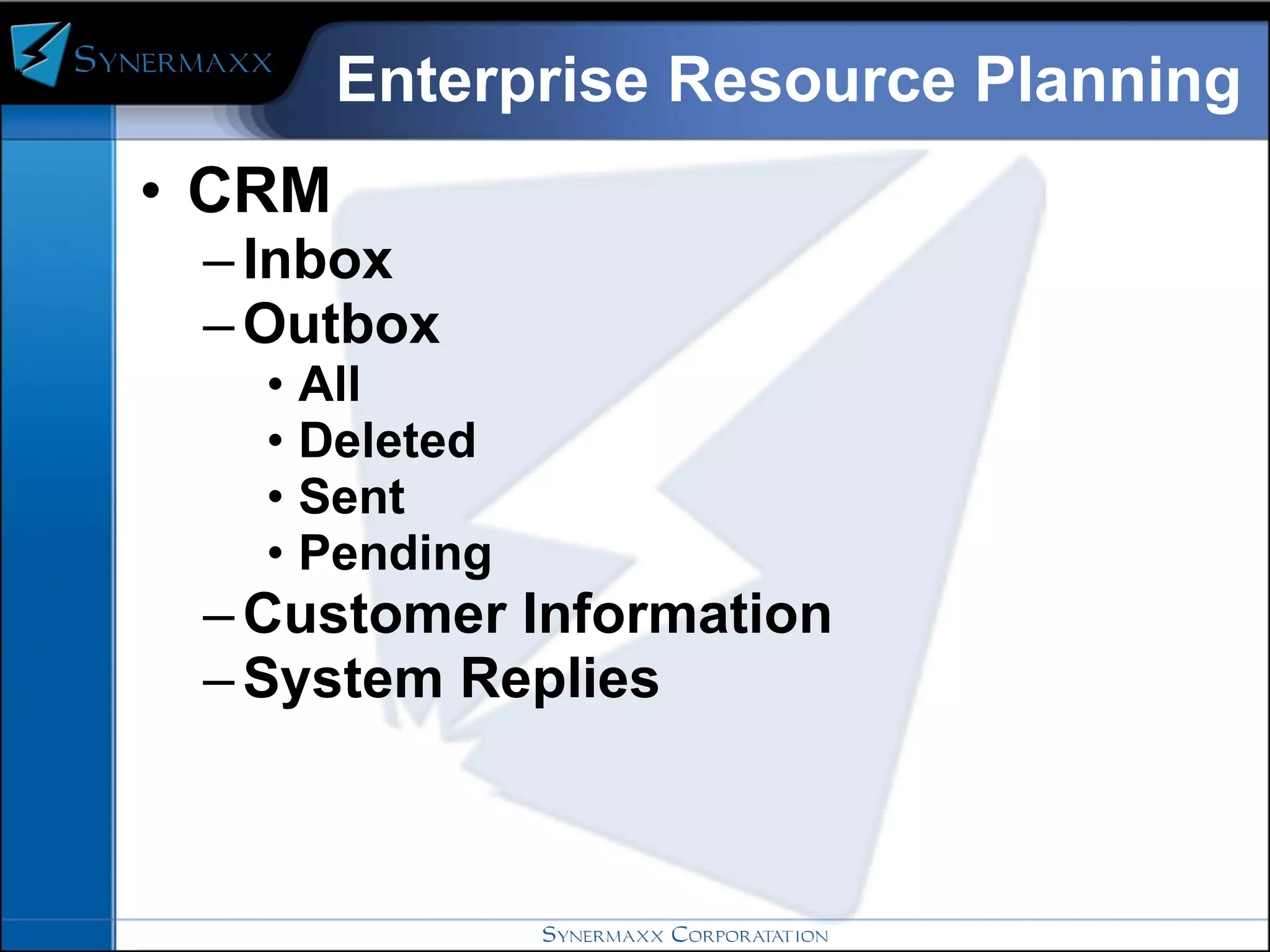
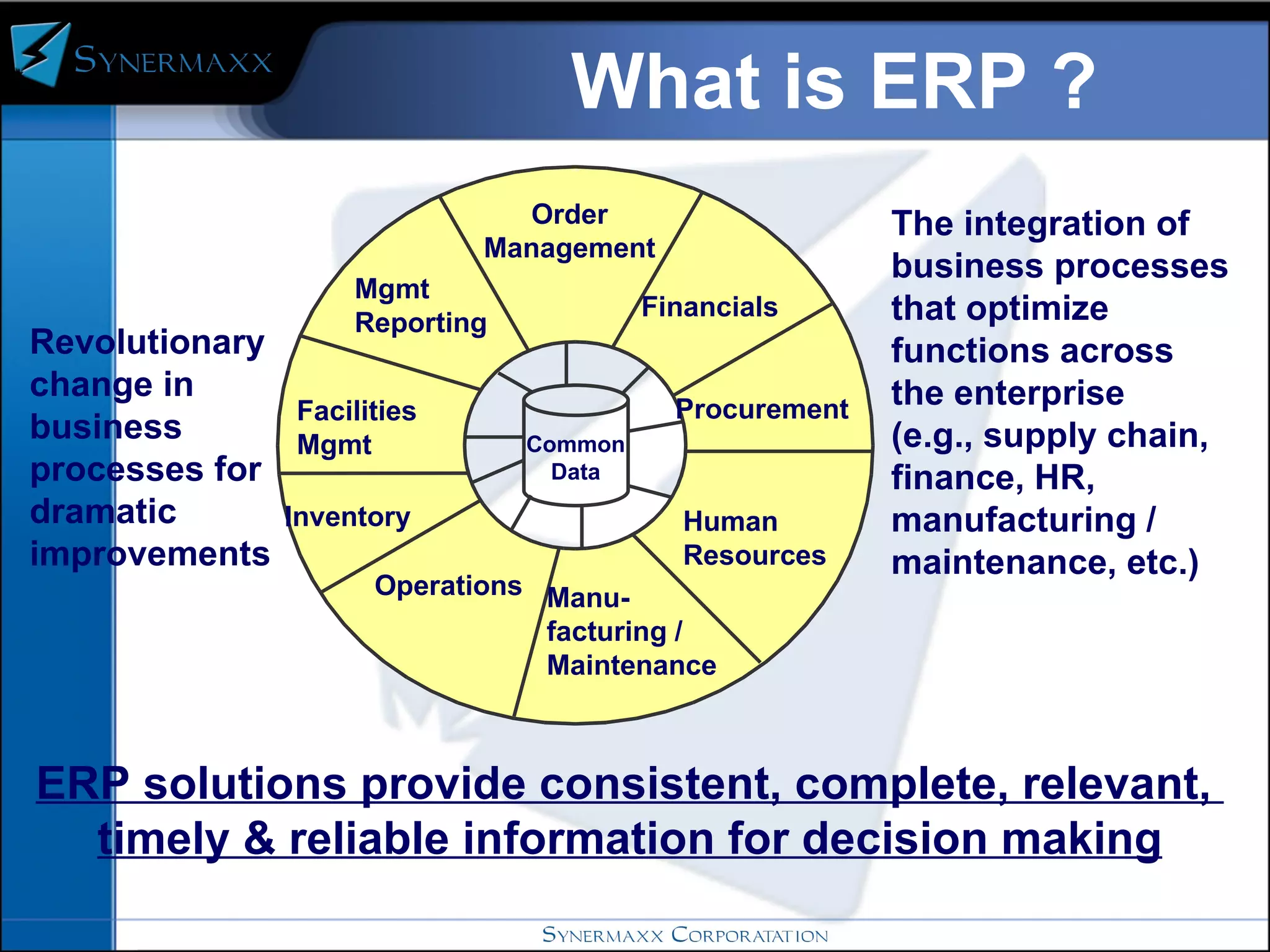
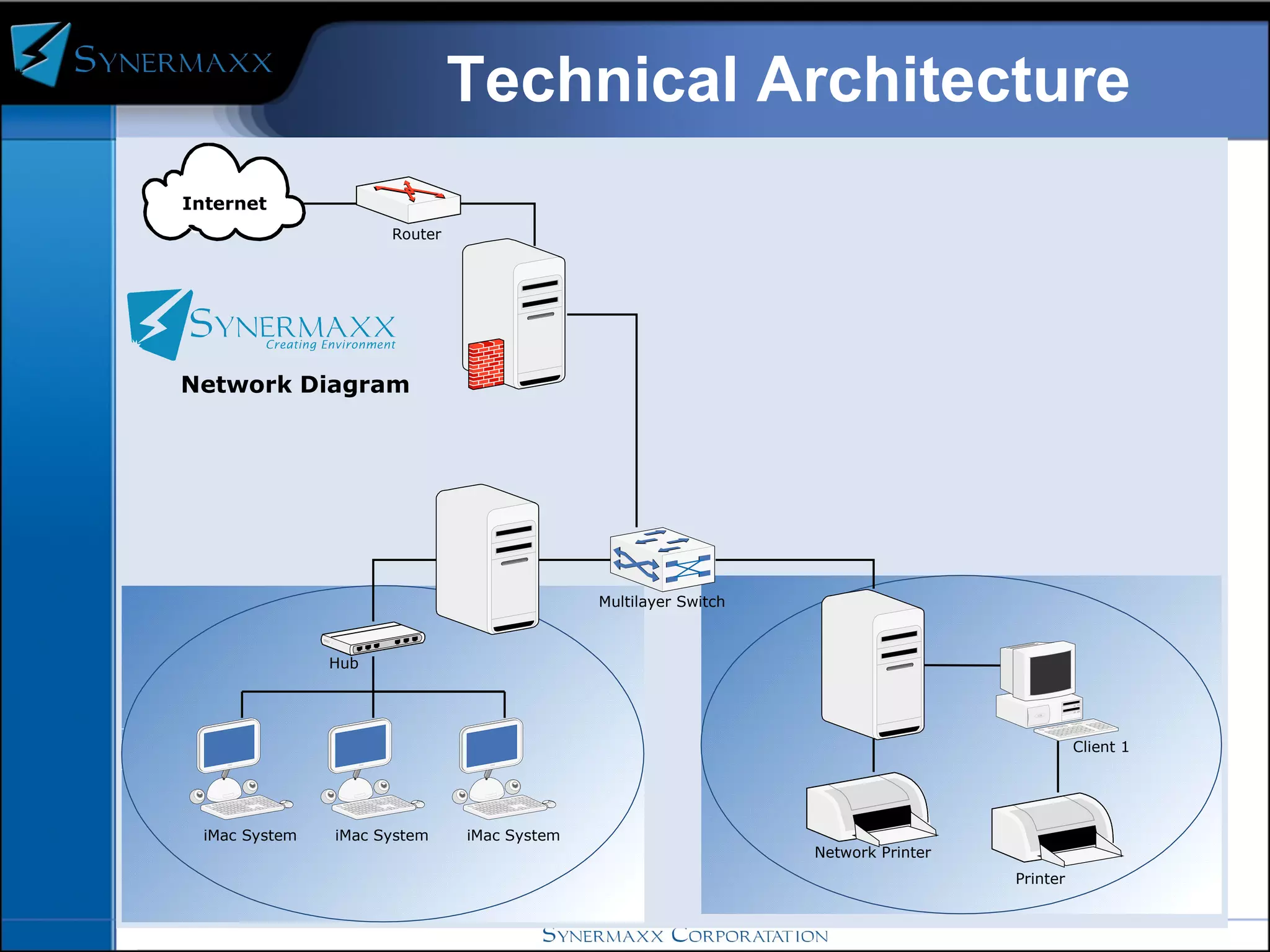
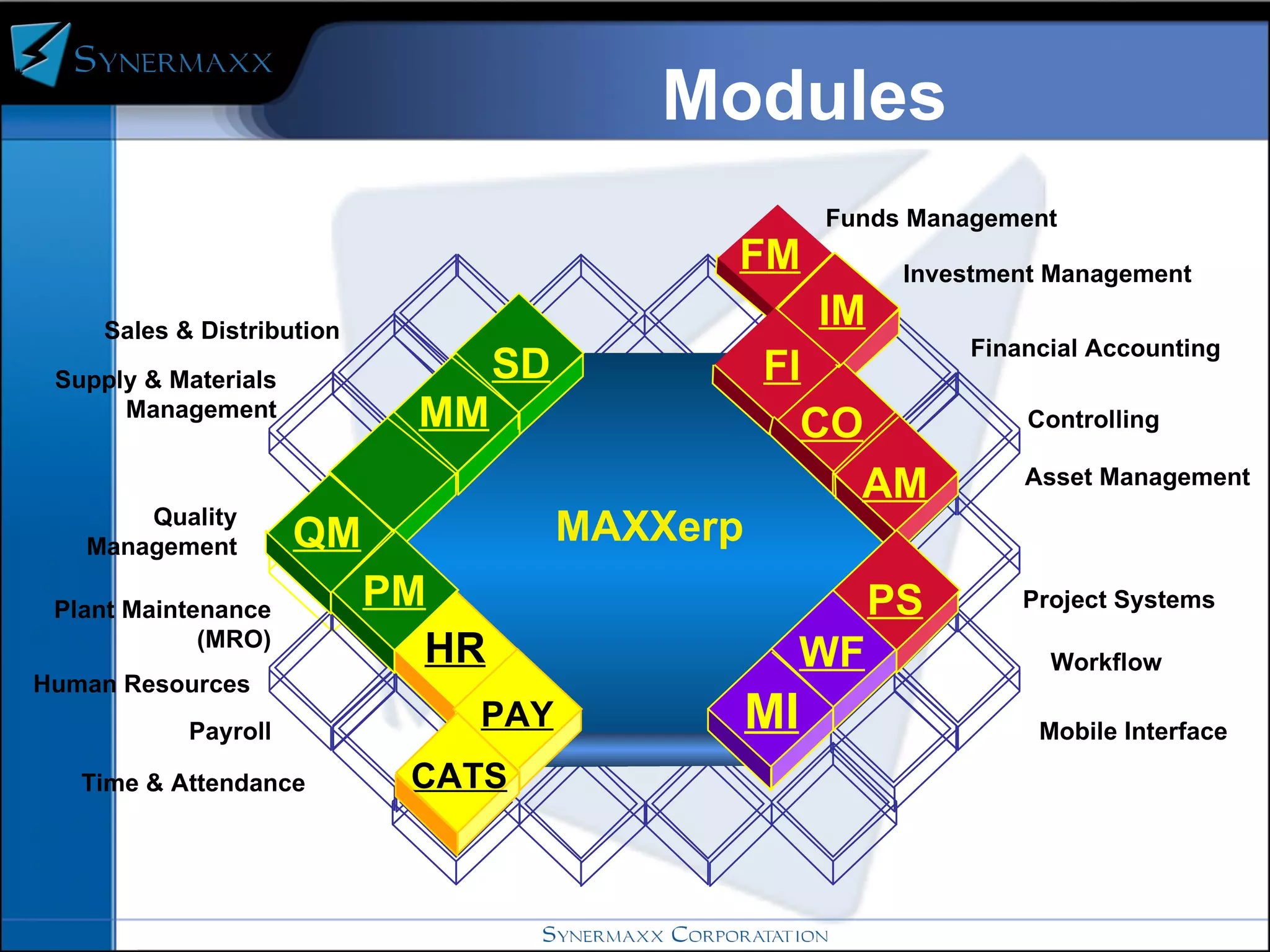
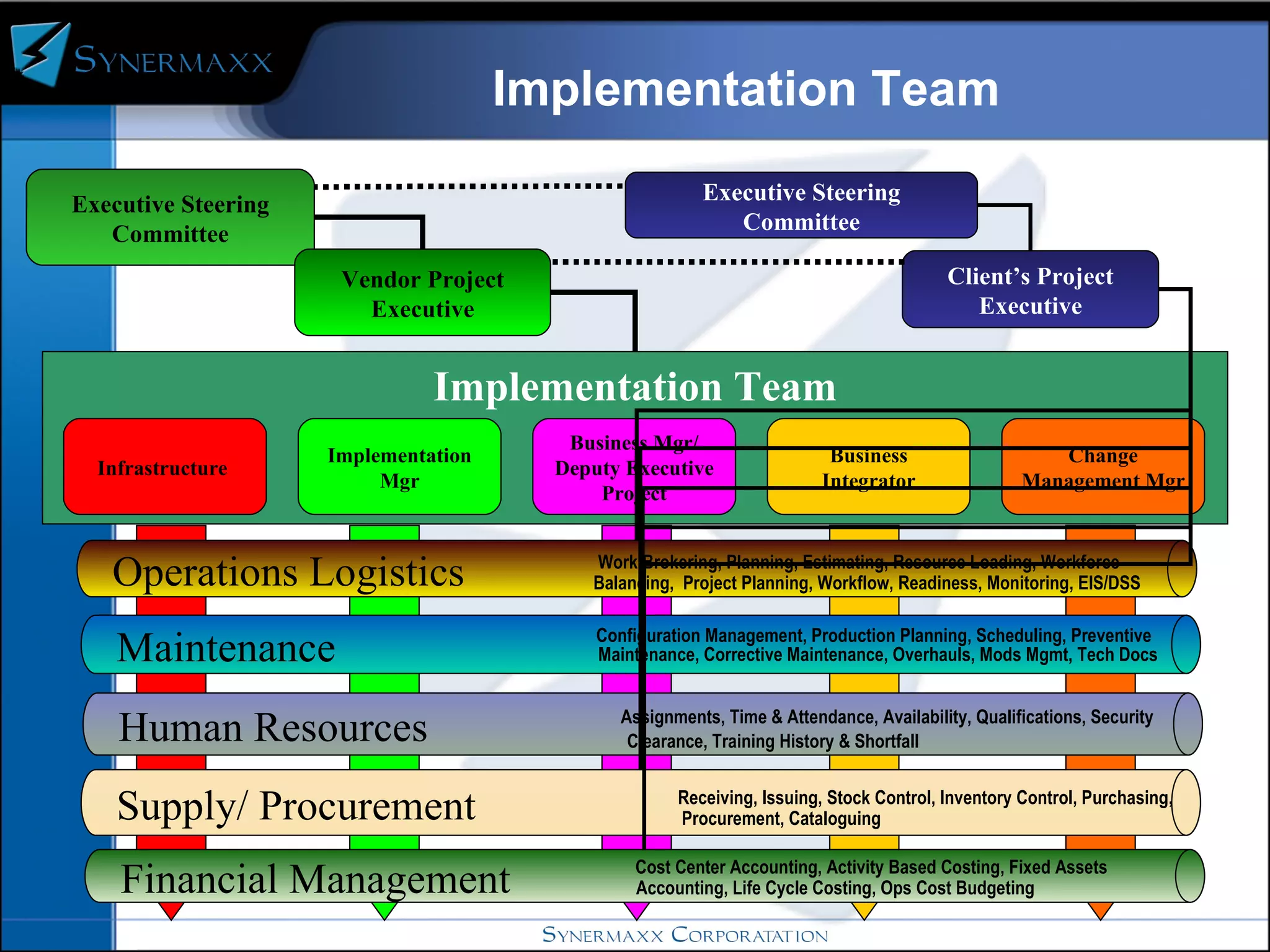
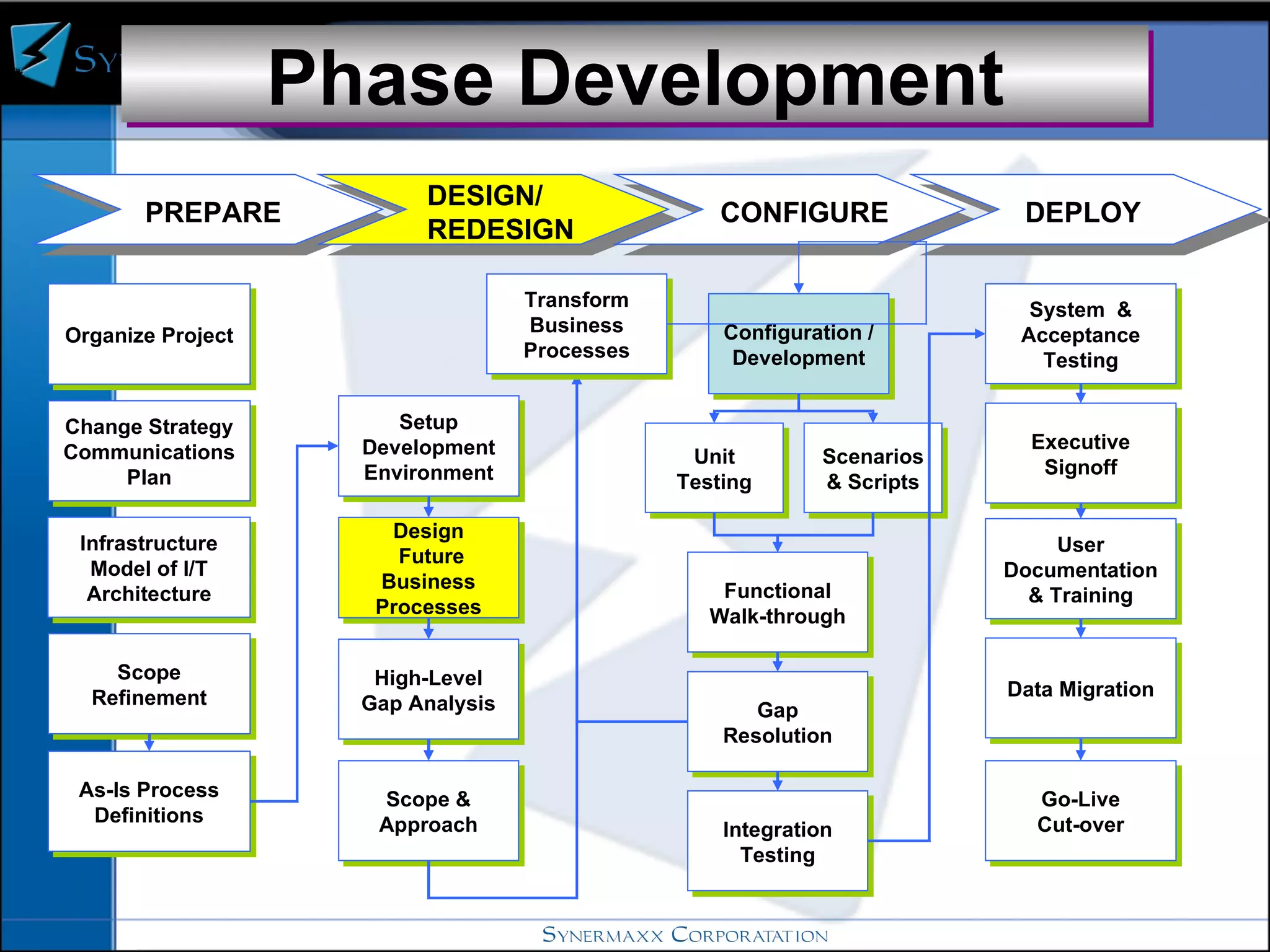
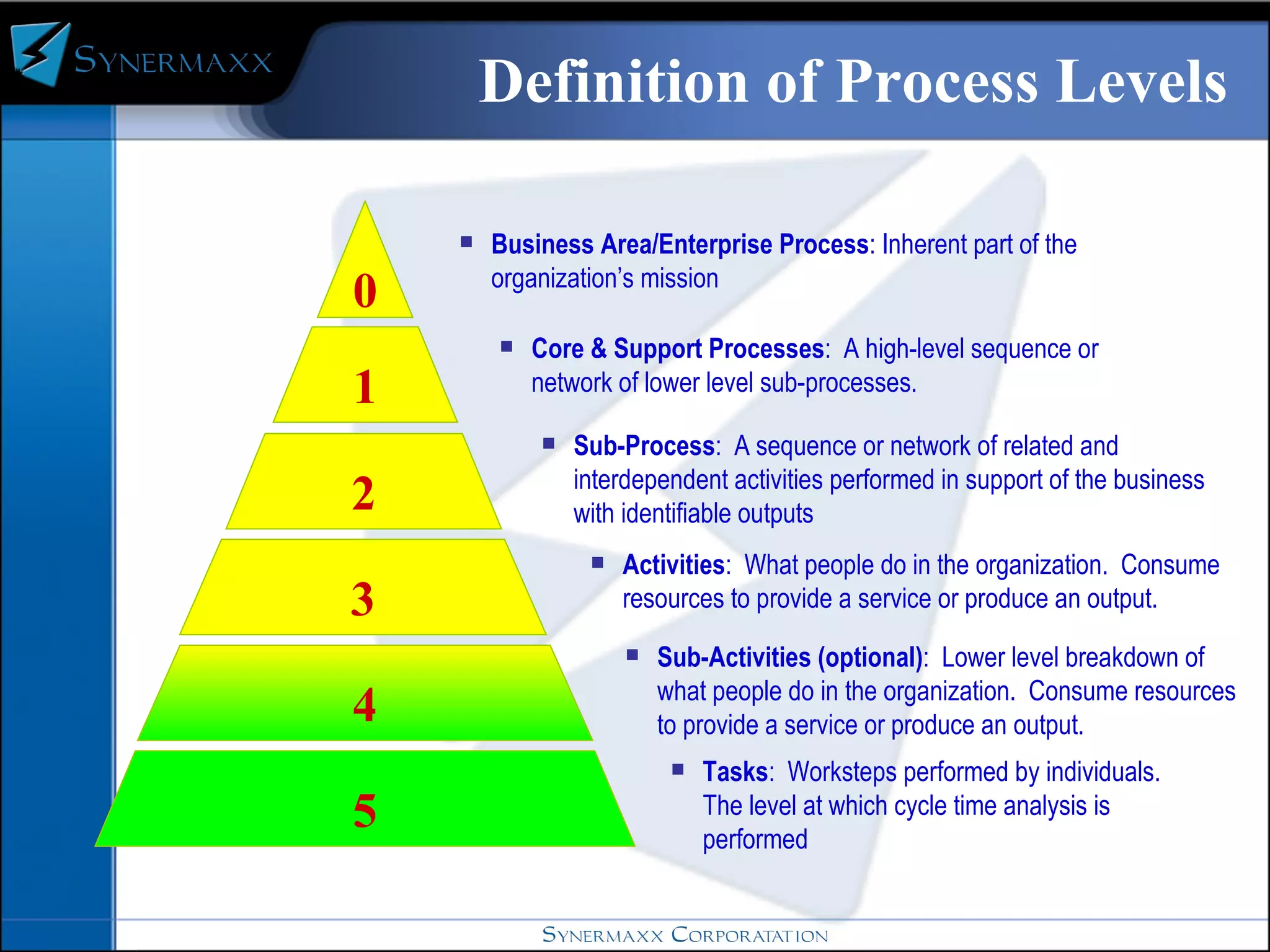
Enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems integrate core business processes across an organization by centralizing data in one place. ERP systems provide advantages like eliminating data synchronization issues between different software applications and reducing security risks. Implementing an ERP system involves defining business processes, identifying gaps between current and future processes, configuring modules, testing, and training users before going live on the new system.




![Enterprise Resource Planning MAINTENANCE Product Item Supplier Supplier Product Customer Outlet Package Material Customer Price Group Mark Up/Down [Permanent] Mark Up/Down [Outlet] Physical Count Module Physical Count Variance History User Change Password](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/erpsolutions2-090613004211-phpapp02/75/Erp-Solutions-2-12-2048.jpg)



![Enterprise Resource Planning ACCOUNT RECEIVABLE Billing Statement A/R Countering Ageing Monitoring Report Purchase Request & Check Summary A/R Collection Module Payment Summary Report CM/DM Module A/R History Report A/R History Report [Customer/AR #] Monthly Account Receivable Statement of Account](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/erpsolutions2-090613004211-phpapp02/75/Erp-Solutions-2-16-2048.jpg)
![Enterprise Resource Planning REPORTS Statement of Account for Countering DR & RR Variance Price Group Billing Variance Itemized Billing Variance Packing List Variance Pull Out Variance Sales Report Un-served Orders [Outlet] Liquidation Report Pending Report DR Summary Report Inventory Report Pull Out Report [Good/Bad] Sold-out Transaction Report Summarized Ageing Report Inventory Report Inventory Per Customer](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/erpsolutions2-090613004211-phpapp02/75/Erp-Solutions-2-17-2048.jpg)