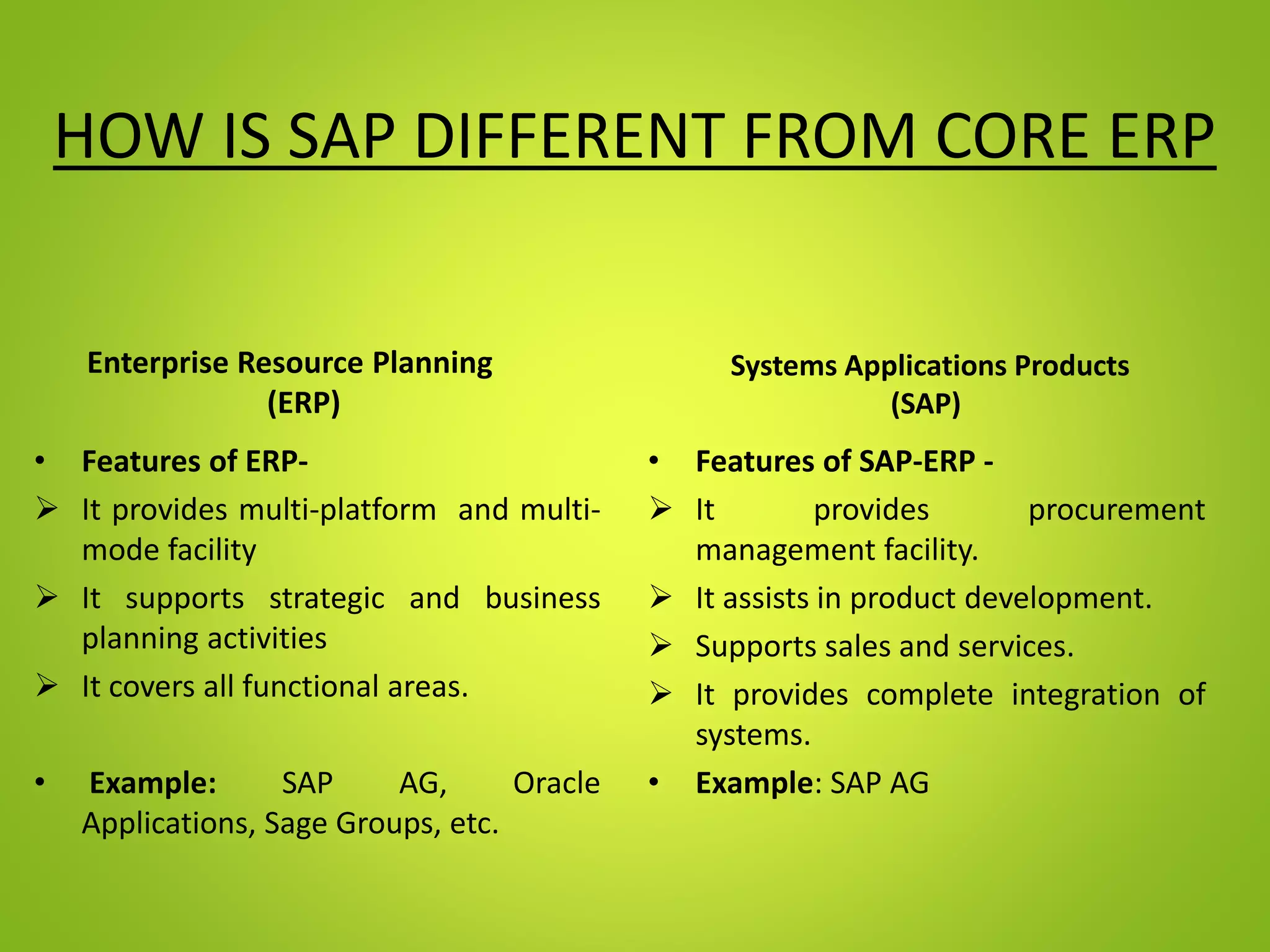
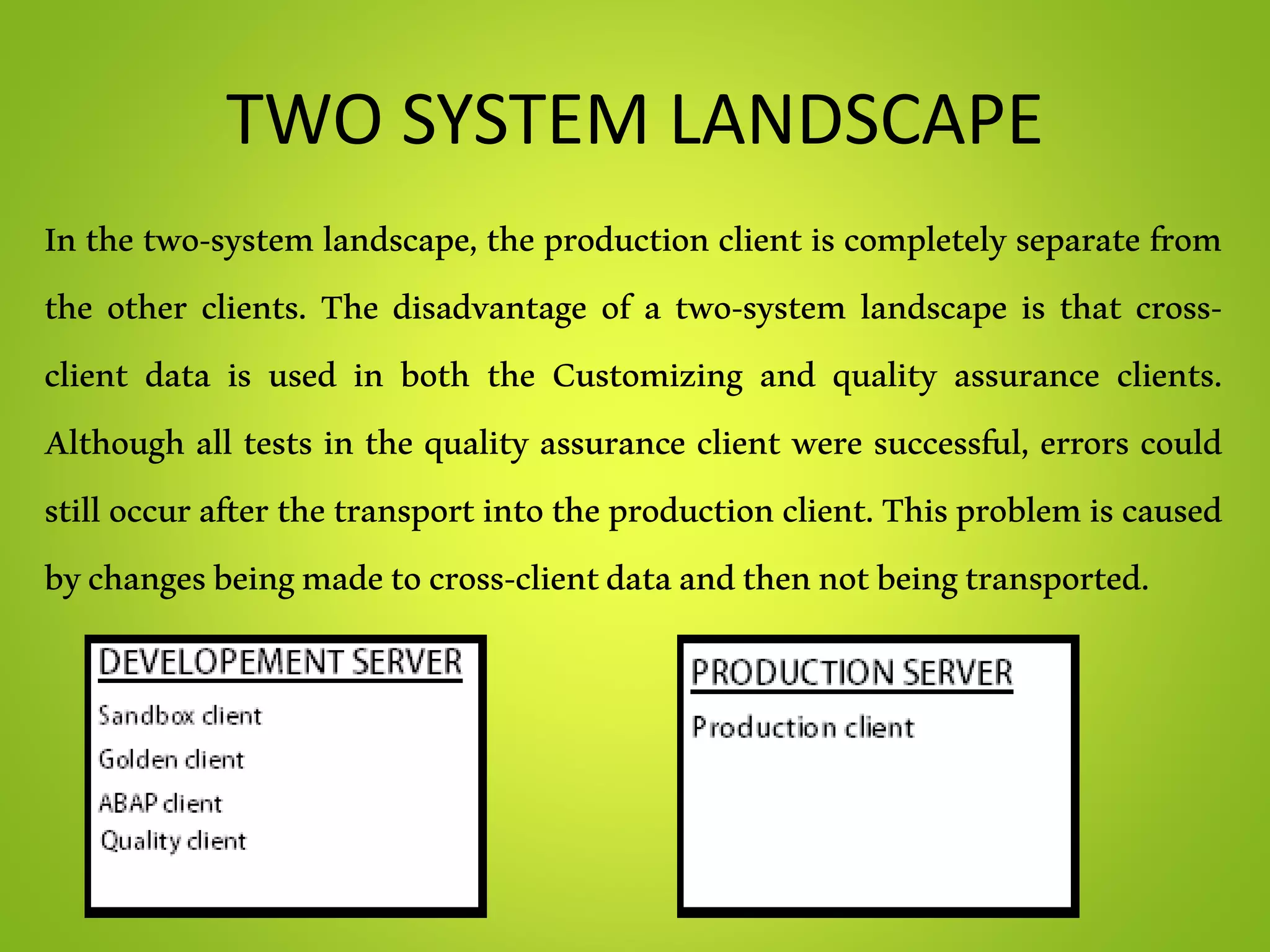
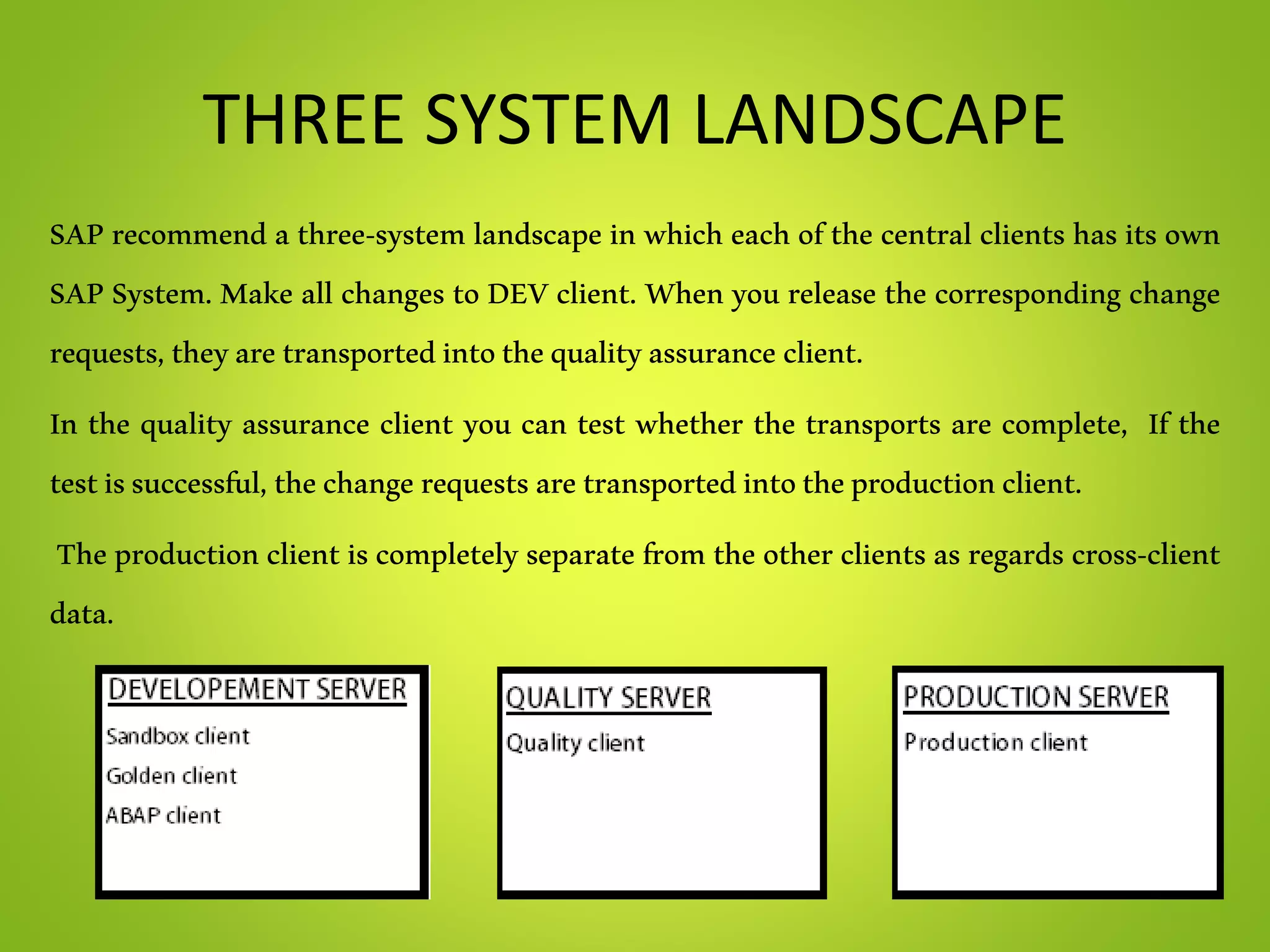
