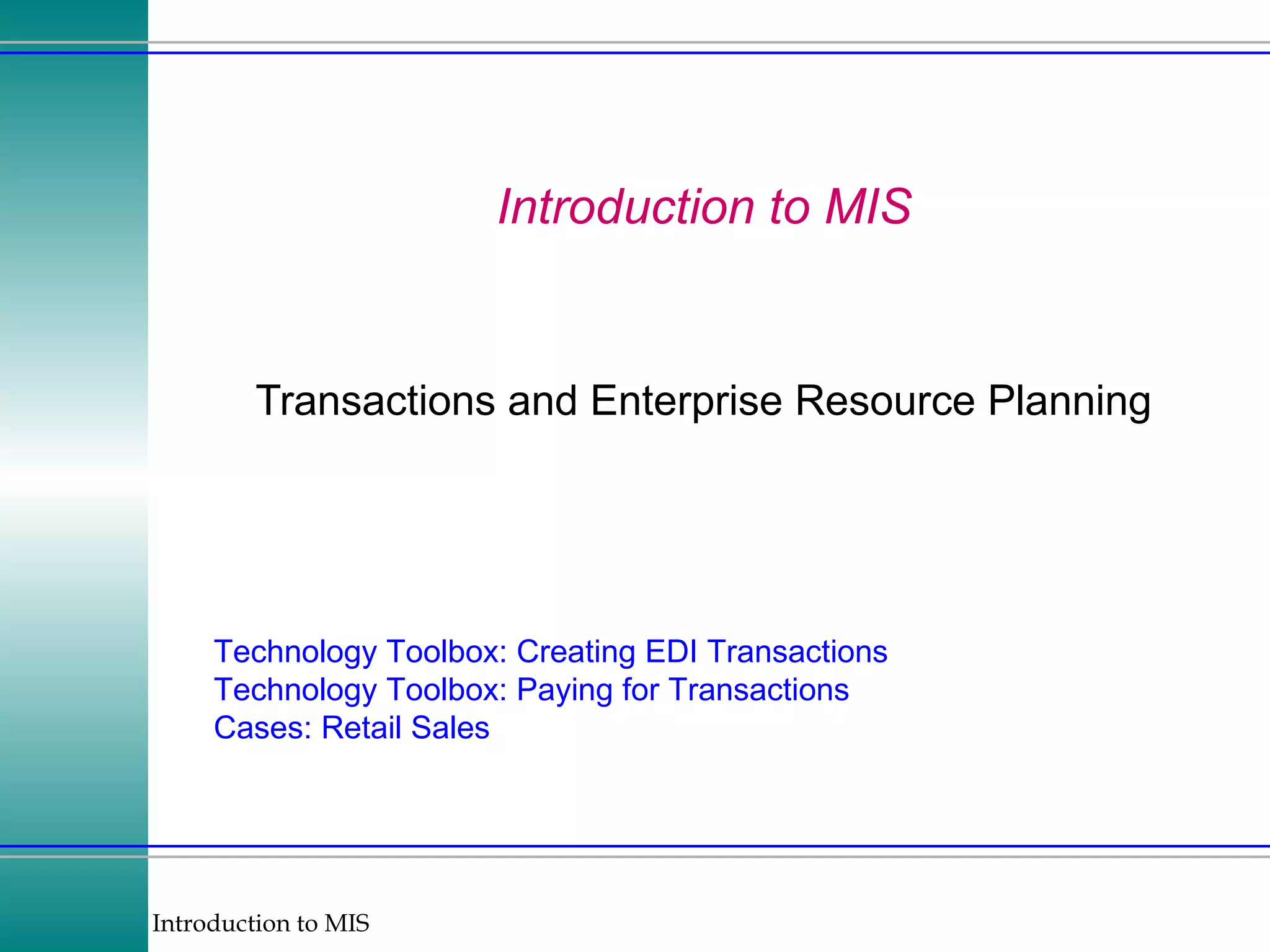
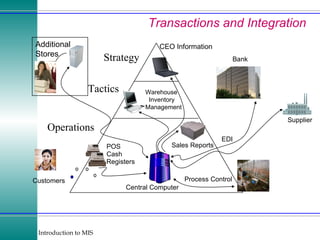
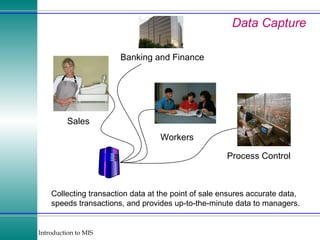
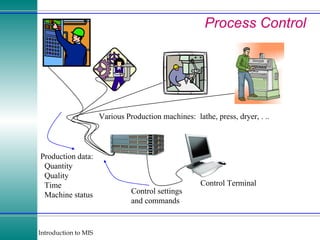
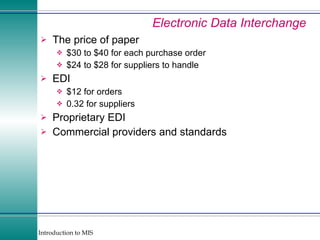
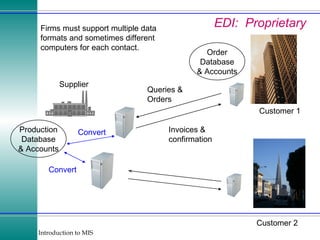
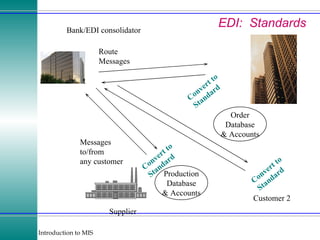
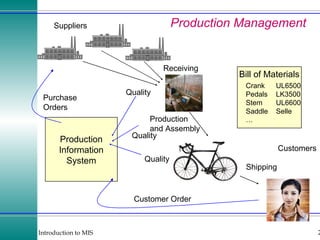
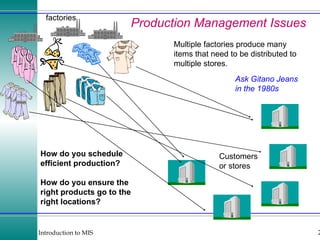
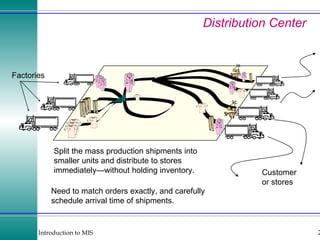
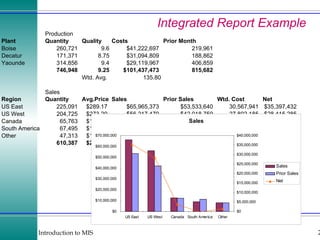
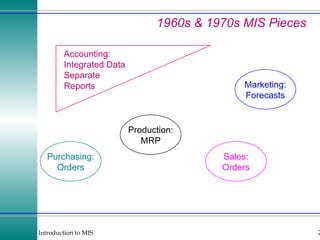
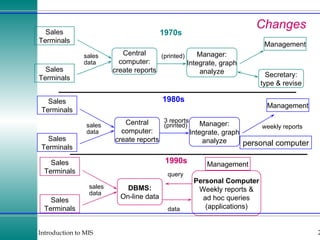
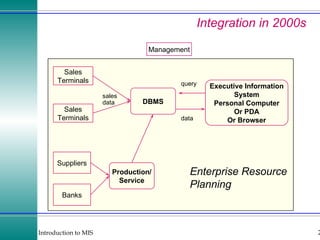
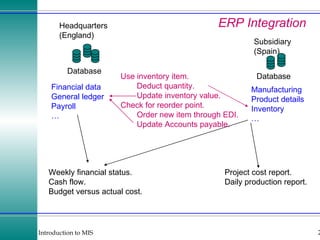
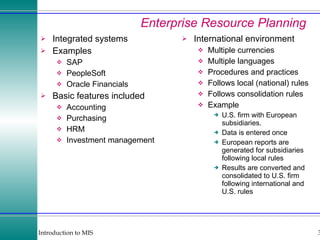
