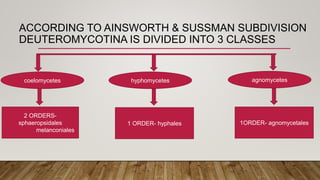
This document discusses the classification of Deuteromycota (fungi imperfecti), which reproduce asexually through a parasexual cycle and lack a known sexual stage. It describes their key characteristics and divisions according to different systems. Deuteromycota are divided into 3 classes - Coelomycetes, Loculoascomycetes, and Hyphomycetes. The classes are further divided into orders and families based on their asexual reproductive structures.