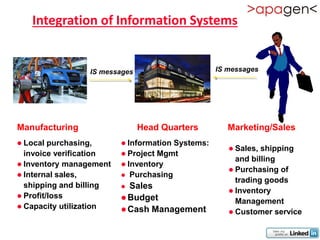
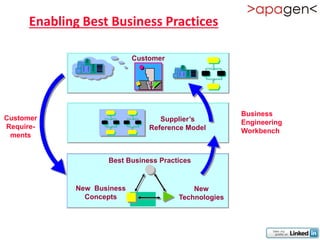
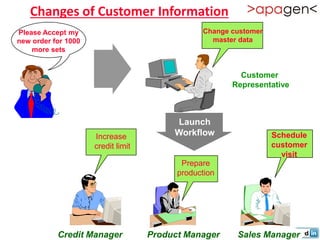
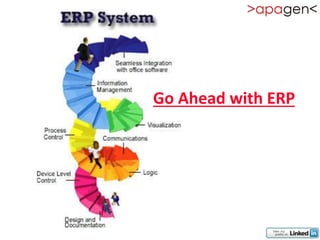
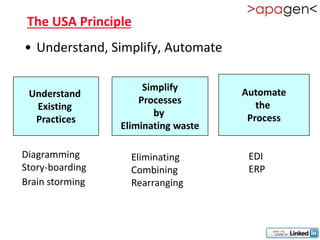
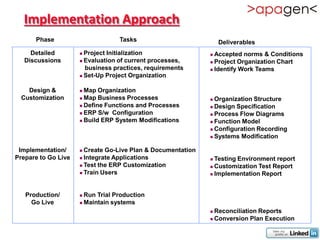
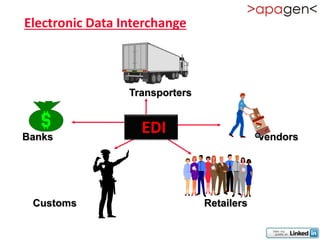
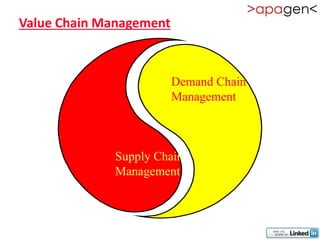
ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) is a software solution that integrates all departments and functions of a company into a single system. It facilitates company-wide information sharing, increases customer service, and organizes data input. ERP evolved from earlier systems like MRP (Materials Requirement Planning) and MRP II. Implementing ERP requires reengineering business processes, customizing the software to a company's needs, training users, and ongoing upgrades. The benefits of ERP include improved integration, customer service, decision making