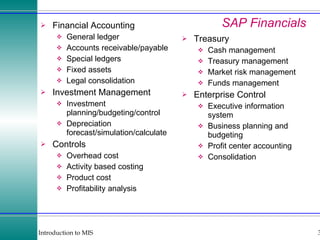
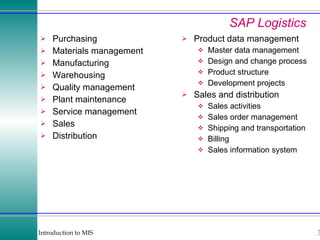
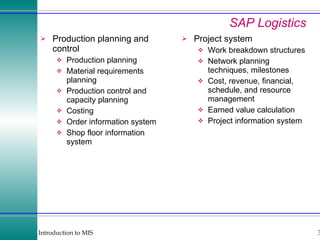
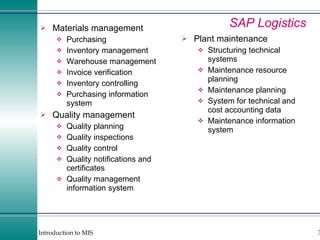
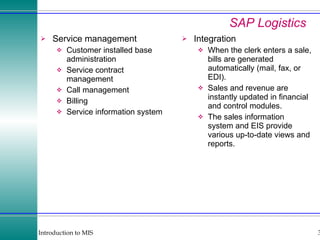
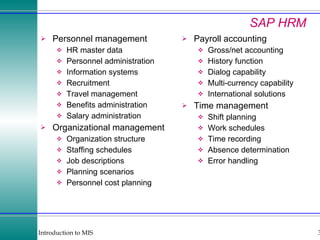
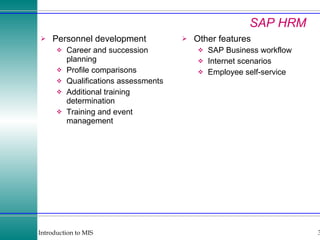
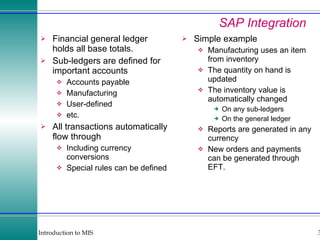
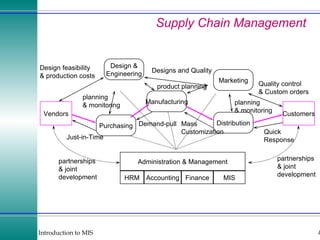
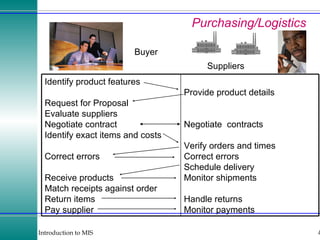
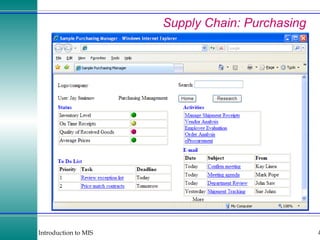
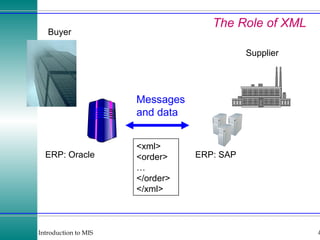
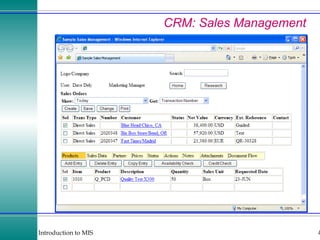
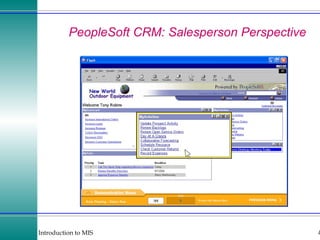
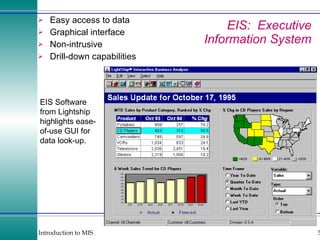
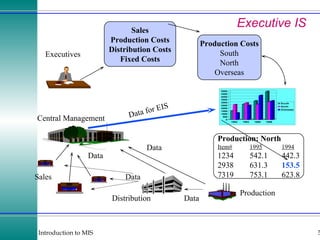
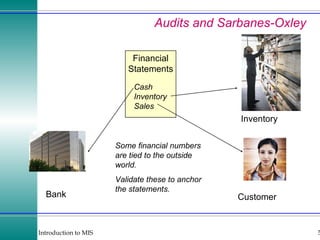
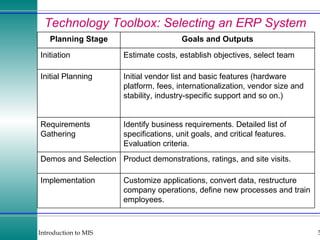
This document discusses enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems and how they integrate transaction data across various business functions such as accounting, finance, human resources, production, logistics and customer relationship management. ERP systems allow a company to capture transaction data at the source, and share it across departments to facilitate reporting, analysis and improved decision making. The integration of data helps make businesses more efficient by combining operational information.