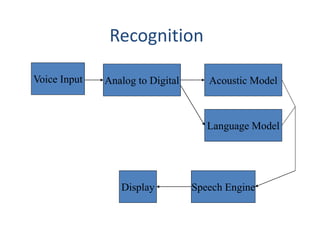
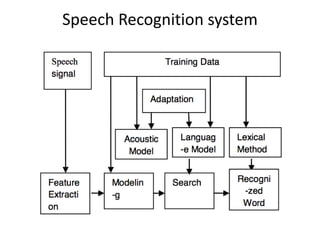
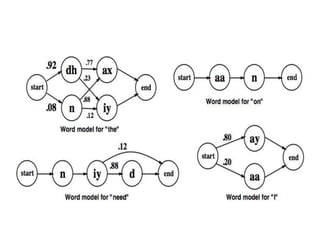
The document discusses speech recognition, also called automatic speech recognition, which enables computers to understand and process voice input for various applications. It covers the components of a speech recognition system, including sound recording, feature extraction, recognition using Hidden Markov Models, and the importance of language and acoustic models. Additionally, it highlights tools like CMU Sphinx and Jasper for developing voice-controlled applications.














![Resources
• List of publications
http://cmusphinx.sourceforge.net/wiki/research/
Speech Recognition With CMU Sphinx [Blog by N.
Shmyrev, Sphinx developer]
• Speech recognition seminars at Leiden Institute for
Advanced Computer Science, Netherlands
• http://www.liacs.nl/~erwin/speechrecognition.html
http://www.liacs.nl/~erwin/SR2003/
http://www.liacs.nl/~erwin/SR2005/
http://www.liacs.nl/~erwin/SR2006/
http://www.liacs.nl/~erwin/SR2009/](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spee-150806204452-lva1-app6892/85/Speech-Recognition-19-320.jpg)
![References
• [1] Anushree Srivastava, Nivedita Singh and
Shivangi Vaish, Speech Recognition For Hindi
Language, International Journal of Engineering
Research & Technology (IJERT) April – 2013 .
• Wiqas Ghai and Navdeep Singh, “Analysis of
Automatic Speech Recognition Systems for
Indo-Aryan Languages: Punjabi A Case Study”,
Vol-2, Issue-1, March 2012.
• Website : http://cmusphinx.sourceforge.net/](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spee-150806204452-lva1-app6892/85/Speech-Recognition-20-320.jpg)