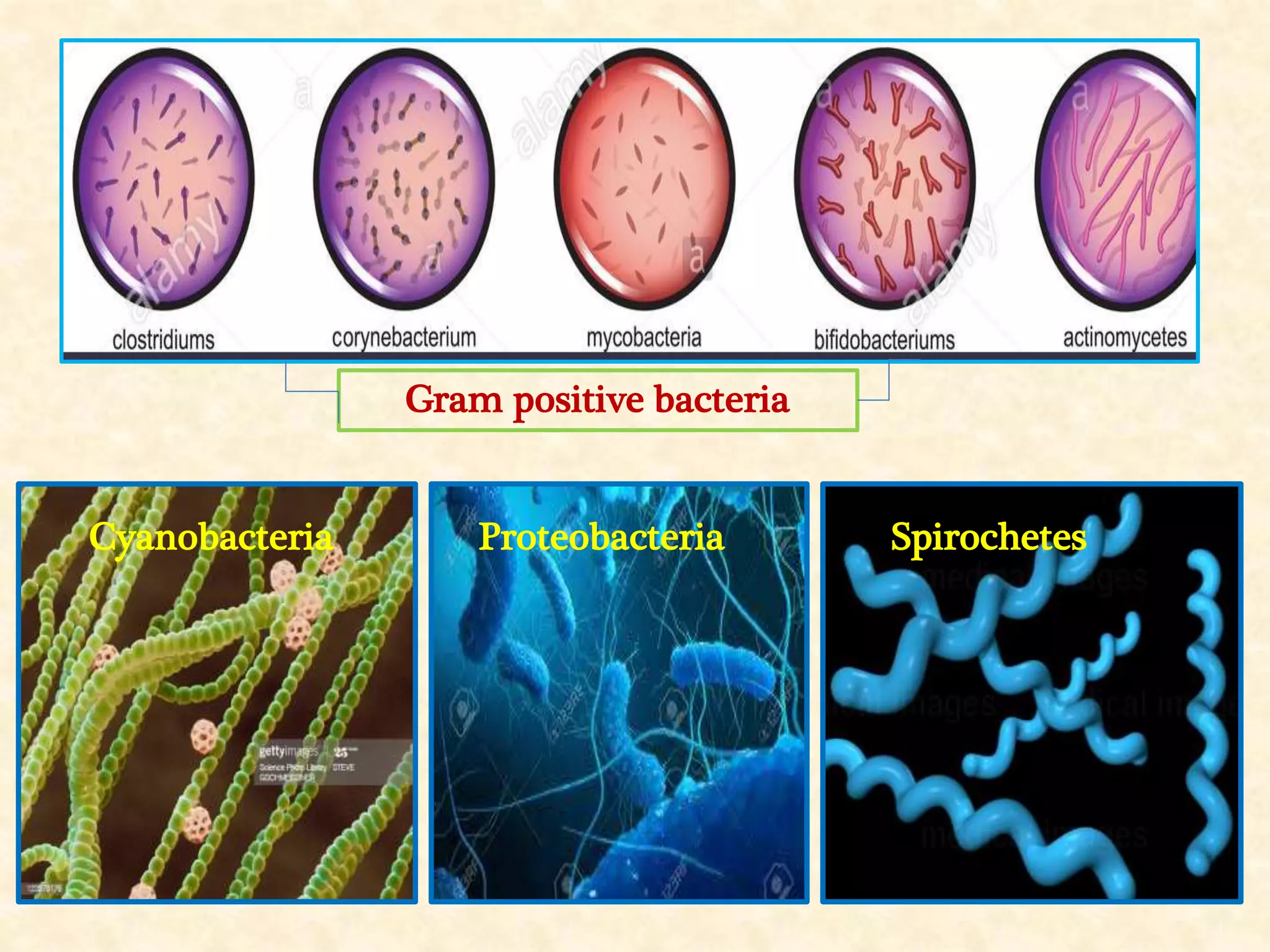
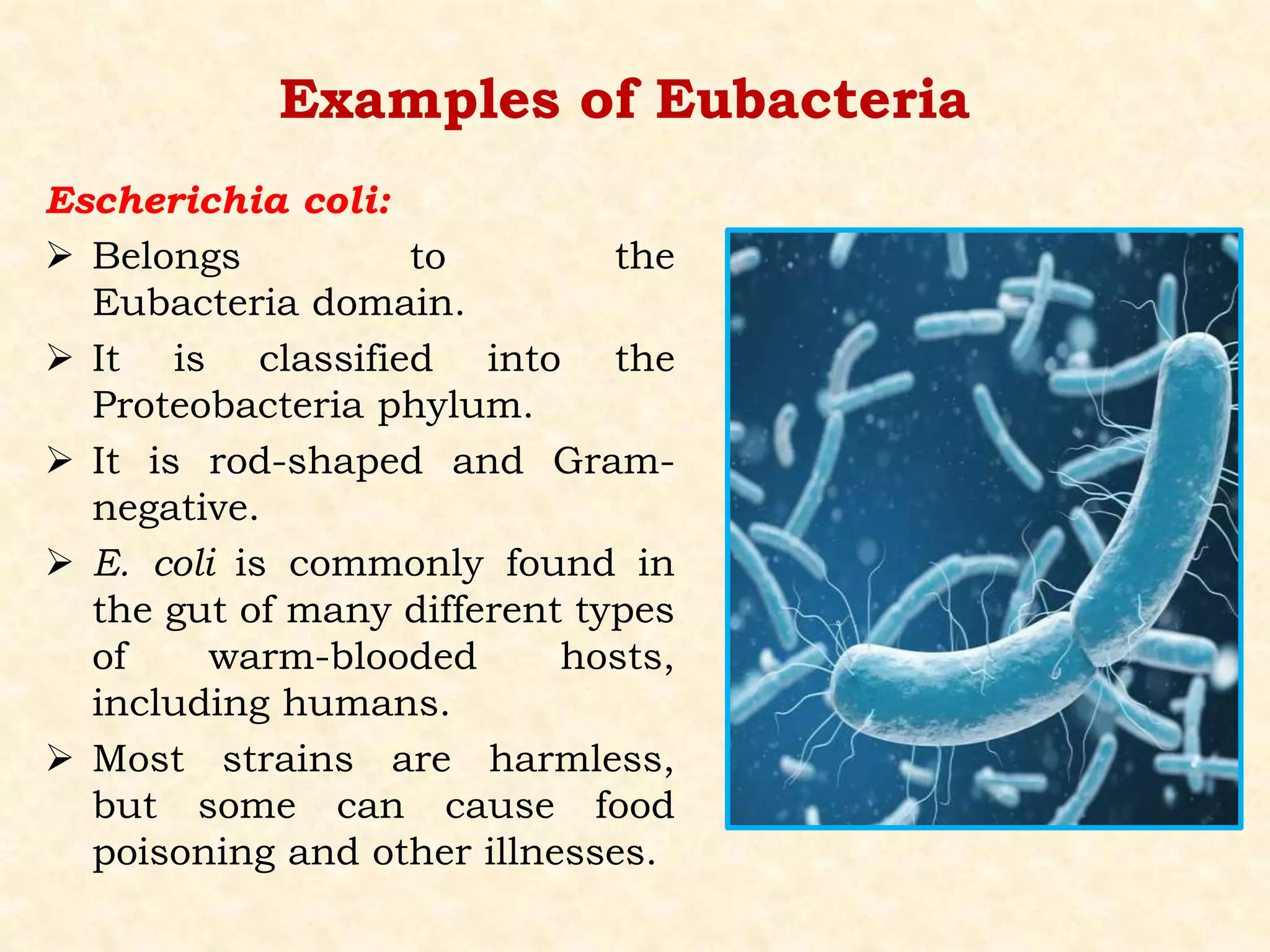
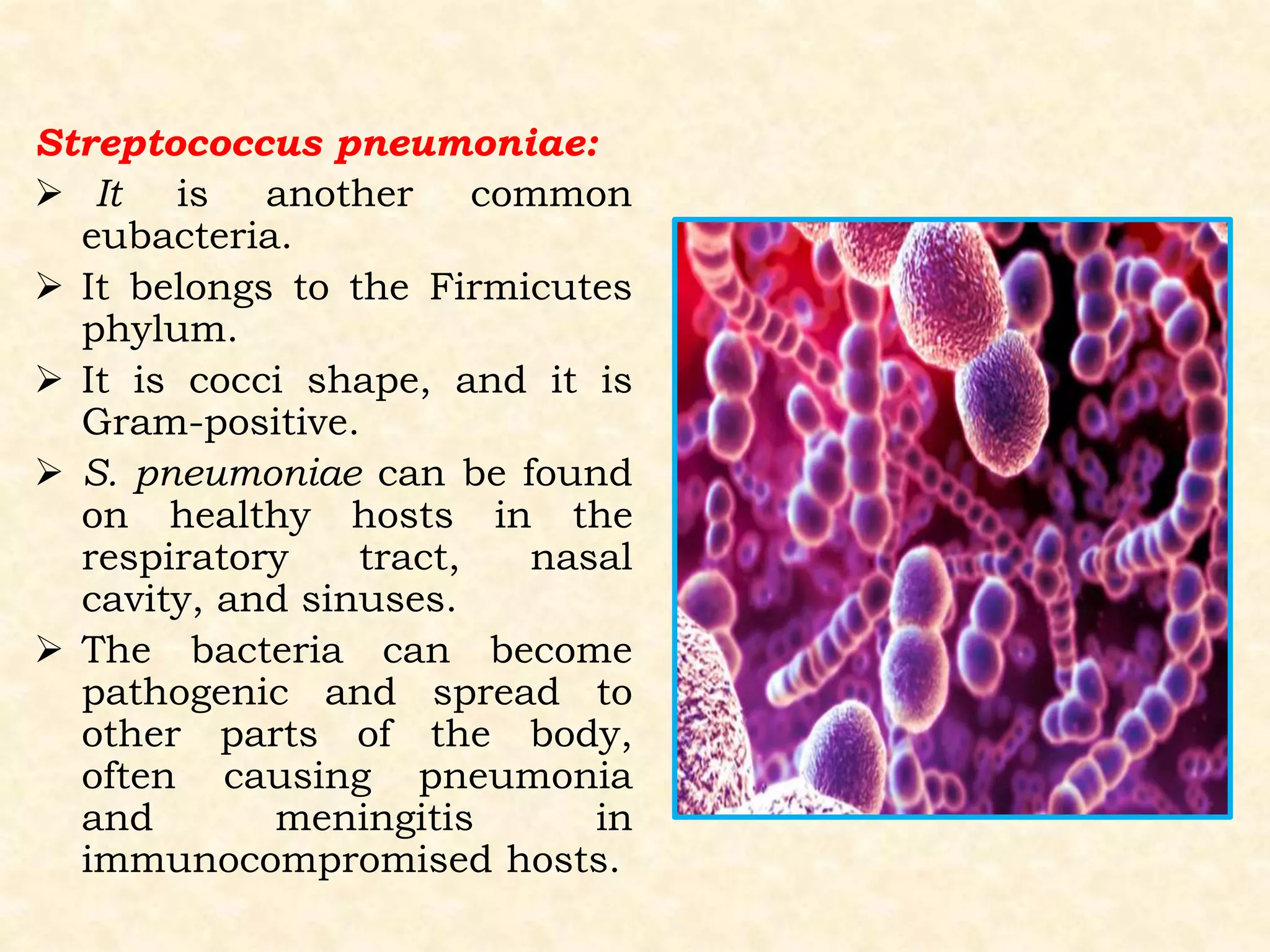
This document summarizes the characteristics of eubacteria. Eubacteria are single-celled prokaryotic microorganisms that are enclosed by a cell wall made of peptidoglycans. They lack membrane-bound organelles and reproduce through binary fission. The document further describes the key characteristics of five major phyla of eubacteria: Chlamydias, Cyanobacteria, Gram-positive bacteria, Proteobacteria, and Spirochetes. Examples of common eubacteria, such as Escherichia coli and Streptococcus pneumoniae, are also provided.