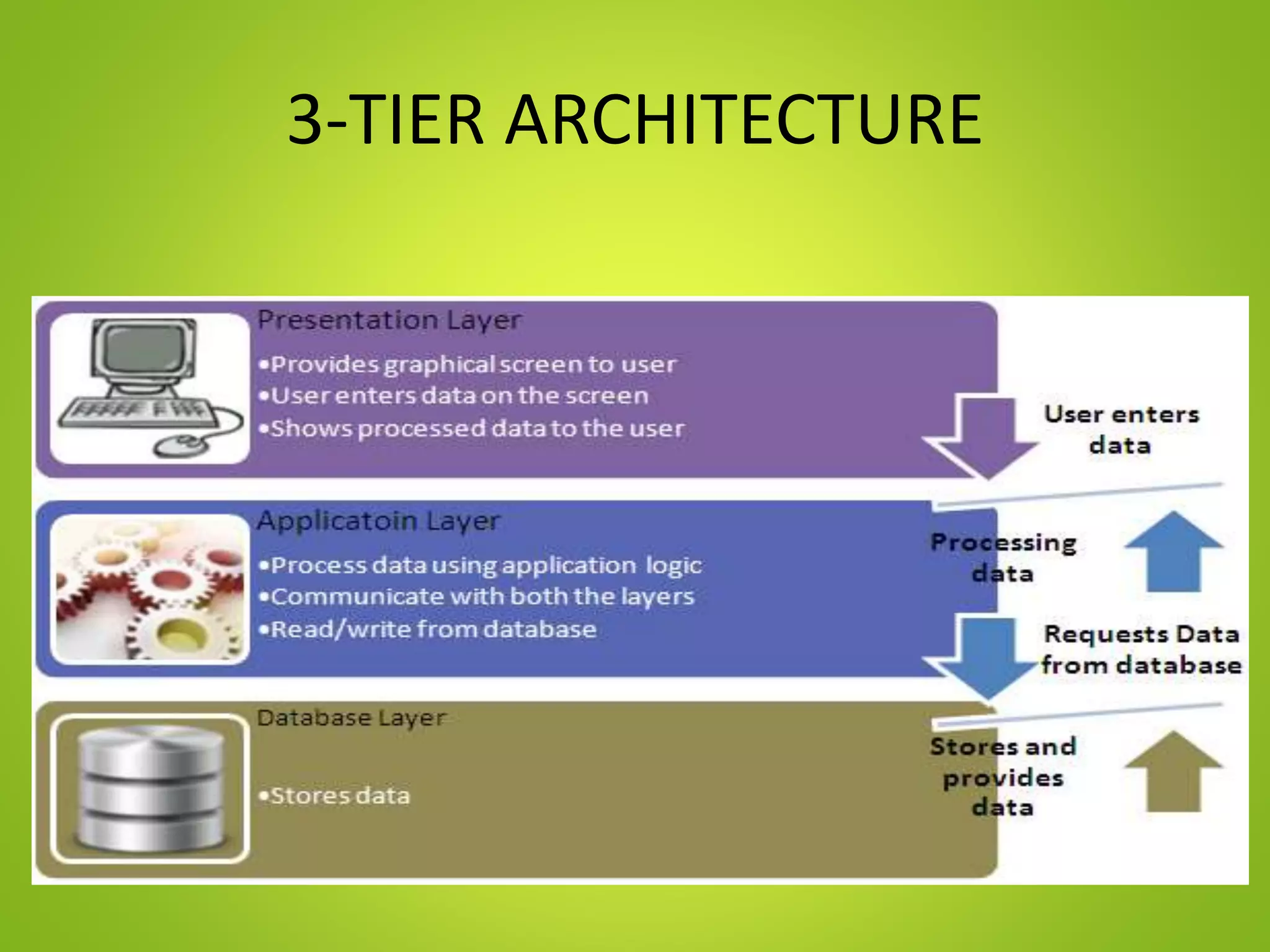
This document provides an overview of SAP and its components. It describes SAP as an enterprise resource planning software developed by SAP SE. Key points include:
- SAP is a leading ERP software that integrates various business functions like finance, supply chain, production etc.
