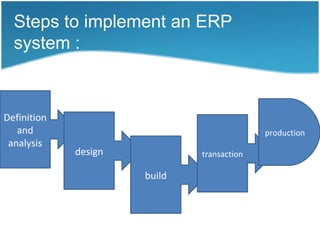
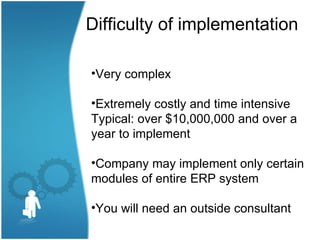
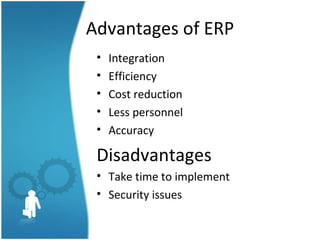
This document provides an overview of enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems. It defines ERP as a business strategy and set of applications that optimize collaborative processes across an enterprise. The goal of ERP is to acquire, retain, and grow profitable customers. ERP offers integrated solutions for key business functions. Implementing an ERP system is a complex, costly, and time-intensive process that typically takes over a year and $10 million. The benefits of ERP include increased integration, efficiency, accuracy and cost reduction, while the challenges include time needed for implementation and ongoing security issues.