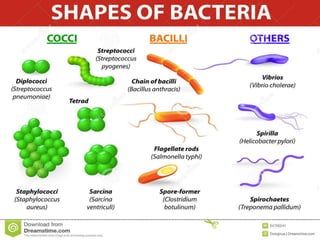
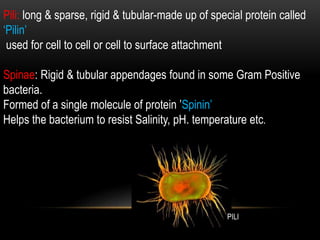
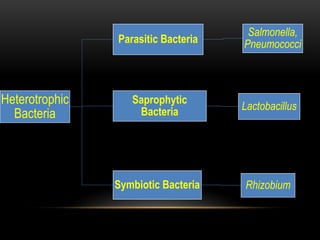
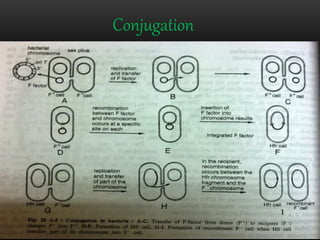
Bacteria are the simplest and smallest prokaryotic microorganisms. They are ubiquitous, existing everywhere from atmospheric heights of 6km to ocean depths of 5km. Bacteria exhibit a wide range of shapes and many are motile with flagella or pili. They reproduce asexually through binary fission and lack true sexual reproduction. Bacteria play important economic roles through causing diseases, food spoilage, increasing soil fertility through nitrogen fixation, and use in biotechnology and pollution control.