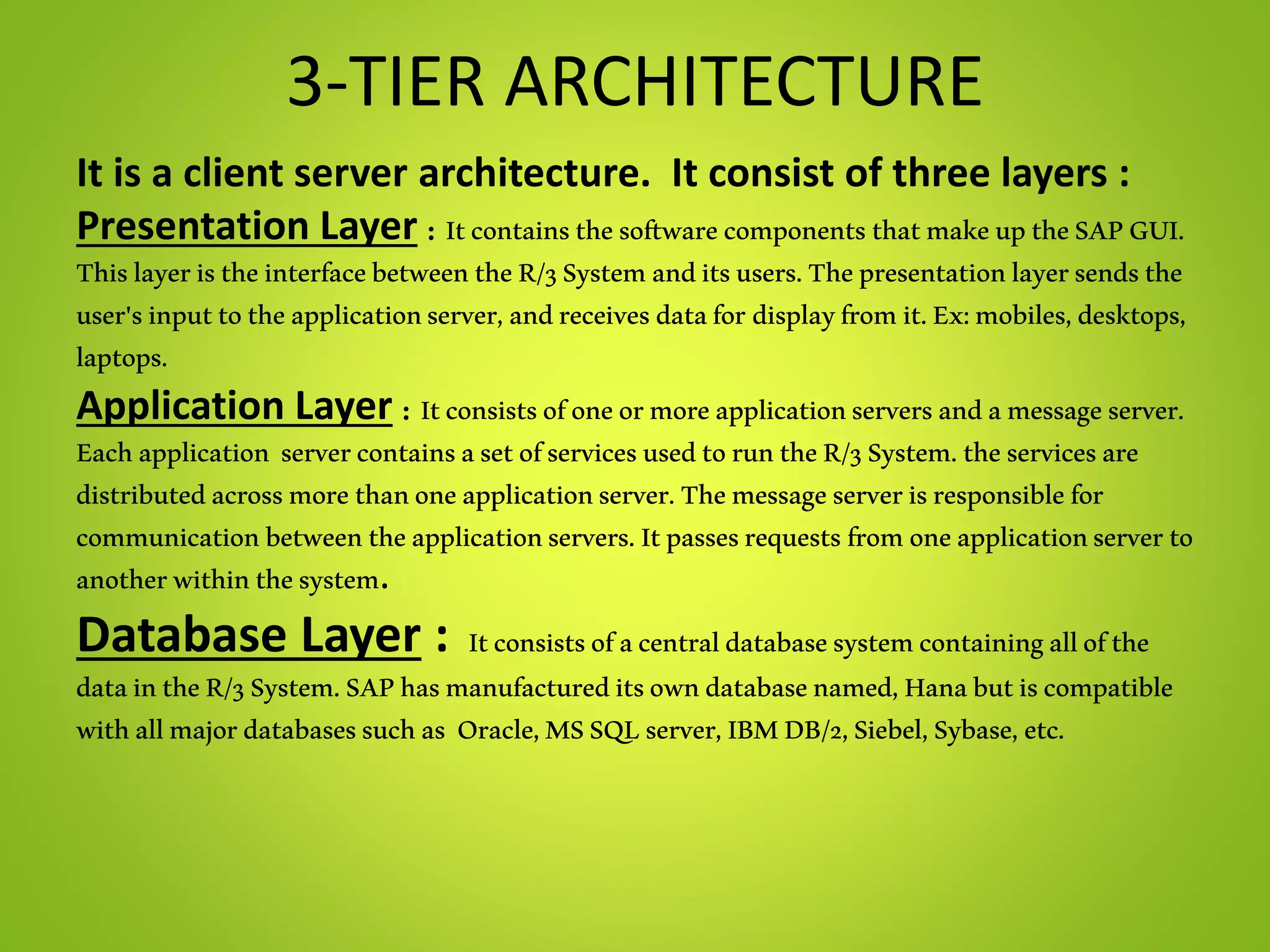
- It uses a 3-tier architecture with presentation, application and database layers.
