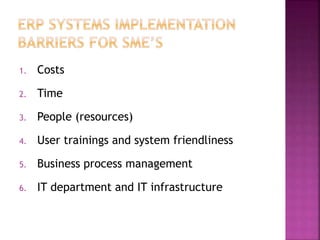
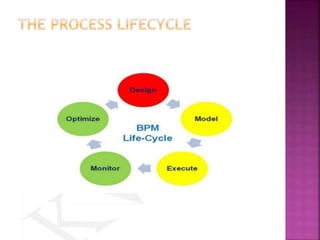
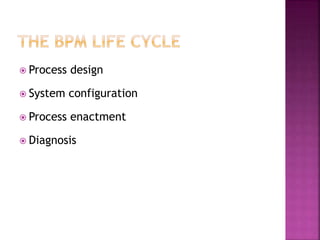
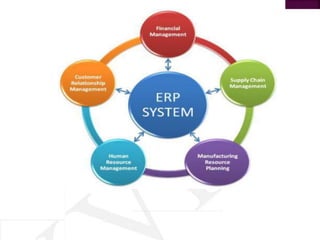
This document provides an overview of ERP software solutions, addressing various aspects such as vendor options, business process management, and functional modules for small to large enterprises. It emphasizes the importance of understanding organizational structures and benchmarking before ERP implementation to avoid chaotic transitions. Key modules discussed include finance, marketing, human resources, and materials management, highlighting the roles these systems play in improving business efficiency and quality management.


![ There are basically two ways of building ERP
solutions:
1. Make a new software
2. Buy software
Option 1: Make [using internal resources]
Option 2: Buy
Option 3: Make [using External resources]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/erpunit2erpsolutionsandfunctionalmodules-171010162817/85/Enterprise-resource-planning-unit-2-ERP-solutions-and-functional-modules-3-320.jpg)