1. The document divides plants into 5 divisions based on their characteristics and complexity. These include thallophyta (algae), bryophyta (mosses and liverworts), pteridophyta (ferns), gymnosperms (cone-bearing plants), and angiosperms (flowering plants).
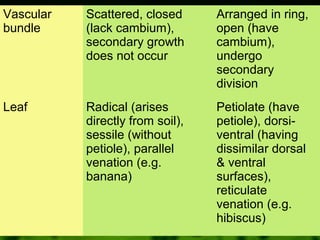
2. Angiosperms are further divided into monocots and dicots based on whether their seeds contain one cotyledon or two. Monocots and dicots differ in features such as their root structure, vascular bundles, leaf and flower structure.
3. The five divisions of plants progress from the simplest thallophyta to the most advanced and complex flowering plants of the ang