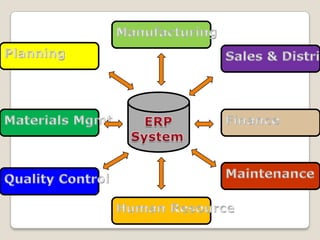
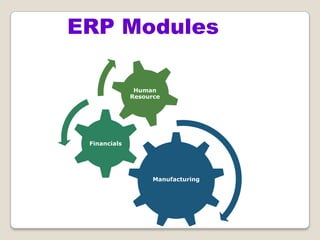
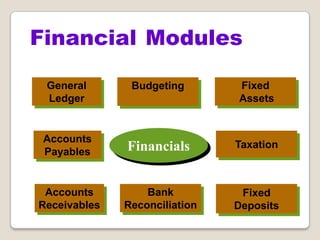
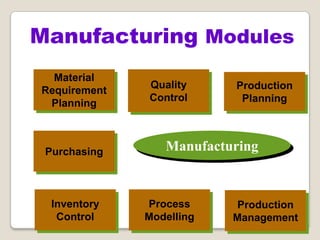
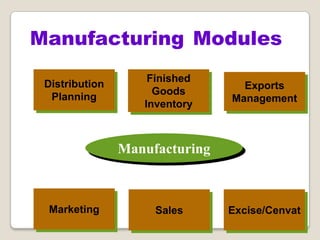
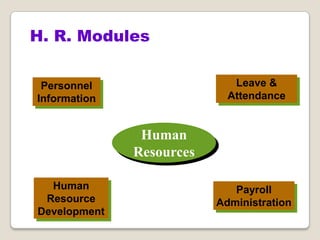
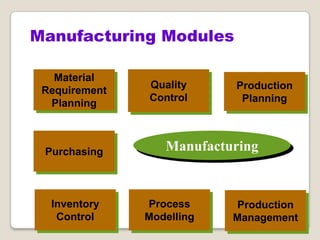
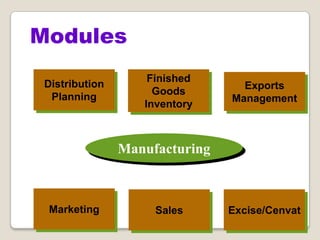
The document discusses Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems. It defines ERP as a business application that integrates all business processes in an organization. ERP provides an integrated view of various functions to help effectively manage resources and improve efficiency. Benefits of ERP include improved productivity, lower costs, reduced inventory and lead times, better analysis and planning capabilities, and increased organizational transparency. The document also discusses key ERP modules, features, vendors, implementation considerations, and common myths about ERP systems.