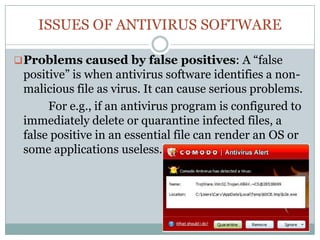
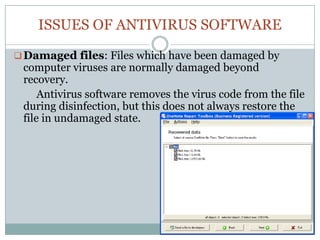
Antivirus software is essential for preventing, detecting, and removing malware, with historical roots dating back to the 1980s. Various identification methods are employed, including signature-based detection, heuristics, and rootkit detection, while popular software includes brands like McAfee and Kaspersky. However, challenges such as unexpected costs, rogue applications, false positives, and declining effectiveness highlight the need for users to be cautious and consider additional protective measures.