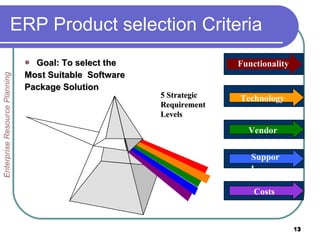
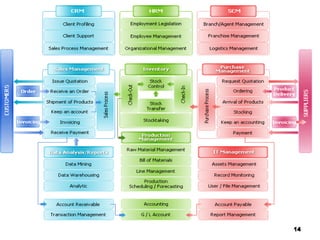
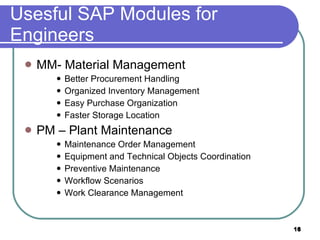
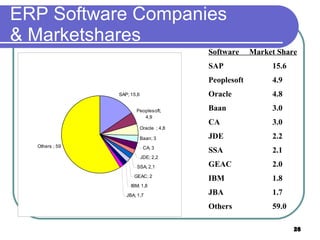
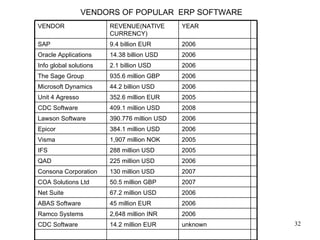
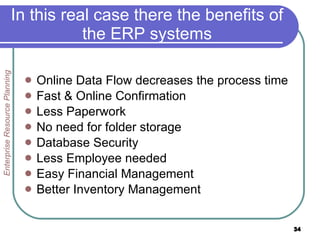
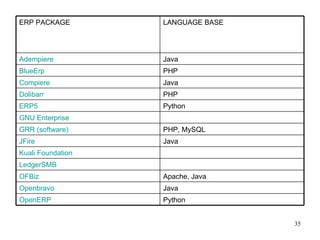
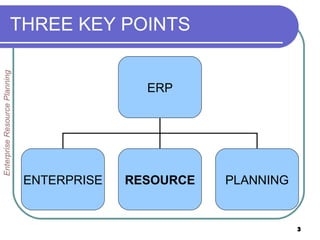
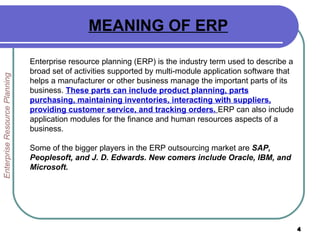
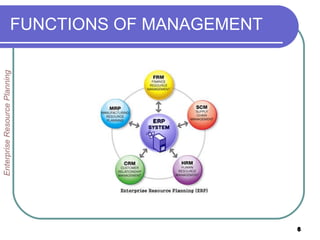
This document provides an overview of enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems. It defines ERP as multi-module software that helps businesses manage important business processes like production, purchasing, inventory, customer service and order tracking in an integrated way. The document outlines the evolution of ERP from isolated systems in the 1960s to more integrated systems today. It also discusses key considerations for ERP selection and implementation like functionality, costs, vendor support and technology.






![ERP – Options OPTION 1 – MAKE [Using Internal resources] Developing a custom-built ERP package, specific to the requirements of the organization, with the help of the in-house IT department OPTION 2 - BUY Going for Tailor-made ERP packages available in the market like SAP, Oracle applications, Baan, PeopleSoft etc. OPTION 3 – MAKE [using External resources] Developing a custom-built ERP package, specific to the requirements of the organization, with the help of a software solution provider. Enterprise Resource Planning](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mainerp-100518032333-phpapp01/85/Enterprise-Resource-Planning-12-320.jpg)