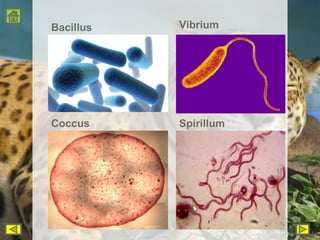
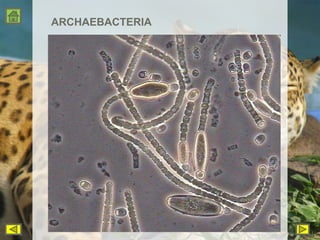
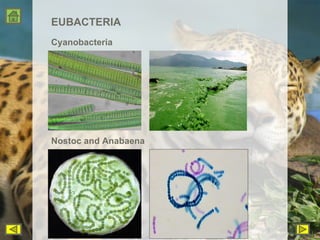
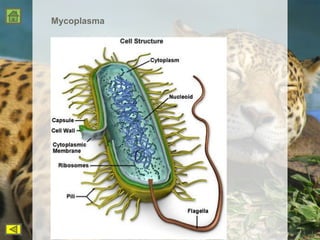
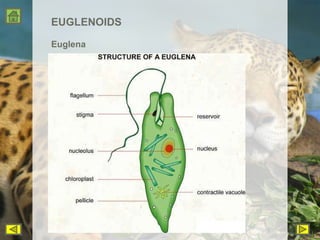
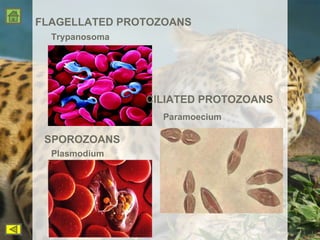
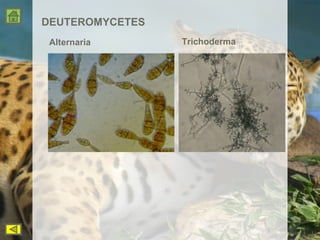
R.H. Whittaker proposed a five kingdom classification system in 1969 that categorized organisms into the kingdoms of Monera, Protista, Fungi, Plantae, and Animalia based on cell structure, organization, nutrition, reproduction, and phylogeny. Monera contained only bacteria, which are grouped by shape. Protista contained all single-celled eukaryotes and linked the other kingdoms. Fungi constituted a unique kingdom of heterotrophic organisms with diversity in morphology and habitat. Plantae included all eukaryotic, chlorophyll-containing organisms commonly called plants. Animalia was characterized by heterotrophic, multicellular eukaryotes that directly or indirectly depend