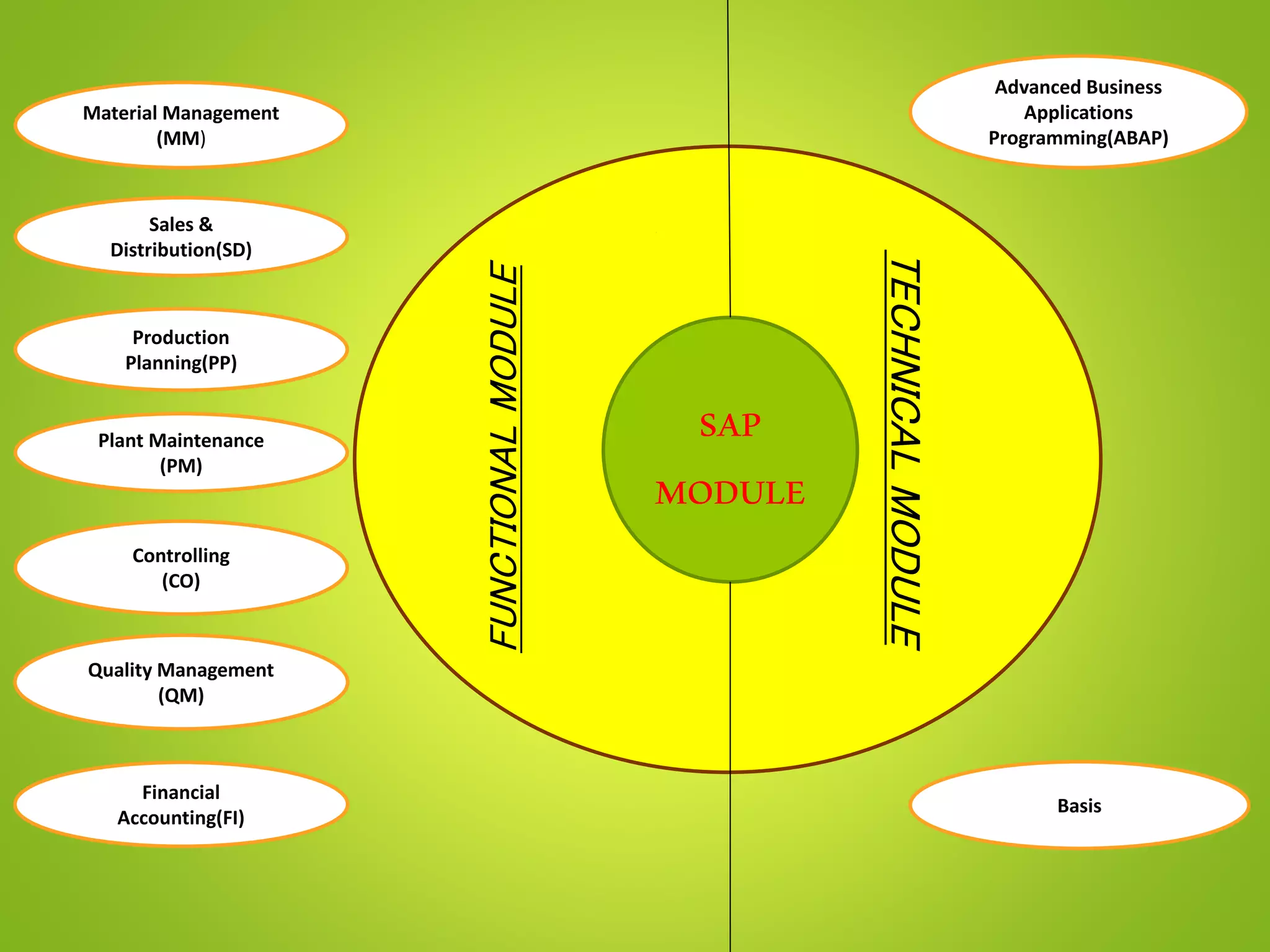
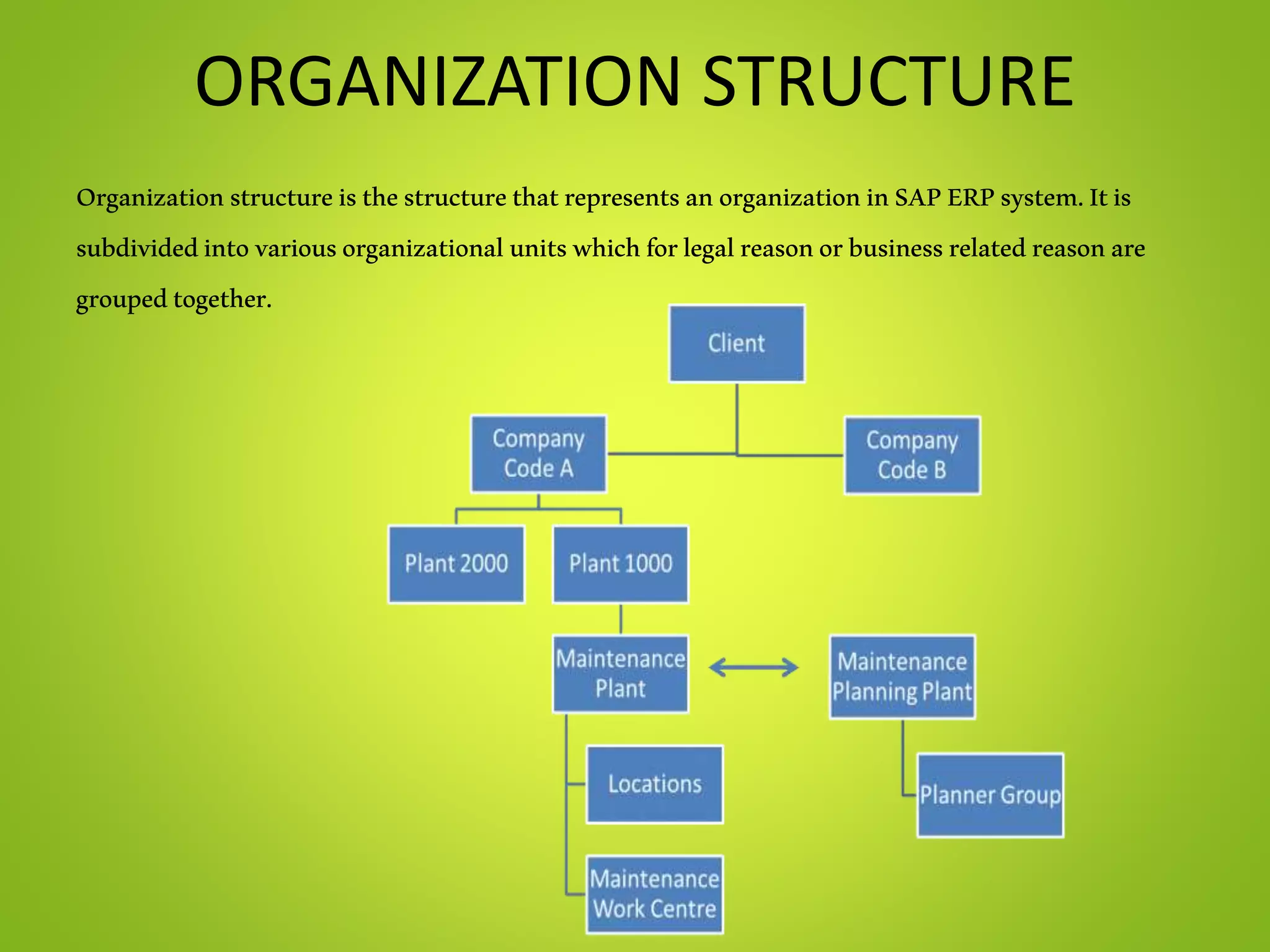
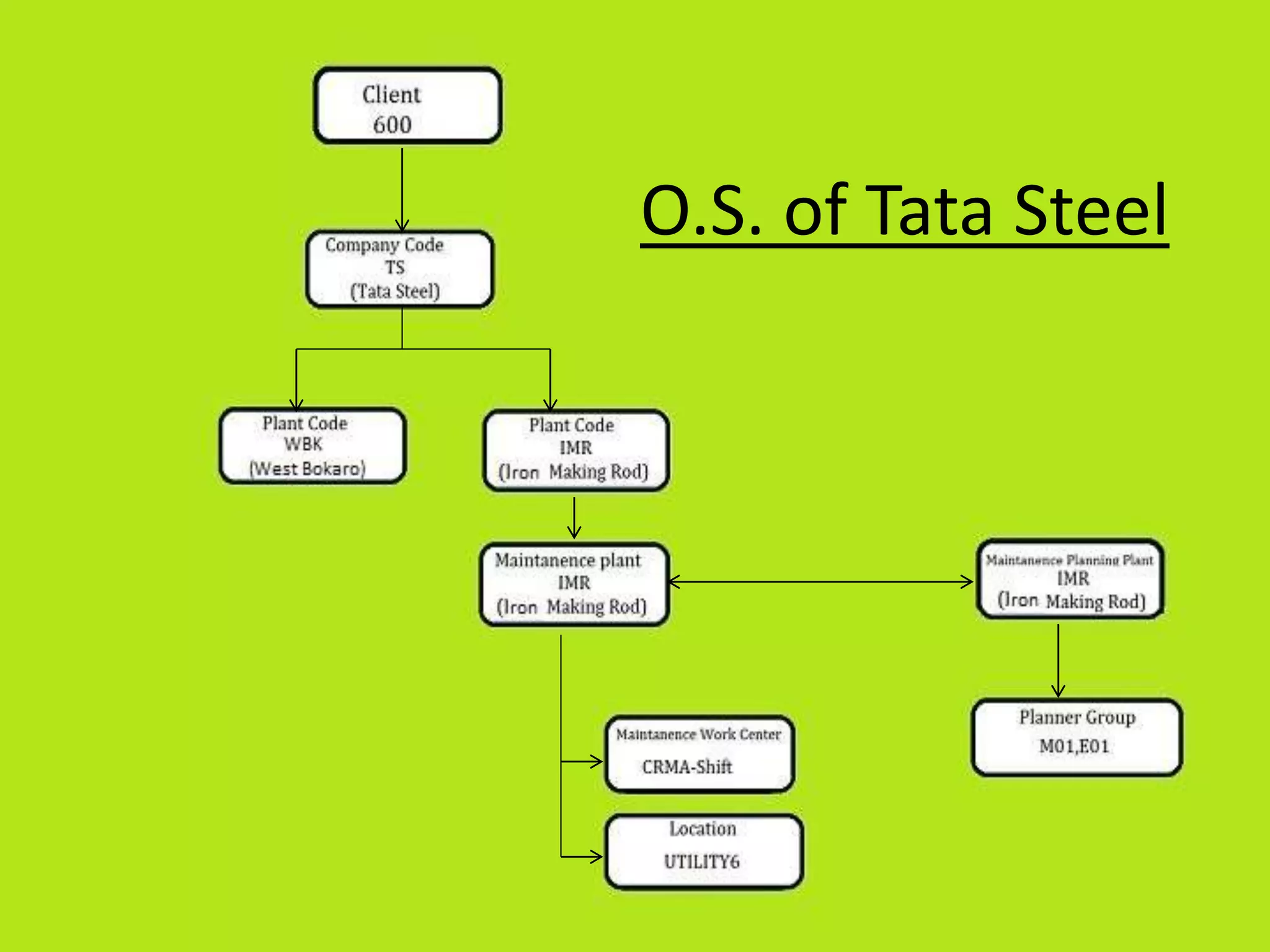
- The document outlines various SAP modules like MM, SD, PP, PM and technical components like landscapes, clients and organization structures.
- Plant maintenance module manages maintenance activities through work orders, preventive maintenance and equipment records.