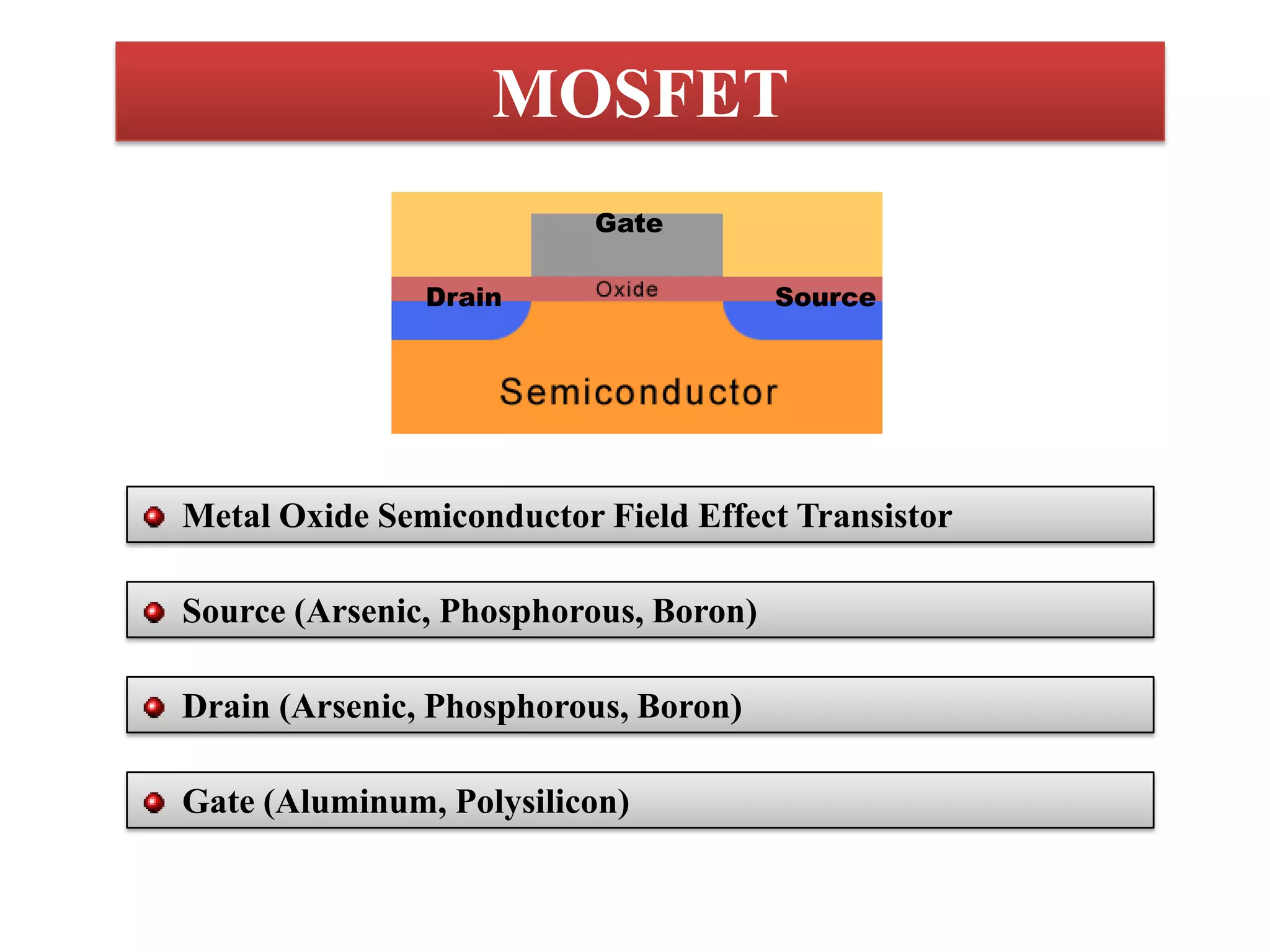
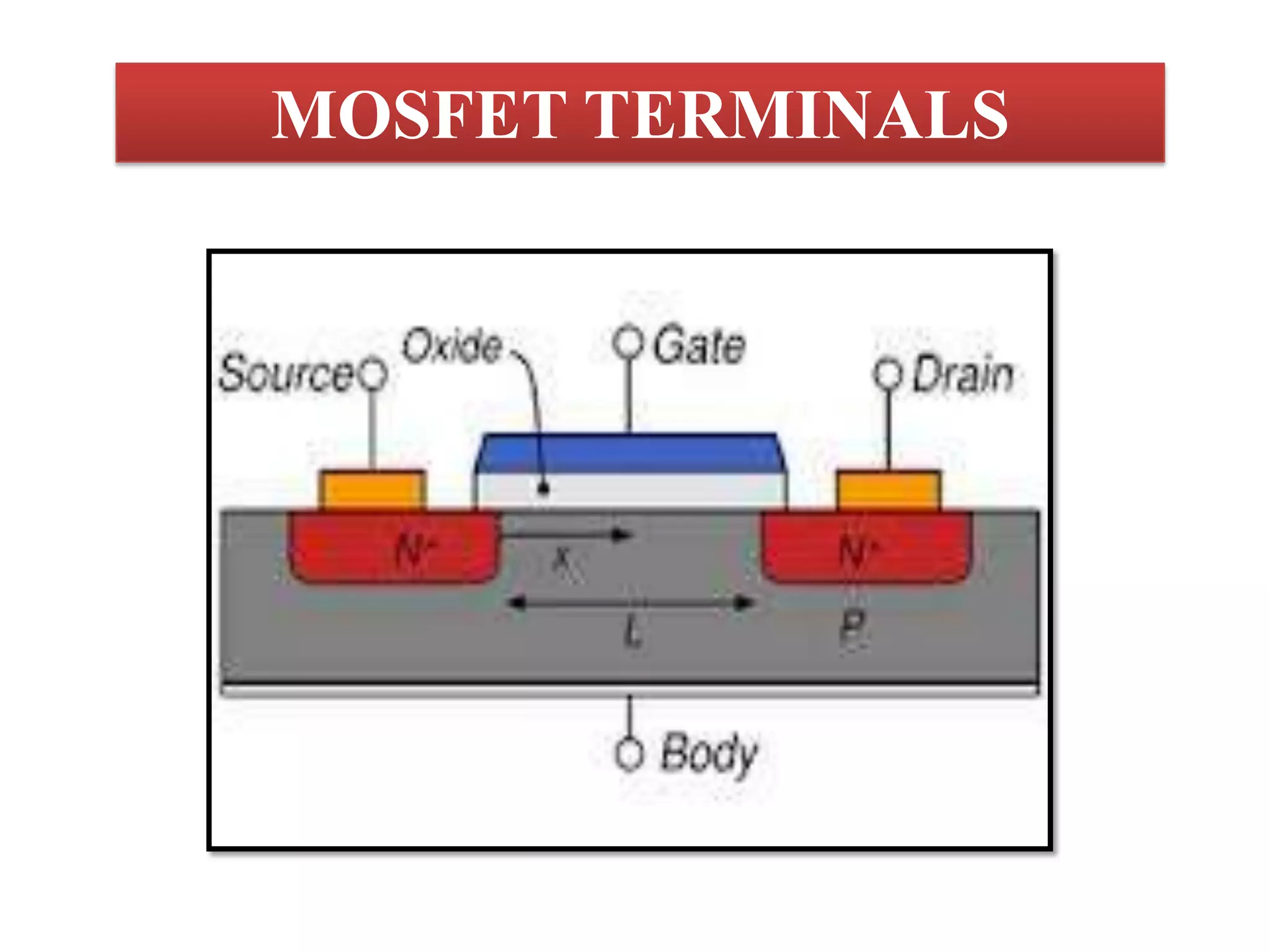
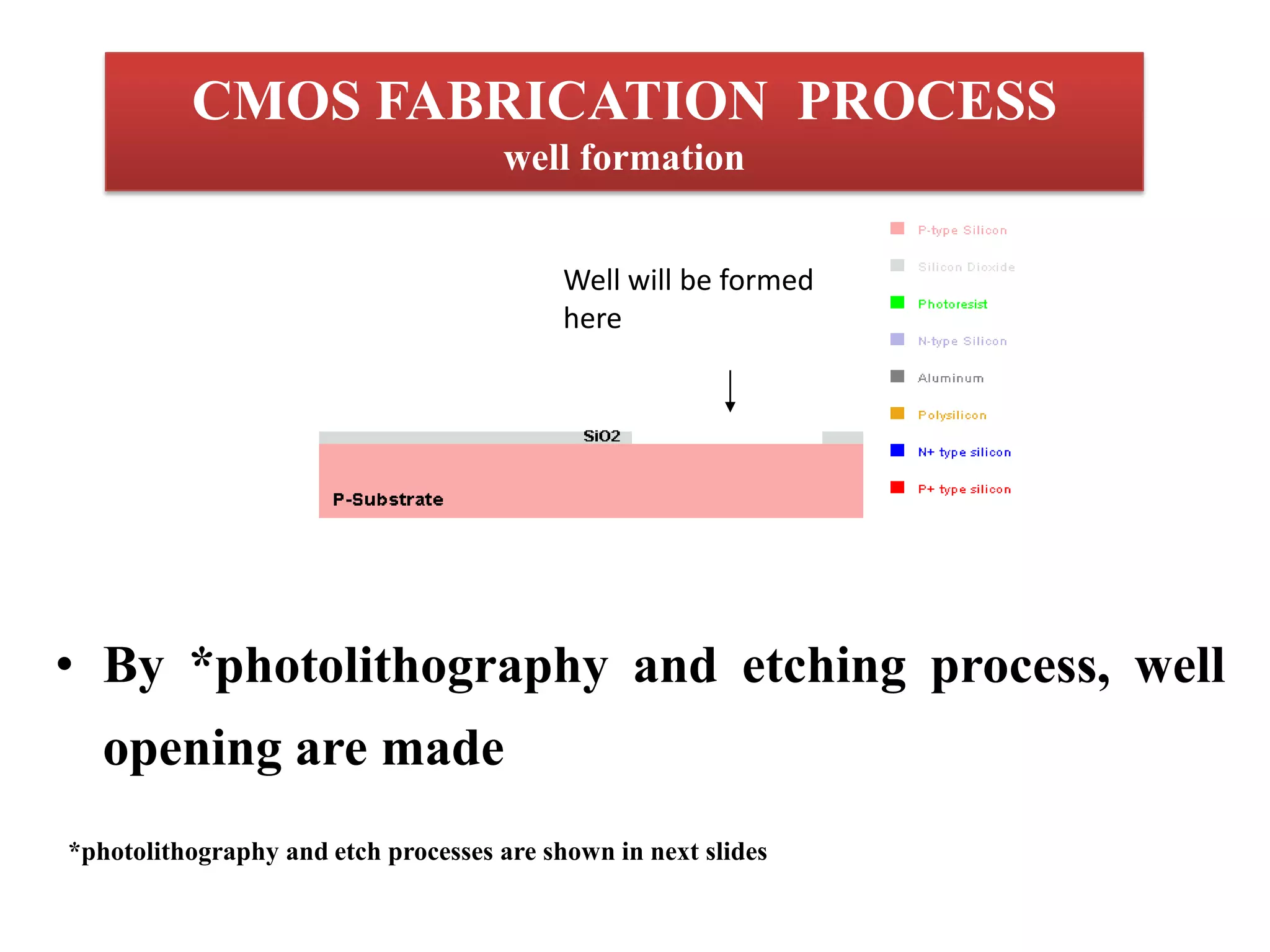
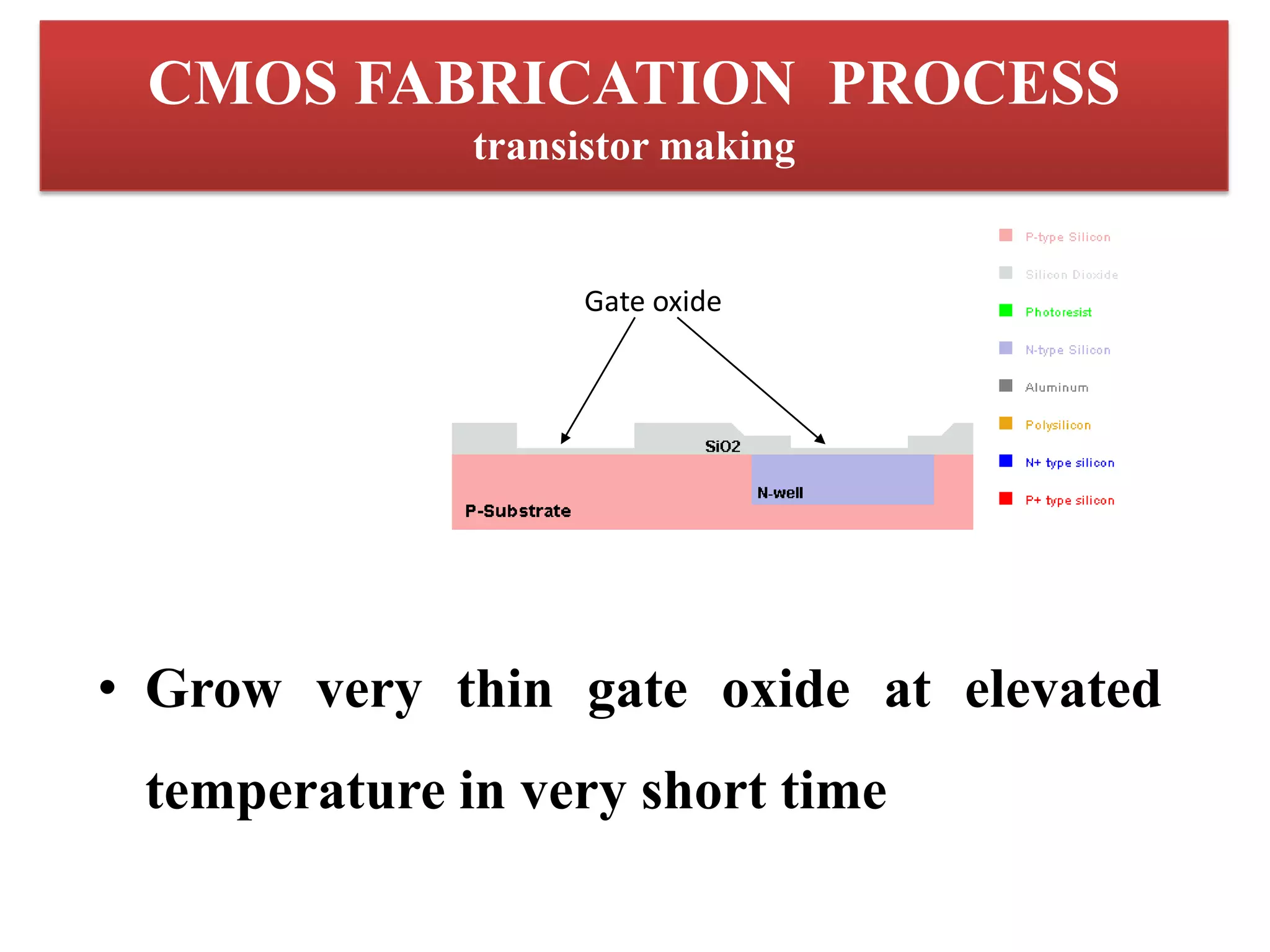
This document provides an introduction to transistors and MOSFETs. It begins by describing the invention of the transistor in 1947 and defining what a transistor is. It then discusses the main types of transistors - BJT and FET, including MOSFET and JFET. The rest of the document focuses on MOSFETs, explaining what they are, their terminals and symbols, types of MOSFETs like n-MOSFET and p-MOSFET, and how MOSFETs work and are fabricated through processes like photolithography, etching, diffusion, and oxidation. It includes diagrams of MOSFET structure and operation. In the end it briefly discusses CMOS fabrication process flow.