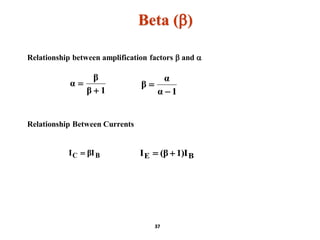
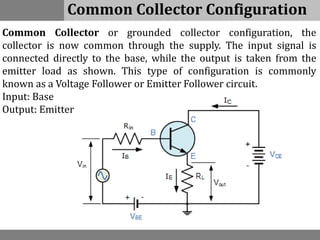
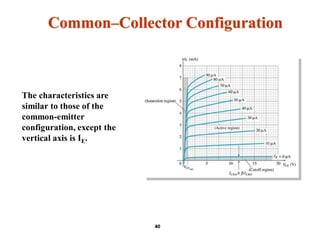
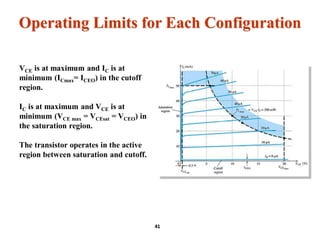
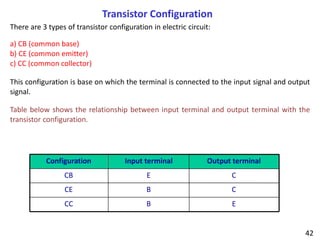
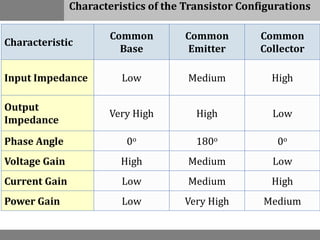
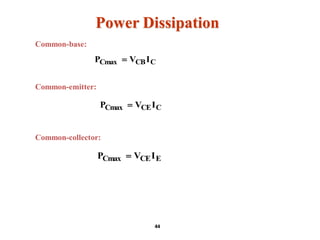
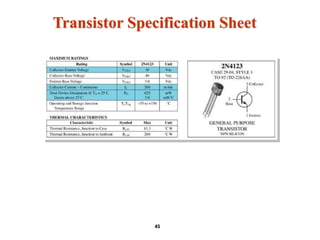
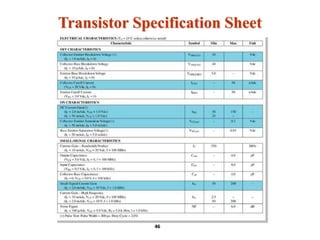
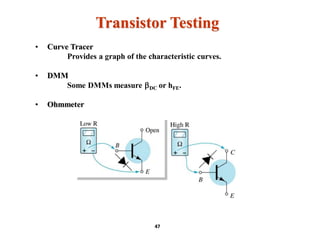
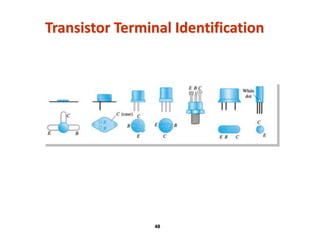
A bipolar junction transistor (BJT) is a semiconductor device used for amplifying and switching electronic signals, featuring two types of currents: collector and emitter currents. Various configurations, including common emitter, common base, and common collector, describe how the transistor is connected within a circuit, each affecting current and voltage gain differently. The operational modes of a BJT can be categorized into cutoff, active, and saturation states, each defining its behavior as an amplifier or switch.