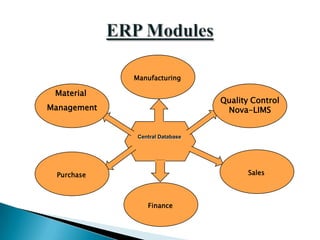
The document discusses enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems. It defines ERP as an integrated suite of software applications that allow organizations to collect and store data from various business functions like finance, manufacturing, sales, etc. in a single database. The key benefits of ERP mentioned are centralized data access, increased operational efficiency, real-time information sharing, and improved decision making. The document also lists some common ERP modules used in pharmaceutical companies and potential advantages and challenges of implementing ERP systems.




![ An integrated system that operates in real
time (or next to real time), without relying on
periodic updates.[citation needed]
A common database, which supports all
applications.
A consistent look and feel throughout each
module.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/abijiterpfinal-120331115143-phpapp01/85/ERP-Software-System-5-320.jpg)





![ The fundamental advantage of ERP is that integrating
the all processes by which businesses operate saves
time and expense. Decisions can be made more
quickly and with fewer errors. Data becomes visible
across the organization. Tasks that benefit from this
integration include:[citation needed]
Sales forecasting, which allows inventory optimization
Chronological history of every transaction through
relevant data compilation in every area of operation.
Order tracking, from acceptance through fulfillment
Revenue tracking, from invoice through cash receipt
Matching purchase orders (what was
ordered), inventory receipts (what arrived), and
costing (what the vendor invoiced)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/abijiterpfinal-120331115143-phpapp01/85/ERP-Software-System-12-320.jpg)




